8th Grade Ch. 7 Chemical Reactions Study guide
... ____ 33. Which of the following changes gives NO evidence that a chemical reaction has taken place? A. A cube of solid forms a puddle of liquid. B. A certain liquid is added to a solid, and bubbles of gas form. C. Two liquids are mixed, and a precipitate forms. D. Heating a blue solid turns the soli ...
... ____ 33. Which of the following changes gives NO evidence that a chemical reaction has taken place? A. A cube of solid forms a puddle of liquid. B. A certain liquid is added to a solid, and bubbles of gas form. C. Two liquids are mixed, and a precipitate forms. D. Heating a blue solid turns the soli ...
O 2
... Chemical reactions occur all around us everyday both in industry and in the home. Unimaginable numbers of these unique and specific reactions exist. With so many reactions occurring in our lives the Chemist needs a way to help organize them into some sort of manageable scheme. There are 5 general ty ...
... Chemical reactions occur all around us everyday both in industry and in the home. Unimaginable numbers of these unique and specific reactions exist. With so many reactions occurring in our lives the Chemist needs a way to help organize them into some sort of manageable scheme. There are 5 general ty ...
synthesis reaction
... A double-replacement reaction is one in which two different compounds exchange positive ions and form two new compounds. The general equation for a double-replacement reaction is: AB + CD AD + CB Pb(NO3)2 + 2KI PbI2 + 2KNO3 In a double-replacement reaction, there are two reactants and two pr ...
... A double-replacement reaction is one in which two different compounds exchange positive ions and form two new compounds. The general equation for a double-replacement reaction is: AB + CD AD + CB Pb(NO3)2 + 2KI PbI2 + 2KNO3 In a double-replacement reaction, there are two reactants and two pr ...
Chem 1100 Chapter Three Study Guide Outline I. Molar Mass and
... 26. How many moles of CuO can be produced from 0.450 mol of Cu2O in the following reaction? 2 Cu2O (s) + O2 (g) Æ 4 CuO (s) a. 1.80 mol b. 0.225 mol c. 0.900 mol d. 0.450 mol 27. 10 g of nitrogen is reacted with 5.0 g of hydrogen to produce ammonia according to the chemical equation shown below. Whi ...
... 26. How many moles of CuO can be produced from 0.450 mol of Cu2O in the following reaction? 2 Cu2O (s) + O2 (g) Æ 4 CuO (s) a. 1.80 mol b. 0.225 mol c. 0.900 mol d. 0.450 mol 27. 10 g of nitrogen is reacted with 5.0 g of hydrogen to produce ammonia according to the chemical equation shown below. Whi ...
IB Chemistry Brakke ECA - Topic 15 T15D12
... Using the average bond enthalpy values in Table 10 of the Data Booklet, calculate the standard enthalpy change for this reaction. ...
... Using the average bond enthalpy values in Table 10 of the Data Booklet, calculate the standard enthalpy change for this reaction. ...
Chemical Basis of Life
... Tertiary (3°) – folding of secondary structures on each other Quaternary (4°) – 2+ polypeptides interact to form a protein Denaturation destroys structure which alters or inhibits ...
... Tertiary (3°) – folding of secondary structures on each other Quaternary (4°) – 2+ polypeptides interact to form a protein Denaturation destroys structure which alters or inhibits ...
F324 summary - Macmillan Academy
... • Novel, useful molecules can be synthesised using organic chemistry. • A chiral molecule is more difficult to synthesise since many other optical isomers may also form – costly in money and time to separate or resolve the isomers. • Enzymes, bacteria, chiral catalysts and chiral-starting points (e. ...
... • Novel, useful molecules can be synthesised using organic chemistry. • A chiral molecule is more difficult to synthesise since many other optical isomers may also form – costly in money and time to separate or resolve the isomers. • Enzymes, bacteria, chiral catalysts and chiral-starting points (e. ...
activity series
... occurs between ions in aqueous solution. A reaction will occur when a pair of ions come together to produce at least one of the following: 1. a precipitate 2. a gas 3. water or some other non-ionized substance. ...
... occurs between ions in aqueous solution. A reaction will occur when a pair of ions come together to produce at least one of the following: 1. a precipitate 2. a gas 3. water or some other non-ionized substance. ...
File
... • Each group should have 4 people and 20 cards. Split the cards up so each person has 5. • On your own piece of paper, write out your 5 chemical equations and balance them. • Then, once all equations are balanced, look at the 20 as a group. You need to split the 20 cards up in to 5 different react ...
... • Each group should have 4 people and 20 cards. Split the cards up so each person has 5. • On your own piece of paper, write out your 5 chemical equations and balance them. • Then, once all equations are balanced, look at the 20 as a group. You need to split the 20 cards up in to 5 different react ...
FIREWORKS EMC summary notes
... are not easily reversed; they are irreversible. In a physical change no new substance is formed. Melting and evaporation are examples of physical changes. Physical changes are usually reversible. You can tell that a reaction has occurred if there is a colour change or when a gas is given off. Most c ...
... are not easily reversed; they are irreversible. In a physical change no new substance is formed. Melting and evaporation are examples of physical changes. Physical changes are usually reversible. You can tell that a reaction has occurred if there is a colour change or when a gas is given off. Most c ...
Hydrogen Chemistry of Basalt Aquifers -- Treiman et
... In contrast to the assertion of Treiman and Wallendahl, the study by Neal and Stanger did not demonstrate that the rocks in the Oman system produced hydrogen by reacting with water. This was only inferred from isotopic measurements and several assumptions about isotope equilibrium and exchange. Dire ...
... In contrast to the assertion of Treiman and Wallendahl, the study by Neal and Stanger did not demonstrate that the rocks in the Oman system produced hydrogen by reacting with water. This was only inferred from isotopic measurements and several assumptions about isotope equilibrium and exchange. Dire ...
Chapter 11.1: Describing Chemical Reactions
... catalyst is a substance that can be added to speed up the reaction but is not used up in a reaction. It is neither a product or a reactant. ...
... catalyst is a substance that can be added to speed up the reaction but is not used up in a reaction. It is neither a product or a reactant. ...
The chemical master equation
... condition is met within a molecule (e.g. IVR putting enough energy in a reactive mode). In a well-mixed system, the collisions necessary for a reaction to occur are random events. ...
... condition is met within a molecule (e.g. IVR putting enough energy in a reactive mode). In a well-mixed system, the collisions necessary for a reaction to occur are random events. ...
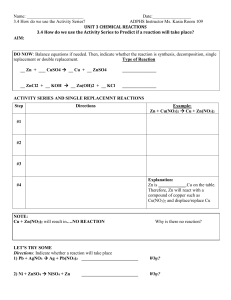
3.4 How do we use the Activity Series
... F2 + 2NaCl Cl2 + 2NaF 1. What is the most reactive nonmetal according to the table?___________________________________ 2. ______________________will react with anything below it 3. Will the above reaction take place?_____________________________________________________ 4. Will the reverse reaction ...
... F2 + 2NaCl Cl2 + 2NaF 1. What is the most reactive nonmetal according to the table?___________________________________ 2. ______________________will react with anything below it 3. Will the above reaction take place?_____________________________________________________ 4. Will the reverse reaction ...
PRACTICE * Naming and Writing Ionic Compounds
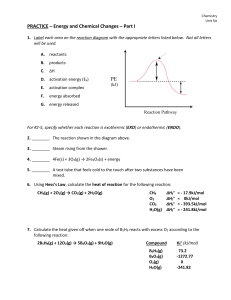
... 1. Label each area on the reaction diagram with the appropriate letters listed below. Not all letters will be used. A. ...
... 1. Label each area on the reaction diagram with the appropriate letters listed below. Not all letters will be used. A. ...
Answers
... 3) An 11.78 g sample of an unknown compound is decomposed and analyzed. The procedure produces 0.36 g of H, 3.73 g of P and 7.69 g of O. Determine the percent composition of hydrogen in the compound. 4) What is the percent of oxygen by mass in water? 5) A sample of ammonia (NH3) contains 7.22 moles ...
... 3) An 11.78 g sample of an unknown compound is decomposed and analyzed. The procedure produces 0.36 g of H, 3.73 g of P and 7.69 g of O. Determine the percent composition of hydrogen in the compound. 4) What is the percent of oxygen by mass in water? 5) A sample of ammonia (NH3) contains 7.22 moles ...
File - Kheriaty Chemistry
... b. What is the chemical formula of that new product? c. What element will O bond to? d. What is the chemical formula of that new product? 16. Potassium oxide reacts with magnesium bromide. a. What element will potassium bond to? b. What is the chemical formula of that new product? c. What element wi ...
... b. What is the chemical formula of that new product? c. What element will O bond to? d. What is the chemical formula of that new product? 16. Potassium oxide reacts with magnesium bromide. a. What element will potassium bond to? b. What is the chemical formula of that new product? c. What element wi ...
Chemical Reaction Basics
... Advanced Chemistry – Chapter 8 A ____________ ____________ is a process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more ____________ substances. Chemical reactions are represented by some type of ____________. The general form is as follows: ...
... Advanced Chemistry – Chapter 8 A ____________ ____________ is a process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more ____________ substances. Chemical reactions are represented by some type of ____________. The general form is as follows: ...
Catalytic, Enantioselective Alkylation of r
... Over the past several years, highly effective methods for enantioselective aldol additions catalyzed by Lewis acids have been developed.1 Analogous alkylations of imines, however, have not been nearly as well studied nor as successful.2 R-Imino esters are almost unstudied in Lewis acid-catalyzed rea ...
... Over the past several years, highly effective methods for enantioselective aldol additions catalyzed by Lewis acids have been developed.1 Analogous alkylations of imines, however, have not been nearly as well studied nor as successful.2 R-Imino esters are almost unstudied in Lewis acid-catalyzed rea ...
double-replacement reaction
... In a single-replacement reaction, a more active metal displaces a less active metal according to the activity series. • In a double-replacement reaction, two aqueous solutions produce a precipitate of an insoluble compound. ...
... In a single-replacement reaction, a more active metal displaces a less active metal according to the activity series. • In a double-replacement reaction, two aqueous solutions produce a precipitate of an insoluble compound. ...
Ei otsikkoa
... Some form the +3 or +4 ion, the latter being rare due to small size & high charge (which easily leads to covalent bonding). Examples: CrCl3, Fe2O3, MnO2 ...
... Some form the +3 or +4 ion, the latter being rare due to small size & high charge (which easily leads to covalent bonding). Examples: CrCl3, Fe2O3, MnO2 ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... Types of Chemical Reactions Chemical reactions can be classified into one of four categories depending on what type and how many reactants are present. We can use a generalized equation to represent each. In the generalized equation, the letters A and B represent positive ions (elements that lose el ...
... Types of Chemical Reactions Chemical reactions can be classified into one of four categories depending on what type and how many reactants are present. We can use a generalized equation to represent each. In the generalized equation, the letters A and B represent positive ions (elements that lose el ...
Chapter 7
... Catalysts are written above the arrow. • Energy is needed to start breaking the chemical bonds. This is called activation energy. Catalysts lower that energy needed by providing a surface on which the reacting particles can come together. ...
... Catalysts are written above the arrow. • Energy is needed to start breaking the chemical bonds. This is called activation energy. Catalysts lower that energy needed by providing a surface on which the reacting particles can come together. ...