Ecosystems and Living Organisms
... niche because of competition with another species (interspecific competition). No two organisms can occupy the same niche Coexistence is possible if niches are reduced Gause study ...
... niche because of competition with another species (interspecific competition). No two organisms can occupy the same niche Coexistence is possible if niches are reduced Gause study ...
Midterm Review
... Pollution, loss of resources, loss of biodiversity 3. When did human population grow rapidly? Industrial Revolution 4. How did hunter-gathers change their environment? Overhunted- led to extinction 5. Developed countries often have… Wealth, more pollution, big ecological footprint, slower population ...
... Pollution, loss of resources, loss of biodiversity 3. When did human population grow rapidly? Industrial Revolution 4. How did hunter-gathers change their environment? Overhunted- led to extinction 5. Developed countries often have… Wealth, more pollution, big ecological footprint, slower population ...
Species Interactions
... • Organisms may develop differences in niches because of competition for resources. • Resource Partitioning – species coexist by using only part of the available resources – Ex: some birds eat the same insects, but hunt for them in different places ...
... • Organisms may develop differences in niches because of competition for resources. • Resource Partitioning – species coexist by using only part of the available resources – Ex: some birds eat the same insects, but hunt for them in different places ...
Ecological and Evolutionary Principles
... • Other subpopulations are sinks, which means that they may receive individuals from other subpopulations, but they are not sources (example, only juveniles disperse, but the subpopulation in question does not have individuals that reproduce successfully. ...
... • Other subpopulations are sinks, which means that they may receive individuals from other subpopulations, but they are not sources (example, only juveniles disperse, but the subpopulation in question does not have individuals that reproduce successfully. ...
7th grade Science
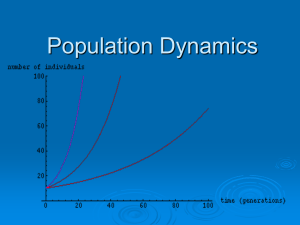
... population reproduce at a constant rate, so that the larger a population gets, the faster it grows ...
... population reproduce at a constant rate, so that the larger a population gets, the faster it grows ...
ECOLOGY
... carnivore, herbivore. Competition: occurs when 2 or more organisms require the same limiting resource. Two types of competition - Intraspecific competition: competition within a population for the same resource - Interspecific competition: competition between individuals of 2 species for the same re ...
... carnivore, herbivore. Competition: occurs when 2 or more organisms require the same limiting resource. Two types of competition - Intraspecific competition: competition within a population for the same resource - Interspecific competition: competition between individuals of 2 species for the same re ...
28 Ecosystems - answers
... 1 (a) All the organisms of one species living in a defined area. Population (b) All the organisms living in the same defined area. Community (c) The place where an organism is usually found. Habitat (d) A self-supporting group of organisms and their environment. Ecosystem 2 (a) Animals compete for f ...
... 1 (a) All the organisms of one species living in a defined area. Population (b) All the organisms living in the same defined area. Community (c) The place where an organism is usually found. Habitat (d) A self-supporting group of organisms and their environment. Ecosystem 2 (a) Animals compete for f ...
populations
... • 1. Density-dependent factors = dependent on the # of organisms in a given area. ...
... • 1. Density-dependent factors = dependent on the # of organisms in a given area. ...
Alien species threaten Indian ecosystems
... NEW DELHI: Invasive alien species like Lantana and Cuscutta pose a threat to the ecosystems and lead to loss of biodiversity of the country, the government today said. Invasive alien species are plants, animals, pathogens and other organisms that are non-native to an ecosystem and which may cause ec ...
... NEW DELHI: Invasive alien species like Lantana and Cuscutta pose a threat to the ecosystems and lead to loss of biodiversity of the country, the government today said. Invasive alien species are plants, animals, pathogens and other organisms that are non-native to an ecosystem and which may cause ec ...
Populations, Communities and Species Interaction
... Co-evolution: predator and prey evolve in response to each other (camouflage, mimicry) ...
... Co-evolution: predator and prey evolve in response to each other (camouflage, mimicry) ...
Limits on Population
... or more organisms fighting for the same resource in a given area Can be within species or between different species ...
... or more organisms fighting for the same resource in a given area Can be within species or between different species ...
Biodiversity, Species Interactions, and Population Control
... Indicator Species Provide early warnings of ecosystem damage Indicator of water quality (trout) Birds as environmental indicators (affected by habitat loss, chemicals) ...
... Indicator Species Provide early warnings of ecosystem damage Indicator of water quality (trout) Birds as environmental indicators (affected by habitat loss, chemicals) ...
Ecosystem Interactions
... COMPETITIVE RELATIONSHIPS (2 TYPES) 2. INTERSPECIFIC 2. Interspecific Between 2 or more species As the population of one species increases, it may limit the density of the competing species ...
... COMPETITIVE RELATIONSHIPS (2 TYPES) 2. INTERSPECIFIC 2. Interspecific Between 2 or more species As the population of one species increases, it may limit the density of the competing species ...
Chapter 20
... easily from individual to individual in crowded populations. Density-independent factors might include food resources, freezes, floods, fires. How Competition Shapes Communities Use the terms from this section: interspecific competition, fundamental niche, realized niche, niche overlap, competitive ...
... easily from individual to individual in crowded populations. Density-independent factors might include food resources, freezes, floods, fires. How Competition Shapes Communities Use the terms from this section: interspecific competition, fundamental niche, realized niche, niche overlap, competitive ...
File
... 10. Explain the difference between density-dependent and density-independent factors on a population’s size. Be able to give at least two examples of each. 11. Name at least four characteristics of r-selected populations and K-selected populations. 12. What are costs are associated with sexual repro ...
... 10. Explain the difference between density-dependent and density-independent factors on a population’s size. Be able to give at least two examples of each. 11. Name at least four characteristics of r-selected populations and K-selected populations. 12. What are costs are associated with sexual repro ...
Ecosystem and Genetic Diversity
... environment have a better chance of surviving and reproducing than those that are not (remember “survival of the fittest?”) Individuals within the same species vary from one another. This causes some to have different characteristics, either physical or behavioral, that may cause one to have a bette ...
... environment have a better chance of surviving and reproducing than those that are not (remember “survival of the fittest?”) Individuals within the same species vary from one another. This causes some to have different characteristics, either physical or behavioral, that may cause one to have a bette ...
Habitat
... 1. What kind of symbiotic relationship does a lichen exhibit? 2. Identify 2 organisms that have a predator/prey relationship? 3. Two male gorillas compete for territory. Is this interspecific or intra-specific competition? 4. The competitive exclusion principle says that no 2 species can occupy the ...
... 1. What kind of symbiotic relationship does a lichen exhibit? 2. Identify 2 organisms that have a predator/prey relationship? 3. Two male gorillas compete for territory. Is this interspecific or intra-specific competition? 4. The competitive exclusion principle says that no 2 species can occupy the ...