* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Science Notes: September 8, 2011 COMPETITON Competition may
Ecosystem services wikipedia , lookup
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Maximum sustainable yield wikipedia , lookup
Human overpopulation wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
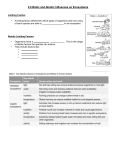
Science Notes: September 8, 2011 COMPETITON Competition may occur for many reasons. Usually this has to do with resources like food and water, but also for other reasons like living space. Competition occurs when two or more organisms compete for the same resources. Example: in The Gila woodpecker makes nesting holes the saguaro cactus. Because there are more organisms than holes they must compete with each other for the shelter these holes provide. Competition limits population size. When resources are scarce some individuals in a population might not survive to raise any young. In nature the most intense competition is between species. It's because they usually need the same kinds of food and shelter... Competition occurs WITHIN species and BETWEEN species... PLEASE ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTION NOW IN YOUR NOTES: What point am I trying to make above? (what is the difference?) ...For example after the woodpecker (above) abandons its nest, the holes may be inhabited by snakes, owls or lizards, for example. LIMITING FACTORS: In any ecosystem the availability of food, water, living space, mates, places to live and other resources are limited. A limiting factor is anything that restricts the number of individuals in a population. Limiting factors include living and non-living features of the ecosystem. The same limiting factor can affect more than one population in an area. For example, a lack of rain can limit plant growth. As a result there would be fewer seed produced than if there was normal rainfall. For mice that eat seeds the reduction in their food supply could be a limiting factor. A smaller mouse population could then be a limiting factor for hawks, owls or snakes that feed on mice. CARRYING CAPACITY: (1) Carrying capacity is the largest number of individuals (2) in one species (3) that an ecosystem can support (4) over time. Like a credit card... …you might be able to go over the limit for a short time, but there are consequences. Examples: (T-Chart) If the population exceeds the environment's carrying capacity some individuals may not have enough resources. As a result, they could die or be forced to move. QUESTIONS? I have two for you: 1. How are limiting factors related to carrying capacity? 2. Why are food and water the limiting factors that usually have the greatest effect on population size?