Biochemistry Midterm Review
... much of the work inside organisms. They also act as enzymes helping to control metabolic reactions in organisms. Amino acids contain two functional groups, the carboxyl group (-COOH) and the amino group (-NH2). Basic Structure of Amino acid H ...
... much of the work inside organisms. They also act as enzymes helping to control metabolic reactions in organisms. Amino acids contain two functional groups, the carboxyl group (-COOH) and the amino group (-NH2). Basic Structure of Amino acid H ...
The MOLECULES of LIFE
... conservative mutation from tryptophan (W), other than to itself, is to ______, which has a score of ______. Answer: tyrosine, 2 11. Many soluble human proteins can be expressed in the E. coli bacteria or using an in vitro translation system. How can these proteins fold without the cellular machiner ...
... conservative mutation from tryptophan (W), other than to itself, is to ______, which has a score of ______. Answer: tyrosine, 2 11. Many soluble human proteins can be expressed in the E. coli bacteria or using an in vitro translation system. How can these proteins fold without the cellular machiner ...
Principles of BIOCHEMISTRY
... Structural proteins – usually stable (lens protein crystallin lives during the whole life of the organism) Regulatory proteins - short lived (altering the amounts of these proteins can rapidly change the rate of metabolic processes) How can a cell distinguish proteins that are meant for degradation? ...
... Structural proteins – usually stable (lens protein crystallin lives during the whole life of the organism) Regulatory proteins - short lived (altering the amounts of these proteins can rapidly change the rate of metabolic processes) How can a cell distinguish proteins that are meant for degradation? ...
Macromolecules
... of a protein determines its function! • The levels of protein structure are: – Primary structure: polypeptide chain – Secondary structure: polypeptides in coils or sheets – Tertiary structure: coils or sheets form a tangle – Quaternary structure: more than one tangle combine to make a very complex p ...
... of a protein determines its function! • The levels of protein structure are: – Primary structure: polypeptide chain – Secondary structure: polypeptides in coils or sheets – Tertiary structure: coils or sheets form a tangle – Quaternary structure: more than one tangle combine to make a very complex p ...
Natural Polymers - Wikispaces
... Nature uses natural polymers to make life possible, as all living things are made from these polymers. In many ways, these natural polymers are more important than other polymers. ...
... Nature uses natural polymers to make life possible, as all living things are made from these polymers. In many ways, these natural polymers are more important than other polymers. ...
Bio/CS 251 Bioinformatics
... The Oxygen atom attracts electrons much more forcefully than does a Hydrogen atom. In this way, oxygen is a strongly electronegative atom. As a result the O-H bond is said to be polarized, such that one of the atoms has a partial negative charge, and the other a partial positive charge. Molecules, s ...
... The Oxygen atom attracts electrons much more forcefully than does a Hydrogen atom. In this way, oxygen is a strongly electronegative atom. As a result the O-H bond is said to be polarized, such that one of the atoms has a partial negative charge, and the other a partial positive charge. Molecules, s ...
CAP5510 - Bioinformatics
... Genome sequence now accumulate so quickly that, in less than a week, a single laboratory can produce more bits of data than Shakespeare managed in a lifetime, although the latter make better reading. -- G A Pekso, Nature 401: 115-116 (1999) ...
... Genome sequence now accumulate so quickly that, in less than a week, a single laboratory can produce more bits of data than Shakespeare managed in a lifetime, although the latter make better reading. -- G A Pekso, Nature 401: 115-116 (1999) ...
Biochem Fall 2011 Sample Exam I – Protein Structure
... secreted during labor to effect delivery of the fetus. Oxytocin in therapeutically delivered to accelerate contractions in a labor that is not progressing. The primary sequences of the two peptides are shown below. Vasopressin: ...
... secreted during labor to effect delivery of the fetus. Oxytocin in therapeutically delivered to accelerate contractions in a labor that is not progressing. The primary sequences of the two peptides are shown below. Vasopressin: ...
Microbiology(Hons)[Paper-IV] - Ramakrishna Mission Vidyamandira
... b) What are thermoduric microorganisms? c) How does TMAO reduces shelf life of modified atmosphere packaged fish? d) What are the antimicrobial barriers present in egg white? e) Write down the advantages and disadvantages of slow freezing in food preservation. ...
... b) What are thermoduric microorganisms? c) How does TMAO reduces shelf life of modified atmosphere packaged fish? d) What are the antimicrobial barriers present in egg white? e) Write down the advantages and disadvantages of slow freezing in food preservation. ...
The Leucine Binding Fluorescence Analysis of the Leucine Specific
... transport system. These two proteins are nearly identical in tertiary structure and share about 80% of their amino acid content. These periplasmic binding proteins serve as initial receptors of active transport and chemotaxis for many substrates. Although they are very similar in both structure and ...
... transport system. These two proteins are nearly identical in tertiary structure and share about 80% of their amino acid content. These periplasmic binding proteins serve as initial receptors of active transport and chemotaxis for many substrates. Although they are very similar in both structure and ...
Biology 105
... Covalent bonds of carbon atoms - forms the background of a molecule (carbon-carbon or carbon-hydrogen) Called organic because once thought to only be created by living things. ...
... Covalent bonds of carbon atoms - forms the background of a molecule (carbon-carbon or carbon-hydrogen) Called organic because once thought to only be created by living things. ...
File
... The coils and folds of ___________________________structure result from ____________________ bonds between repeating constituents of the polypeptide backbone. Typical secondary structures are a coil called an _______________ and a folded structure called a ________________________ _____________ ...
... The coils and folds of ___________________________structure result from ____________________ bonds between repeating constituents of the polypeptide backbone. Typical secondary structures are a coil called an _______________ and a folded structure called a ________________________ _____________ ...
amino acid , peptide and protein metabolism
... 1.) What structural level of a protein is affected by denaturation? How is this different from the structural level of a protein affected by hydrolysis? ...
... 1.) What structural level of a protein is affected by denaturation? How is this different from the structural level of a protein affected by hydrolysis? ...
Unit 3: Chapter 6
... i. ___________________ - Enzymes have an ___________ temperature at which they work (__________________) - As temperature increases, enzyme activity increases for the most part - If temp is too high, protein becomes _______________ (change in _________) and no longer works. COOKED! ...
... i. ___________________ - Enzymes have an ___________ temperature at which they work (__________________) - As temperature increases, enzyme activity increases for the most part - If temp is too high, protein becomes _______________ (change in _________) and no longer works. COOKED! ...
BCAA 4:1:1 - ProAction
... BCAA 4:1:1 is an innovative product because the special ESTERDRIVE formula ensures that rapidly dissolves and is absorbed at gastrointestinal level. BCAA are metabolized in the mitochondria; valine is converted into a molecule of succinyl-CoA, a Krebs cycle intermediate; isoleucine generates one mol ...
... BCAA 4:1:1 is an innovative product because the special ESTERDRIVE formula ensures that rapidly dissolves and is absorbed at gastrointestinal level. BCAA are metabolized in the mitochondria; valine is converted into a molecule of succinyl-CoA, a Krebs cycle intermediate; isoleucine generates one mol ...
5.3 Presentation: Protein Synthesis
... • Cells respond to their environments by producing different types and amounts of proteins • The cell produces proteins that are structural (forms part of cell materials) or functional (enzymes and hormones). • All of an organisms cells have the same DNA, but the cells differ on the expression of th ...
... • Cells respond to their environments by producing different types and amounts of proteins • The cell produces proteins that are structural (forms part of cell materials) or functional (enzymes and hormones). • All of an organisms cells have the same DNA, but the cells differ on the expression of th ...
Functional Groups, I
... cell membranes; precursor for other steroids (sex hormones); atherosclerosis ...
... cell membranes; precursor for other steroids (sex hormones); atherosclerosis ...
Cell Architecture 2 Dr Mahjabeen
... of G-actin (globular or free actin) polymerizes to F- actin (filamentous), in presence of K & Mg. • Formin • Polarity: _ pointed end and + barbed end • Treadmilling • Stable- muscle cells and microvilli • Dissociate and reassemble • Profilin & Cofilin ...
... of G-actin (globular or free actin) polymerizes to F- actin (filamentous), in presence of K & Mg. • Formin • Polarity: _ pointed end and + barbed end • Treadmilling • Stable- muscle cells and microvilli • Dissociate and reassemble • Profilin & Cofilin ...
Determination of Protein Concentration
... may absorb UV light or modify the molar absorptivities of tyrosine and tryptophan, and thus the UV detection is highly sensitive to pH and ionic strength at which measurement is taken. Many other cellular components, and particularly nucleic acids, also absorb UV light. The ratio of A 280 /A 260 is ...
... may absorb UV light or modify the molar absorptivities of tyrosine and tryptophan, and thus the UV detection is highly sensitive to pH and ionic strength at which measurement is taken. Many other cellular components, and particularly nucleic acids, also absorb UV light. The ratio of A 280 /A 260 is ...
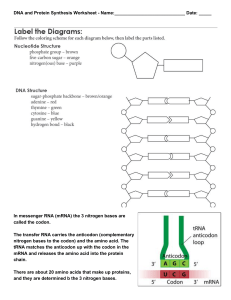
File
... 16. tRNA brings amino acids to the nucleus or ribosome? 17. A polypeptide is a sequence of proteins or amino acids? 18. tRNA has codons or anti-codons? 19. tRNA transfers amino acids during translation or transcription? 20. Ribosomes are the site where translation or transcription takes place? ...
... 16. tRNA brings amino acids to the nucleus or ribosome? 17. A polypeptide is a sequence of proteins or amino acids? 18. tRNA has codons or anti-codons? 19. tRNA transfers amino acids during translation or transcription? 20. Ribosomes are the site where translation or transcription takes place? ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.









![Microbiology(Hons)[Paper-IV] - Ramakrishna Mission Vidyamandira](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017635075_1-cacd0a5e5aa4de554a7e55477a5947cd-300x300.png)