Living Things and the Environment
... 13. What are some ways weather conditions can limit population growth? ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ Adapting to the Environment/Competition (p. 723-724) 14. A characteristic that allows a species to live successfully in its environment. ____ ...
... 13. What are some ways weather conditions can limit population growth? ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ Adapting to the Environment/Competition (p. 723-724) 14. A characteristic that allows a species to live successfully in its environment. ____ ...
Species Richness: The number of species present in a community
... Let’s Practice 1. Some plants displace others by having leaf and root systems that allow them to absorb more sunlight and soil nutrients than their competition. 2. Other plants produce chemicals that inhibit the growth or germination of seeds of competing species. ...
... Let’s Practice 1. Some plants displace others by having leaf and root systems that allow them to absorb more sunlight and soil nutrients than their competition. 2. Other plants produce chemicals that inhibit the growth or germination of seeds of competing species. ...
Several factors such as history, gene flow or genetic drift shape the
... by highly mobile taxa (seed of plants, vertebrates, flying insects). Comparative phylogeographic analyses focusing on distantly related but co-distributed species with proposed different dispersal abilities are an approved strategy to inference the effect of historical and/or contemporaneous process ...
... by highly mobile taxa (seed of plants, vertebrates, flying insects). Comparative phylogeographic analyses focusing on distantly related but co-distributed species with proposed different dispersal abilities are an approved strategy to inference the effect of historical and/or contemporaneous process ...
File
... o takes into account all aspects of the organism’s existence the jobs and relationships it has, all the things it needs to survive, its habitat, etc. if there was no competition, an organism’s niche could be very large (fundamental niche), but because competition does exist, organisms are limite ...
... o takes into account all aspects of the organism’s existence the jobs and relationships it has, all the things it needs to survive, its habitat, etc. if there was no competition, an organism’s niche could be very large (fundamental niche), but because competition does exist, organisms are limite ...
interactions among organisms
... INTERACTIONS AMONG ORGANISMS Classification and Definition Neutralism: find when two species interact, but one does not affect the other. Mutualism: the relationship between two species benefiting each other is not obligatory either is temporary. Symbiosis: the relationship between the two species i ...
... INTERACTIONS AMONG ORGANISMS Classification and Definition Neutralism: find when two species interact, but one does not affect the other. Mutualism: the relationship between two species benefiting each other is not obligatory either is temporary. Symbiosis: the relationship between the two species i ...
Chapters 4 and 5 Review
... c. evolutionary adjustments between interacting members of an ecosystem d. the act of one organism killing and eating another for food. ab. a symbiotic relationship in which both species benefit ...
... c. evolutionary adjustments between interacting members of an ecosystem d. the act of one organism killing and eating another for food. ab. a symbiotic relationship in which both species benefit ...
Interactions Between Organisms - mvhs
... • Competition = when two species compete for the same resource • Competition can lead to competitive exclusion or resource partitioning ...
... • Competition = when two species compete for the same resource • Competition can lead to competitive exclusion or resource partitioning ...
Exam 4 Review - Iowa State University
... A person lifts a finger. The dog eventually sits. The dog gets fed. In time, even beginning to lift a finger leads to the dog sitting. Goslings are receptive to learning who their mother is early in their development and will follow the first thing they see upon hatching. When its humidity increases ...
... A person lifts a finger. The dog eventually sits. The dog gets fed. In time, even beginning to lift a finger leads to the dog sitting. Goslings are receptive to learning who their mother is early in their development and will follow the first thing they see upon hatching. When its humidity increases ...
Ecological Relationships and Succession
... aurelia, develop a hypothesis to explain why interspecific competition has an effect on the relative population size of ...
... aurelia, develop a hypothesis to explain why interspecific competition has an effect on the relative population size of ...
Maintaining Sustainable Environments Requires Knowledge
... peregrine’s return, the bird’s status has been downgraded from endangered to threatened. ...
... peregrine’s return, the bird’s status has been downgraded from endangered to threatened. ...
Chapter 4-3 predation, herbivores and keystone species
... (herbivore) feeds on producers (plants). • Eg: Aphids and plants, horses and plants, and rabbits and vegetables/plants. ...
... (herbivore) feeds on producers (plants). • Eg: Aphids and plants, horses and plants, and rabbits and vegetables/plants. ...
AP Biology - Naber Biology
... 7. Use Inquiry Figure 54.3 to determine the realized niche and fundamental niche of the two barnacle species. If Balanus has a fundamental niche that is equal to its realized niche, use arrows to show the area both species would cover for both types of niches. Your diagram will have a fundamental a ...
... 7. Use Inquiry Figure 54.3 to determine the realized niche and fundamental niche of the two barnacle species. If Balanus has a fundamental niche that is equal to its realized niche, use arrows to show the area both species would cover for both types of niches. Your diagram will have a fundamental a ...
Document
... The carrying capacity is different for different species. When can the carrying capacity change? When conditions in the environment change ...
... The carrying capacity is different for different species. When can the carrying capacity change? When conditions in the environment change ...
Chapter Fourteen Vocabulary
... competition: ecological relationship in which two organisms attempt to obtain the same resource. predation: process by which one organism hunts and kills another organism for food. symbiosis: ecological relationship between members of at least two different species that live in direct contact with o ...
... competition: ecological relationship in which two organisms attempt to obtain the same resource. predation: process by which one organism hunts and kills another organism for food. symbiosis: ecological relationship between members of at least two different species that live in direct contact with o ...
Ecology - Science
... All the organisms living in an area and the nonliving features of their environment ...
... All the organisms living in an area and the nonliving features of their environment ...
Chapter 5 Notes
... o Has no biologically important gaseous compounds; phosphorus erodes from rock and is absorbed by plant roots Ecological Niches: The totality of an organism’s adaptations, its use of resources, and the lifestyle to which it fits. Includes its habitat, it’s distinctive lifestyle, and its role in ...
... o Has no biologically important gaseous compounds; phosphorus erodes from rock and is absorbed by plant roots Ecological Niches: The totality of an organism’s adaptations, its use of resources, and the lifestyle to which it fits. Includes its habitat, it’s distinctive lifestyle, and its role in ...
Populations and Conservation Study Guide
... c. Circle the time period where the graph resembles the exponential population growth graph. WHERE IT LOOKS LIKE A J CURVE) 29.Contrast density-dependent and density-independent factors. Provide examples with your answer. DENSITY- ...
... c. Circle the time period where the graph resembles the exponential population growth graph. WHERE IT LOOKS LIKE A J CURVE) 29.Contrast density-dependent and density-independent factors. Provide examples with your answer. DENSITY- ...
Ecosystem: Stability and Change
... Movement of Matter and Energy Replacement of Organisms Ecological Succession- the natural replacement of one community in particular area with a different, and usually more complex community, over a period of time ...
... Movement of Matter and Energy Replacement of Organisms Ecological Succession- the natural replacement of one community in particular area with a different, and usually more complex community, over a period of time ...
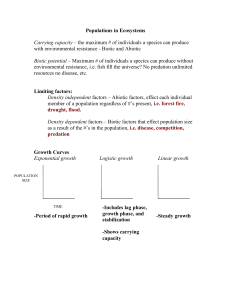
Populations in Ecosystems
... Biotic relationships Predation – organism that eats another organism Scavenger – organism that eats dead organism Competition – Interaction between two organisms for a limited resource Parasitism – Relationship between two organisms where 1 is harmed and one benefits Mutualism – 2 organisms live to ...
... Biotic relationships Predation – organism that eats another organism Scavenger – organism that eats dead organism Competition – Interaction between two organisms for a limited resource Parasitism – Relationship between two organisms where 1 is harmed and one benefits Mutualism – 2 organisms live to ...