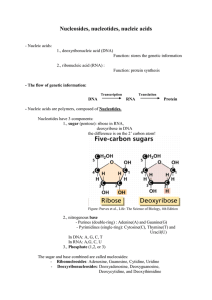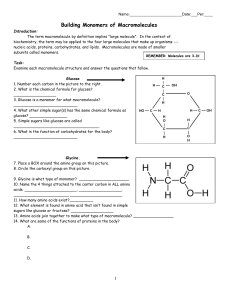
Building Monomers of Macromolecules
... 12. What element is found in amino acid that isn’t found in simple sugars like glucose or fructose? __________________ 13. Amino acids join together to make what type of macromolecule? _________________ 14. What are some of the functions of proteins in the body? A. B. C. D. ...
... 12. What element is found in amino acid that isn’t found in simple sugars like glucose or fructose? __________________ 13. Amino acids join together to make what type of macromolecule? _________________ 14. What are some of the functions of proteins in the body? A. B. C. D. ...
Topic 2: Molecular biology (21 hours)
... • Proteomics and the production of proteins by cells form polypeptides. cultured in fermenters offer many opportunities for the • There are 20 different amino acids in polypeptides food, pharmaceutical and other industries. synthesized on ribosomes. Aims: • Amino acids can be linked together in any ...
... • Proteomics and the production of proteins by cells form polypeptides. cultured in fermenters offer many opportunities for the • There are 20 different amino acids in polypeptides food, pharmaceutical and other industries. synthesized on ribosomes. Aims: • Amino acids can be linked together in any ...
Practice Exam - mvhs
... part of the active site from a nonpolar amino acid to a positively charged amino acid. Use what you know about protein structure to explain how changing this amino acid could potentially improve (change) the enzyme’s ability to perform its function. __________________________________________________ ...
... part of the active site from a nonpolar amino acid to a positively charged amino acid. Use what you know about protein structure to explain how changing this amino acid could potentially improve (change) the enzyme’s ability to perform its function. __________________________________________________ ...
file1
... Subfamilies are not clearly defined in databases - divided proteins from PFAM database into subfamilies based on SWISSPROT data - keyword search limited to enzymatic activity string in SWISSPROT - put into groups, then checked for obvious mistakes - also eliminated divisions “easily discernable by s ...
... Subfamilies are not clearly defined in databases - divided proteins from PFAM database into subfamilies based on SWISSPROT data - keyword search limited to enzymatic activity string in SWISSPROT - put into groups, then checked for obvious mistakes - also eliminated divisions “easily discernable by s ...
B2.10a - Science @ St John`s
... Jon and Felice were trying to make a model to explain how DNA controls the sequence of amino acids in which proteins are made. They had some coloured popper beads in red, green, white, yellow, blue and orange. They decided to use the first letter of each colour as the code for that colour of bead. J ...
... Jon and Felice were trying to make a model to explain how DNA controls the sequence of amino acids in which proteins are made. They had some coloured popper beads in red, green, white, yellow, blue and orange. They decided to use the first letter of each colour as the code for that colour of bead. J ...
Chapter 5: Structure and Function of Macromolecules
... A polypeptide is a polymer of amino acids connected in a specific sequence (pp. 71-74, FIGURES 5.15-5.16, TABLE 5.1) Polypeptides are constructed from 20 different amino acids, each with a characteristic side chain (R group). The carboxyl and amino groups of adjacent amino acids link together in p ...
... A polypeptide is a polymer of amino acids connected in a specific sequence (pp. 71-74, FIGURES 5.15-5.16, TABLE 5.1) Polypeptides are constructed from 20 different amino acids, each with a characteristic side chain (R group). The carboxyl and amino groups of adjacent amino acids link together in p ...
Proteins
... Another major compound of living things is protein. Proteins make up the bulk of all solid material within your body and other living organisms. Proteins are the most structurally sophisticated molecules known. They vary extensively in structure with each type of protein having a unique three-dimens ...
... Another major compound of living things is protein. Proteins make up the bulk of all solid material within your body and other living organisms. Proteins are the most structurally sophisticated molecules known. They vary extensively in structure with each type of protein having a unique three-dimens ...
Preparation of enzymatically active recombinant class III
... • They show no homology to class I and II proteins [2]. • The class III enzymes are characterized by their dependence on nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+). ...
... • They show no homology to class I and II proteins [2]. • The class III enzymes are characterized by their dependence on nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+). ...
Information on Formula
... Results are super fast to say the least. If you want to obtain a rock hard body be confident , stronger and exert maximum performance with a fitter healthier body ,you can do it all without using steroids and alike! ...
... Results are super fast to say the least. If you want to obtain a rock hard body be confident , stronger and exert maximum performance with a fitter healthier body ,you can do it all without using steroids and alike! ...
FREE Sample Here - Find the cheapest test bank for your
... Mechanism 1: Covalent modification – no change in the abundance of a protein. Here, preexisting protein is made active or inactive by covalently modifying it (involves making or breaking covalent bonds). Examples include phosphorylation, carboxylation, glycosylation, or proenzyme activation by break ...
... Mechanism 1: Covalent modification – no change in the abundance of a protein. Here, preexisting protein is made active or inactive by covalently modifying it (involves making or breaking covalent bonds). Examples include phosphorylation, carboxylation, glycosylation, or proenzyme activation by break ...
Protein Synthesis:
... protein growth, and release factors, proteins which mimic tRNA, enter the A site and release the protein in to the cytoplasm. Synthesis of proteins can take place extremely quickly. This is aided by multiple ribosomes being able to attach themselves to one mRNA chain, thus allowing multiple proteins ...
... protein growth, and release factors, proteins which mimic tRNA, enter the A site and release the protein in to the cytoplasm. Synthesis of proteins can take place extremely quickly. This is aided by multiple ribosomes being able to attach themselves to one mRNA chain, thus allowing multiple proteins ...
Protein Synthesis:
... protein growth, and release factors, proteins which mimic tRNA, enter the A site and release the protein in to the cytoplasm. Synthesis of proteins can take place extremely quickly. This is aided by multiple ribosomes being able to attach themselves to one mRNA chain, thus allowing multiple proteins ...
... protein growth, and release factors, proteins which mimic tRNA, enter the A site and release the protein in to the cytoplasm. Synthesis of proteins can take place extremely quickly. This is aided by multiple ribosomes being able to attach themselves to one mRNA chain, thus allowing multiple proteins ...
Quale Vita? - uniroma1.it
... constant, in some cases they do not make H bonds with solutes, in other cases they attack the organic material (e.g. ammonia) ...
... constant, in some cases they do not make H bonds with solutes, in other cases they attack the organic material (e.g. ammonia) ...
Document
... MODELLER is used for homology or comparative modeling of protein three-dimensional structures (1). The user provides an alignment of a sequence to be modeled with known related structures and MODELLER automatically calculates a model containing all non-hydrogen atoms. MODELLER implements comparative ...
... MODELLER is used for homology or comparative modeling of protein three-dimensional structures (1). The user provides an alignment of a sequence to be modeled with known related structures and MODELLER automatically calculates a model containing all non-hydrogen atoms. MODELLER implements comparative ...
Organic Compounds Test ~Please DO NOT write on the test!~ 1
... B. multiple units of a macromolecules that are bonded together C. same as a molecule D. the entire structure of a macromolecule 10. A major characteristic that all lipids have in common is A. They all contain phosphorus B. They all contain nitrogen C. None of them are very high in energy content D. ...
... B. multiple units of a macromolecules that are bonded together C. same as a molecule D. the entire structure of a macromolecule 10. A major characteristic that all lipids have in common is A. They all contain phosphorus B. They all contain nitrogen C. None of them are very high in energy content D. ...
Lysosomes - Denver Public Schools
... Cell membrane surrounds disease-causing bacteria or large object, forming phagosome Lysosome joins with phagosome, breaking down the object or bacteria with enzymes ...
... Cell membrane surrounds disease-causing bacteria or large object, forming phagosome Lysosome joins with phagosome, breaking down the object or bacteria with enzymes ...
prions - Cloudfront.net
... • Make sure when undergoing or performing surgical procedures, to use sterile utensils. • Prions are not easily destroyed. The use of boiling techniques, alcohol , acid, standard autoclaving methods, or radiation will not kill them. • “ In fact, infected brains that have been sitting in formaldehyde ...
... • Make sure when undergoing or performing surgical procedures, to use sterile utensils. • Prions are not easily destroyed. The use of boiling techniques, alcohol , acid, standard autoclaving methods, or radiation will not kill them. • “ In fact, infected brains that have been sitting in formaldehyde ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.