DNA and RNA - Xavier High School
... 2. How did Watson and Crick’s model explain why there are equal amounts of thymine and adenine in DNA? 3. Why did Hershey and Chase grow viruses in cultures that contained both radioactive phosphorus and radioactive sulfur? What might have happened if they only used one? ...
... 2. How did Watson and Crick’s model explain why there are equal amounts of thymine and adenine in DNA? 3. Why did Hershey and Chase grow viruses in cultures that contained both radioactive phosphorus and radioactive sulfur? What might have happened if they only used one? ...
BNFO601 Introduction to Bioinformatics Flow of Information
... Just as the properties of proteins are determined by their structure, so it is with DNA. Everyone has heard about DNA, the double helix. What made the structure compelling when it was first conceived 50 years ago was the explanation it provided for the replication of the genetic material (Figure 2). ...
... Just as the properties of proteins are determined by their structure, so it is with DNA. Everyone has heard about DNA, the double helix. What made the structure compelling when it was first conceived 50 years ago was the explanation it provided for the replication of the genetic material (Figure 2). ...
Cell Division
... DNA coils to form Chromosomes A Gene is a section of DNA Genetic info is encoded in sequence of base triplets, called codons ...
... DNA coils to form Chromosomes A Gene is a section of DNA Genetic info is encoded in sequence of base triplets, called codons ...
Slides - gserianne.com
... – DNA is a anti-parallel, double-stranded helical polynucleotide containing deoxyribose – Four bases are used in DNA: • Purines (double ring): Adenine (A), Guanine (G) • Pyrimidines (single ring): Cytosine (C), Thymine (T) ...
... – DNA is a anti-parallel, double-stranded helical polynucleotide containing deoxyribose – Four bases are used in DNA: • Purines (double ring): Adenine (A), Guanine (G) • Pyrimidines (single ring): Cytosine (C), Thymine (T) ...
DNA Replication
... DNA BIG Picture • Chromosomes are made of DNA. • DNA has your genes on it. • DNA has the instructions for making all proteins for the organism. • DNA is unique to each individual. • DNA determines how an organism looks and ...
... DNA BIG Picture • Chromosomes are made of DNA. • DNA has your genes on it. • DNA has the instructions for making all proteins for the organism. • DNA is unique to each individual. • DNA determines how an organism looks and ...
Amino Acids
... If compound how many elements and how many atoms of each element are there? What type of formula is this? HW: Please Print out Review sheet for Quarterly and make sure to study all info – Bring this sheet to class tomorrow. ...
... If compound how many elements and how many atoms of each element are there? What type of formula is this? HW: Please Print out Review sheet for Quarterly and make sure to study all info – Bring this sheet to class tomorrow. ...
chapter 10
... 3. RNA is chemically similar to DNA except that its sugars have an additional oxygen atom, and the base thymine is replaced by a structurally similar base called a. uracil. c. cytosine. b. alanine. d. codon. 4. In RNA molecules, adenine is complementary to a. cytosine. c. thymine. b. guanine. d. ura ...
... 3. RNA is chemically similar to DNA except that its sugars have an additional oxygen atom, and the base thymine is replaced by a structurally similar base called a. uracil. c. cytosine. b. alanine. d. codon. 4. In RNA molecules, adenine is complementary to a. cytosine. c. thymine. b. guanine. d. ura ...
The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
... involves many enzymes: replication 2. the DNA codes for the production of messenger RNA (mRNA) during transcription 3. In eucaryotic cells, the mRNA is processed and migrates from the nucleus to the cytoplasm 4. Messenger RNA carries coded information to the ribosomes. The ribosomes “read” thi ...
... involves many enzymes: replication 2. the DNA codes for the production of messenger RNA (mRNA) during transcription 3. In eucaryotic cells, the mRNA is processed and migrates from the nucleus to the cytoplasm 4. Messenger RNA carries coded information to the ribosomes. The ribosomes “read” thi ...
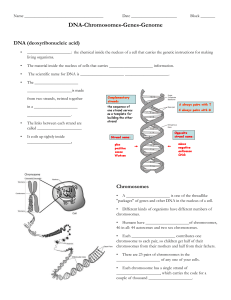
DNA-Chromosomes-Genes-Genome student notesheet
... _____________________: the chemical inside the nucleus of a cell that carries the genetic instructions for making living organisms. ...
... _____________________: the chemical inside the nucleus of a cell that carries the genetic instructions for making living organisms. ...
Genetic Variation
... Genes: are the units of heredity that is a sequence of bases (A,T,G,C) that give instructions on how to assemble a certain ...
... Genes: are the units of heredity that is a sequence of bases (A,T,G,C) that give instructions on how to assemble a certain ...
protein synthesis
... (this is the structural gene: codes for a single protein) B. The promoter site on the DNA contains a sequence called a TATA box - recognized by RNA polymerase - can be up to 25 bases away from point of transcription ...
... (this is the structural gene: codes for a single protein) B. The promoter site on the DNA contains a sequence called a TATA box - recognized by RNA polymerase - can be up to 25 bases away from point of transcription ...
BIOMOLECULES
... “R” groups represent one of the 20 Amino Acids! (so, each amino acid has something different in that spot) ...
... “R” groups represent one of the 20 Amino Acids! (so, each amino acid has something different in that spot) ...
m5zn_7de32f5a588b6c7
... Nitrogenous base; these bases are classified based on their chemical structures into two groups: Purine; double ringed structure (Adenine and Guanine). Pyrimidine; single ring structures (cytosine and thymine). ...
... Nitrogenous base; these bases are classified based on their chemical structures into two groups: Purine; double ringed structure (Adenine and Guanine). Pyrimidine; single ring structures (cytosine and thymine). ...
3. What are macromolecules? LARGE ORGANIC
... Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight. All compounds can be classified in two broad categories --- organic and inorganic compounds. Organic compounds are ma ...
... Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight. All compounds can be classified in two broad categories --- organic and inorganic compounds. Organic compounds are ma ...
Chapter 3: The Chemistry of Organic Molecules
... regulate which chemical reactions will happen and when they will occur. • Not very efficient if cells are undergoing all reaction all at once. ...
... regulate which chemical reactions will happen and when they will occur. • Not very efficient if cells are undergoing all reaction all at once. ...
Operons - Haiku Learning
... Use the amino acid chart from question #3 …glycine…serine…glycine… 4. Which of the following DNA strands would code for the amino acid sequence shown above? ...
... Use the amino acid chart from question #3 …glycine…serine…glycine… 4. Which of the following DNA strands would code for the amino acid sequence shown above? ...
Making Copies of DNA
... throughout cells and cause most of the differences that you can see among organisms. Proteins act as chemical triggers and messengers for many of the processes within cells. Proteins help determine how tall you grow, what colors you can see, and whether your hair is curly or straight. Proteins exist ...
... throughout cells and cause most of the differences that you can see among organisms. Proteins act as chemical triggers and messengers for many of the processes within cells. Proteins help determine how tall you grow, what colors you can see, and whether your hair is curly or straight. Proteins exist ...
GE & Profiling iQuiz
... When the DNA from individuals is analysed a unique DNA profile is made and a result similar to a bar code is obtained. This DNA profile formation is also known as genetic ...
... When the DNA from individuals is analysed a unique DNA profile is made and a result similar to a bar code is obtained. This DNA profile formation is also known as genetic ...
Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis
... – Made up of amino acids linked together into chains called polypeptides • 20 different amino acids occur in nature • for a protein to function properly it must be made ...
... – Made up of amino acids linked together into chains called polypeptides • 20 different amino acids occur in nature • for a protein to function properly it must be made ...
Protein Synthesis
... template strand and takes it from the nucleus to ribosomes in the cytoplasm • Main goal: make a copy of the code and get it out of the nucleus! Question: Why can’t DNA leave the nucleus? ...
... template strand and takes it from the nucleus to ribosomes in the cytoplasm • Main goal: make a copy of the code and get it out of the nucleus! Question: Why can’t DNA leave the nucleus? ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.