chemical reactions
... Safety Note: Wear gloves when working with alkali and alkaline earth metals. Perform this reaction using a very small piece of the active metal in 200 mL of room temperature water in a 600-mL or 800-mL beaker with a fine mesh wire gauze covering the beaker. Use a document camera, or similar, to pro ...
... Safety Note: Wear gloves when working with alkali and alkaline earth metals. Perform this reaction using a very small piece of the active metal in 200 mL of room temperature water in a 600-mL or 800-mL beaker with a fine mesh wire gauze covering the beaker. Use a document camera, or similar, to pro ...
syllabus for entrance examination - NTU.edu
... ELECTRONIC EFFECTS AND REACTION TYPES The nature of the ...
... ELECTRONIC EFFECTS AND REACTION TYPES The nature of the ...
Introduction to Chemistry
... Ionic- Two elements bond by transferring electrons to create ions that attract together (+ is attracted to - after an electron is transferred) ...
... Ionic- Two elements bond by transferring electrons to create ions that attract together (+ is attracted to - after an electron is transferred) ...
The collision theory of reactions
... The collision theory says that N2 and H2 will only react when they collide. The more frequently they collide, the faster the rate of reaction. Increasing the pressure brings H2 and N2 closer together, so they collide more often. Increasing the temperature makes molecules move faster, increasing the ...
... The collision theory says that N2 and H2 will only react when they collide. The more frequently they collide, the faster the rate of reaction. Increasing the pressure brings H2 and N2 closer together, so they collide more often. Increasing the temperature makes molecules move faster, increasing the ...
CHEMISTRY FINAL EXAM REVIEW SHEET
... Proton: +1 charge, located in nucleus, relative mass = 1 amu Neutron: No charge, located in nucleus, relative mass = 1 amu Electron: -1 charge, located outside of nucleus, relative mass = 1/1840 amu Atomic Number = number of protons in an element. Mass Number = number of protons + neutrons in an ele ...
... Proton: +1 charge, located in nucleus, relative mass = 1 amu Neutron: No charge, located in nucleus, relative mass = 1 amu Electron: -1 charge, located outside of nucleus, relative mass = 1/1840 amu Atomic Number = number of protons in an element. Mass Number = number of protons + neutrons in an ele ...
Science24-UnitA-Section3.1-3.2
... When you study for school, do you put things that are similar together? Do you look for patterns when you try solving a mathematics problem? Similarly, in chemistry, you can group chemical reactions together according to particular patterns in which the reactions occur. The most common types of reac ...
... When you study for school, do you put things that are similar together? Do you look for patterns when you try solving a mathematics problem? Similarly, in chemistry, you can group chemical reactions together according to particular patterns in which the reactions occur. The most common types of reac ...
Chemistry (Theory)
... (b) (i) Nitrogen is chemically less reactive. This is because of the high stability of its molecule, N2. In N2, the two nitrogen atoms form a triple bond. This triple bond has very high bond strength, which is very difficult to break. It is because of nitrogen’s small size that it is able to form p ...
... (b) (i) Nitrogen is chemically less reactive. This is because of the high stability of its molecule, N2. In N2, the two nitrogen atoms form a triple bond. This triple bond has very high bond strength, which is very difficult to break. It is because of nitrogen’s small size that it is able to form p ...
02-Atoms-Molecules
... Concentration – higher reacting particle concentrations produce faster reactions Catalysts – increase the rate of a reaction without being chemically changed Enzymes – biological catalysts ...
... Concentration – higher reacting particle concentrations produce faster reactions Catalysts – increase the rate of a reaction without being chemically changed Enzymes – biological catalysts ...
Review Packet
... 31. Anything that takes up space and has mass is called a. matter b. mass c. volume d. stuff 32. A change in the force of Earth’s gravity on an object will affect its a. mass b. density c. weight d. kinetic energy 33. Chemical proprieties a. include changes of state of a substance b. include mass an ...
... 31. Anything that takes up space and has mass is called a. matter b. mass c. volume d. stuff 32. A change in the force of Earth’s gravity on an object will affect its a. mass b. density c. weight d. kinetic energy 33. Chemical proprieties a. include changes of state of a substance b. include mass an ...
Packet
... 31. Anything that takes up space and has mass is called a. matter b. mass c. volume d. stuff 32. A change in the force of Earth’s gravity on an object will affect its a. mass b. density c. weight d. kinetic energy 33. Chemical proprieties a. include changes of state of a substance b. include mass an ...
... 31. Anything that takes up space and has mass is called a. matter b. mass c. volume d. stuff 32. A change in the force of Earth’s gravity on an object will affect its a. mass b. density c. weight d. kinetic energy 33. Chemical proprieties a. include changes of state of a substance b. include mass an ...
sample paper chemistry clas xi set 3
... 25. (a) Give two properties of Water which are due to Hydrogen bonding. (b) Explain the Structure of H2O2. 26. An org. compound contain 69% carbon and 4.8% Hydrogen, the remainder being oxygen, Calculate the masses of carbon dioxide and water produced when 0.20 g of this compound is subjected to com ...
... 25. (a) Give two properties of Water which are due to Hydrogen bonding. (b) Explain the Structure of H2O2. 26. An org. compound contain 69% carbon and 4.8% Hydrogen, the remainder being oxygen, Calculate the masses of carbon dioxide and water produced when 0.20 g of this compound is subjected to com ...
Chemical Reactions
... indicate relative, not absolute, amounts of reactants and products. 2. The relative masses of the reactants and products of a chemical reaction can be determined from the reaction’s coefficients. 3. The reverse reaction for a chemical equation has the same relative amounts of substances as the forwa ...
... indicate relative, not absolute, amounts of reactants and products. 2. The relative masses of the reactants and products of a chemical reaction can be determined from the reaction’s coefficients. 3. The reverse reaction for a chemical equation has the same relative amounts of substances as the forwa ...
The Chemical Basis of Life
... rates of chemical reactions, but are not consumed (used up) in the reaction. Enzymes are biological catalysts (proteins). ...
... rates of chemical reactions, but are not consumed (used up) in the reaction. Enzymes are biological catalysts (proteins). ...
Chemistry - El Camino College
... a. ___________ formulas in which each pair of shared electrons is represented by a line (e.g.: O=C=O). b. __________ formulas that show only the number of each type of atom in the molecule (e.g.: CO2) c. Atoms such as __ and __ can form single, double, and even triple covalent bonds with other atoms ...
... a. ___________ formulas in which each pair of shared electrons is represented by a line (e.g.: O=C=O). b. __________ formulas that show only the number of each type of atom in the molecule (e.g.: CO2) c. Atoms such as __ and __ can form single, double, and even triple covalent bonds with other atoms ...
Answer Key - La Quinta High School
... takes place. However, the only evidence for this reaction is the release of heat energy, which should be evident as a temperature change for the mixture. Since water has a relatively high specific heat capacity, however, if the acid and base solutions are very dilute, the temperature may change only ...
... takes place. However, the only evidence for this reaction is the release of heat energy, which should be evident as a temperature change for the mixture. Since water has a relatively high specific heat capacity, however, if the acid and base solutions are very dilute, the temperature may change only ...
Unit 13 Worksheet Answers
... They each cause more collisions so the reaction can happen faster. The temperature also causes the collisions to happen with more energy so there are more effective collisions. 4) It has been found that rates are more rapid at the beginning of a reaction than toward the end, assuming the temperature ...
... They each cause more collisions so the reaction can happen faster. The temperature also causes the collisions to happen with more energy so there are more effective collisions. 4) It has been found that rates are more rapid at the beginning of a reaction than toward the end, assuming the temperature ...
Chapter 2 Outline
... steroid based e.g. testosterone, progesterone C. Proteins – structural building blocks of the body 1. composed of amino acid monomers 2. Chemical composition CHON 3. Enzymes are protein catalysts a. Substrate – material enzyme is working on b. Binding site (active site) – place where substrate bonds ...
... steroid based e.g. testosterone, progesterone C. Proteins – structural building blocks of the body 1. composed of amino acid monomers 2. Chemical composition CHON 3. Enzymes are protein catalysts a. Substrate – material enzyme is working on b. Binding site (active site) – place where substrate bonds ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes
... 11) Ionic bonds are formed when A) atoms share electrons. B) two or more atoms lose electrons at the same time. C) electrons are completely transferred from one atom to another. D) hydrogen forms bonds with negatively charged atoms in the same or different molecule. E) a pair of electrons is shared ...
... 11) Ionic bonds are formed when A) atoms share electrons. B) two or more atoms lose electrons at the same time. C) electrons are completely transferred from one atom to another. D) hydrogen forms bonds with negatively charged atoms in the same or different molecule. E) a pair of electrons is shared ...
Ch 11 Chemical Reactions
... products, using “+” and “→” Count the atoms of each type appearing on both sides Treat polyatomic ions like an “element” if they are unchanged by the reaction Balance the elements one at a time by adding coefficients (the numbers in front) where you need more - save balancing the pure elements until ...
... products, using “+” and “→” Count the atoms of each type appearing on both sides Treat polyatomic ions like an “element” if they are unchanged by the reaction Balance the elements one at a time by adding coefficients (the numbers in front) where you need more - save balancing the pure elements until ...
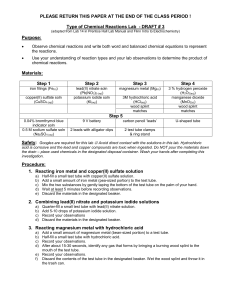
Type of Chemical Reactions Lab
... for the conduction of electricity and the indicator just shows us that a reaction is taking place that changes pH. The reaction would take place without either of these present… we just wouldn’t know it. b) Then write the state symbols for each chemical (s, l, g, aq). c) Then balance the equation us ...
... for the conduction of electricity and the indicator just shows us that a reaction is taking place that changes pH. The reaction would take place without either of these present… we just wouldn’t know it. b) Then write the state symbols for each chemical (s, l, g, aq). c) Then balance the equation us ...
4 - Ms McRae`s Science
... a)yes bec an increase in the temperature of the HCl will increase the velocity of the reactant particles which will increase the number of collisions AND increase the number of effective collisions i.e. ones that have sufficient energy (activation energy) to react b) skipping this one for now until ...
... a)yes bec an increase in the temperature of the HCl will increase the velocity of the reactant particles which will increase the number of collisions AND increase the number of effective collisions i.e. ones that have sufficient energy (activation energy) to react b) skipping this one for now until ...
Erik`s Chemistry: Thermochemistry - ECHS Chemistry
... 1. Heat content is accounted for by a change in "heat flow" or enthalpy of the reaction system. 1. Endothermic reaction: H > 0 (i.e., H products >H reactants). Heat absorbed goes to increase the enthalpy of the reaction system. 2. Exothermic reaction: H < 0 (i.e., H products < H reactants). Heat is ...
... 1. Heat content is accounted for by a change in "heat flow" or enthalpy of the reaction system. 1. Endothermic reaction: H > 0 (i.e., H products >H reactants). Heat absorbed goes to increase the enthalpy of the reaction system. 2. Exothermic reaction: H < 0 (i.e., H products < H reactants). Heat is ...
File - chemistryattweed
... and was interested in the effect of heat on the chemistry of gases. In the early 1900s, Haber reacted nitrogen with hydrogen, using an iron catalyst, to form ammonia. Ammonia can be readily converted to a range of valuable products. In 1908 he had improved the reaction and in 1911 he was rewarded wi ...
... and was interested in the effect of heat on the chemistry of gases. In the early 1900s, Haber reacted nitrogen with hydrogen, using an iron catalyst, to form ammonia. Ammonia can be readily converted to a range of valuable products. In 1908 he had improved the reaction and in 1911 he was rewarded wi ...
Extra Unit 3 Problems for the Web Site (Honors
... a) 33.8 g b) 49.0 g c) 24.5 g d) 122g 14. A compound is analyzed and found to contain 12.1% carbon, 16.2% oxygen, and 71.7% chlorine. What is the empirical formula of this compound? a) COCl b) COCl2 c) CO2Cl d) CO2Cl2 e) COCl4 15. A certain compound has an empirical formula of NH2O. Its molar mass ...
... a) 33.8 g b) 49.0 g c) 24.5 g d) 122g 14. A compound is analyzed and found to contain 12.1% carbon, 16.2% oxygen, and 71.7% chlorine. What is the empirical formula of this compound? a) COCl b) COCl2 c) CO2Cl d) CO2Cl2 e) COCl4 15. A certain compound has an empirical formula of NH2O. Its molar mass ...
+ 2 HCL(aq) CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
... Chemical Formula: States what elements a compound contains and the exact number of atoms of these elements. Oxidation Number: positive or negative number on the periodic table that indicates how many electrons an element has gained, lost or shared when bonding with another element. Polyatomic Atom: ...
... Chemical Formula: States what elements a compound contains and the exact number of atoms of these elements. Oxidation Number: positive or negative number on the periodic table that indicates how many electrons an element has gained, lost or shared when bonding with another element. Polyatomic Atom: ...