chapter 7
... B. Different species’ interactions and influences on their environments are not completely clear. C. Ecological communities are constantly changing, establishing communities, responding to disturbances, and seeking stability. D. For the continuing survival of our environment, we should remember the ...
... B. Different species’ interactions and influences on their environments are not completely clear. C. Ecological communities are constantly changing, establishing communities, responding to disturbances, and seeking stability. D. For the continuing survival of our environment, we should remember the ...
SpeciesInteractions
... A population is the number of a particular species living in a particular area. When a species first moves into an area, e.g. a feral animal or after a big disturbance, its population will usually increase rapidly. However, a time will come when the organism will have outgrown the carrying capacity ...
... A population is the number of a particular species living in a particular area. When a species first moves into an area, e.g. a feral animal or after a big disturbance, its population will usually increase rapidly. However, a time will come when the organism will have outgrown the carrying capacity ...
15 Competition 2010
... MAJOR CONCEPTS 1) Facilitation is the alternative to competition; it is understudied. 2) Consumers compete by using a resource that reduces availability to others. 3) Competition occurs through exploitation of shared resources or direct interference. 4) Responses of plant and animal species to intra ...
... MAJOR CONCEPTS 1) Facilitation is the alternative to competition; it is understudied. 2) Consumers compete by using a resource that reduces availability to others. 3) Competition occurs through exploitation of shared resources or direct interference. 4) Responses of plant and animal species to intra ...
PRACTICE ECOLOGY QUESTIONS 1 Choose terms from the list
... a. ferns b. mosses c. lichens d. tree seedlings ...
... a. ferns b. mosses c. lichens d. tree seedlings ...
5.1 outline
... Ecological Stability, Complexity, and Sustainability Living systems maintain some degree of stability or sustainability through constant change in response to changing environmental conditions. ...
... Ecological Stability, Complexity, and Sustainability Living systems maintain some degree of stability or sustainability through constant change in response to changing environmental conditions. ...
Chapter 1 Section 2: Unifying Themes of Biology
... One species is better _________ to the niche and the other will either be pushed _______ or become _____________. The niche will be ____________. The two species will further ___________. Ecological _____________ are species that occupy similar niches but live in different _______________ re ...
... One species is better _________ to the niche and the other will either be pushed _______ or become _____________. The niche will be ____________. The two species will further ___________. Ecological _____________ are species that occupy similar niches but live in different _______________ re ...
primary productivity - Broadneck High School
... Fishing down the marine food web. After the large fish at the top of the food web are fished out, fisheries go after smaller fish and invertebrates at lower levels in the food web while their trawling destroys animals and plants on the sea floor. Time increases toward the right along the blue arrow ...
... Fishing down the marine food web. After the large fish at the top of the food web are fished out, fisheries go after smaller fish and invertebrates at lower levels in the food web while their trawling destroys animals and plants on the sea floor. Time increases toward the right along the blue arrow ...
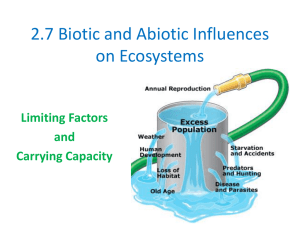
2.7 Biotic and Abiotic Influences on Ecosystems
... • The maximum population size of a particular species that a given ecosystem can sustain. • As population's size increases, the demand for resources, such as food, water, shelter, and space also increase. • Eventually, there will not be enough resources for each individual. ...
... • The maximum population size of a particular species that a given ecosystem can sustain. • As population's size increases, the demand for resources, such as food, water, shelter, and space also increase. • Eventually, there will not be enough resources for each individual. ...
Maintaining Balance
... *Predators, disease, and parasites help to keep ecosystem balance. If one species begins to dominate an ecosystem, it becomes more susceptible to disease, parasites, or predation. Organism specialization: 1. Habitat: The place in which an organism lives—it provides food, water, cover, and space. 2. ...
... *Predators, disease, and parasites help to keep ecosystem balance. If one species begins to dominate an ecosystem, it becomes more susceptible to disease, parasites, or predation. Organism specialization: 1. Habitat: The place in which an organism lives—it provides food, water, cover, and space. 2. ...
Carrying capacity
... Size of populations lower down on the chain (the amount of food available) ...
... Size of populations lower down on the chain (the amount of food available) ...
File
... as they are still composed of cells. Abiotic Factors: parts of an ecosystem that have never been living or are now no longer composed of cells. ...
... as they are still composed of cells. Abiotic Factors: parts of an ecosystem that have never been living or are now no longer composed of cells. ...
Environmental Science Study Guide for Chapter 8 (Changing
... Environmental Science Study Guide for Chapter 8 (Changing Populations) Answer Key 1. Define population and give an example of one. A population is a group of organisms of the same species that live in a specific geographical area at the same time and interbreed. Ex. Daisies in a field in Ohio breed ...
... Environmental Science Study Guide for Chapter 8 (Changing Populations) Answer Key 1. Define population and give an example of one. A population is a group of organisms of the same species that live in a specific geographical area at the same time and interbreed. Ex. Daisies in a field in Ohio breed ...
Lecture Notes - GEOCITIES.ws
... Parasite feeds off the host Does NOT usually result in immediate death for host ...
... Parasite feeds off the host Does NOT usually result in immediate death for host ...
Abstract
... forest. However, the effects due to synergistic influences of all the tested parameters in the sensitivity analysis may become clearer when studies are conducted while putting into perspective important gradients such as environmental and topographical attributes. This study generated predictive ins ...
... forest. However, the effects due to synergistic influences of all the tested parameters in the sensitivity analysis may become clearer when studies are conducted while putting into perspective important gradients such as environmental and topographical attributes. This study generated predictive ins ...
Outline
... The ecological niche is the sum total of an organism’s use of abiotic/biotic resources in the environment. An organism’s niche is its role in the environment. The competitive exclusion principle can be restated to say that two species cannot coexist in a community if their niches are identical. ...
... The ecological niche is the sum total of an organism’s use of abiotic/biotic resources in the environment. An organism’s niche is its role in the environment. The competitive exclusion principle can be restated to say that two species cannot coexist in a community if their niches are identical. ...
File - Spanish Point Biology
... for necessary resources that are in short supply. Intra-specific competition: Between members of the same species i.e. within a species Inter-specific competition: Between members of different species Plants compete for light, water, minerals and space Animals compete for food, water, shelter, terri ...
... for necessary resources that are in short supply. Intra-specific competition: Between members of the same species i.e. within a species Inter-specific competition: Between members of different species Plants compete for light, water, minerals and space Animals compete for food, water, shelter, terri ...
HL Ecological Relationships Poster
... for necessary resources that are in short supply. Intra-specific competition: Between members of the same species i.e. within a species Inter-specific competition: Between members of different species Plants compete for light, water, minerals and space Animals compete for food, water, shelter, terri ...
... for necessary resources that are in short supply. Intra-specific competition: Between members of the same species i.e. within a species Inter-specific competition: Between members of different species Plants compete for light, water, minerals and space Animals compete for food, water, shelter, terri ...
Lecture 3
... • Darwin also pointed out a subset of Natural Selection: Sexual Selection, where the variation is "being more sexy" (and thus have better than average chance of breeding, and thus passing on "sexiness", compared to other members of the population): peacock tails, bird song, etc. • Sexual Selection ...
... • Darwin also pointed out a subset of Natural Selection: Sexual Selection, where the variation is "being more sexy" (and thus have better than average chance of breeding, and thus passing on "sexiness", compared to other members of the population): peacock tails, bird song, etc. • Sexual Selection ...
Environmental Science
... and each of those offspring survive to reproduce c. If adults are not replaced by new births, the growth rate will be negative and the population will shrink 4. populations usually stay close to the same size because of various factors that kill many individuals before they can reproduce 5. biotic p ...
... and each of those offspring survive to reproduce c. If adults are not replaced by new births, the growth rate will be negative and the population will shrink 4. populations usually stay close to the same size because of various factors that kill many individuals before they can reproduce 5. biotic p ...
Guided Notes Ch 4, 5, 6
... – __________________________________________ occurs such as fire, hurricane, human activities and community is destroyed. – Ecosystem interacts to restore _______________________ conditions. Earth as a System ...
... – __________________________________________ occurs such as fire, hurricane, human activities and community is destroyed. – Ecosystem interacts to restore _______________________ conditions. Earth as a System ...