C) Gifford Pinchot - life.illinois.edu
... A) Parasites alone could cause the observed deformities B) Chemicals alone could cause the observed deformities C) Chemicals combined with parasites increased the likelihood of deformities D) both a and c E) both b and c If you marked D but got this question wrong, see us! 16. (16) Which of the foll ...
... A) Parasites alone could cause the observed deformities B) Chemicals alone could cause the observed deformities C) Chemicals combined with parasites increased the likelihood of deformities D) both a and c E) both b and c If you marked D but got this question wrong, see us! 16. (16) Which of the foll ...
Chapter 8, Section 2 Notes
... Bellringer “As more individuals are produced that can possibly survive, there must…be a struggle for existence, either one individual with another of the same species, or with the individuals of distinct species, or with the physical conditions of life.” - Charles Darwin How does this quote relate t ...
... Bellringer “As more individuals are produced that can possibly survive, there must…be a struggle for existence, either one individual with another of the same species, or with the individuals of distinct species, or with the physical conditions of life.” - Charles Darwin How does this quote relate t ...
1 Community Ecology
... 2) Species composition: identity of species that constitute a community 3) Species diversity: species richness and relative abundance Shannon-Weiner index of diversity: ...
... 2) Species composition: identity of species that constitute a community 3) Species diversity: species richness and relative abundance Shannon-Weiner index of diversity: ...
Competition in Triclads
... are stocked in time • Changes in methods … • But, continues focused on population effects of competition. • Species are immersed in communities and interactions with multiple species may change the outcome of competition. • Presence of common predators may allow for “apparent competition” ...
... are stocked in time • Changes in methods … • But, continues focused on population effects of competition. • Species are immersed in communities and interactions with multiple species may change the outcome of competition. • Presence of common predators may allow for “apparent competition” ...
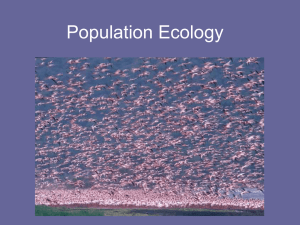
Population Ecology
... given period of time = growth rate. Growth rate = births – deaths • Populations usually stay about the same size from year to year as factors kill many individuals before they can reproduce. ...
... given period of time = growth rate. Growth rate = births – deaths • Populations usually stay about the same size from year to year as factors kill many individuals before they can reproduce. ...
Understanding Our Environment
... compete for exactly the same resources for an extended period of time. One will either become locally extinct, or partition the resource and utilize a sub-set of the same resource. Interactions among species are added to regulation by each species’ response to the physical environment ...
... compete for exactly the same resources for an extended period of time. One will either become locally extinct, or partition the resource and utilize a sub-set of the same resource. Interactions among species are added to regulation by each species’ response to the physical environment ...
Chapter 14 Review
... • An ecological niche is how a species lives. • An ecological niche includes food, temperature, water, and behavior. ...
... • An ecological niche is how a species lives. • An ecological niche includes food, temperature, water, and behavior. ...
Science Notes: September 8, 2011 COMPETITON Competition may
... Competition may occur for many reasons. Usually this has to do with resources like food and water, but also for other reasons like living space. Competition occurs when two or more organisms compete for the same resources. Example: ...
... Competition may occur for many reasons. Usually this has to do with resources like food and water, but also for other reasons like living space. Competition occurs when two or more organisms compete for the same resources. Example: ...
EcologyTestStudyGuide_ANswers
... Pseudoscorpions hide under the wings of beetles for protection and transportation. They don’t sting, and don’t bother the beetles in any way. ...
... Pseudoscorpions hide under the wings of beetles for protection and transportation. They don’t sting, and don’t bother the beetles in any way. ...
questions
... role in shaping ecosystems by directly altering its physical environment, typically creating and enhancing a habitat in a way that benefit other species. We also need to look at what factors affect the size and growth of a population. There are two main factors that determine how much a population c ...
... role in shaping ecosystems by directly altering its physical environment, typically creating and enhancing a habitat in a way that benefit other species. We also need to look at what factors affect the size and growth of a population. There are two main factors that determine how much a population c ...
Competition Competition is an interaction between organisms or
... An example among animals could be the case of cheetahs and lions; since both species feed on similar prey, they are negatively impacted by the presence of the other because they will have less food, however they still persist together, despite the prediction that under competition one will displace ...
... An example among animals could be the case of cheetahs and lions; since both species feed on similar prey, they are negatively impacted by the presence of the other because they will have less food, however they still persist together, despite the prediction that under competition one will displace ...
Species - a group of individuals that is able to breed with each other
... Competition is density dependent when more organisms desire a limited resource, competition for it is more intense. the more similar the requirements of the two groups (the more similar their niches), the more intense the competition. This can lead to the mutual exclusion of competing species, inste ...
... Competition is density dependent when more organisms desire a limited resource, competition for it is more intense. the more similar the requirements of the two groups (the more similar their niches), the more intense the competition. This can lead to the mutual exclusion of competing species, inste ...
The ecological niche is a species` role and environment Competitive
... Taxonomy describes relationships among species Taxonomy: the study of types of organisms and their relationships. ...
... Taxonomy describes relationships among species Taxonomy: the study of types of organisms and their relationships. ...
The problem with invasive species
... Of those that survive, many do not cause “severe harm” to native ecosystems, species or humans (only 15% of establishments) ...
... Of those that survive, many do not cause “severe harm” to native ecosystems, species or humans (only 15% of establishments) ...
Interactions Among Living Things
... Every organism has a variety of adaptations (characteristics) that are suited to its specific conditions which help the organism to survive. ...
... Every organism has a variety of adaptations (characteristics) that are suited to its specific conditions which help the organism to survive. ...
Chapter 11 Section 3
... • Niche – the role of an organism in its habitat, or how it makes its living – Type of food organism eats – How it obtains its food – When and how organism reproduces – Physical conditions needed to survive ...
... • Niche – the role of an organism in its habitat, or how it makes its living – Type of food organism eats – How it obtains its food – When and how organism reproduces – Physical conditions needed to survive ...
4 Review Worksheet
... 3. Three different warbler species live in the same tree. One species feeds at the top of the tree, the second species feeds in the middle part of the tree, and the third species feeds at the bottom of the tree. Do all three species occupy the same niche? Explain. ...
... 3. Three different warbler species live in the same tree. One species feeds at the top of the tree, the second species feeds in the middle part of the tree, and the third species feeds at the bottom of the tree. Do all three species occupy the same niche? Explain. ...