Protein Synthesis: A Real Adventure
... 5. The rRNA student will write down each word as delivered by the tRNA 6. After completing the sentence, a student in the group will tell your teacher the sentence. If correct, you may pick another DNA template, if not the group may go over the same DNA template. Data: Turn in the transcribed DNA (M ...
... 5. The rRNA student will write down each word as delivered by the tRNA 6. After completing the sentence, a student in the group will tell your teacher the sentence. If correct, you may pick another DNA template, if not the group may go over the same DNA template. Data: Turn in the transcribed DNA (M ...
Part 1 – History, DNA Structure, DNA Replication
... Part 1 – History, DNA Structure, DNA Replication DNA History http://www.dnaftb.org/dnaftb/1/concept/index.html Read the text and answer the following questions. 1. What have people wondered since the beginning of human history? _________________________________ 2. Who discovered that individual trai ...
... Part 1 – History, DNA Structure, DNA Replication DNA History http://www.dnaftb.org/dnaftb/1/concept/index.html Read the text and answer the following questions. 1. What have people wondered since the beginning of human history? _________________________________ 2. Who discovered that individual trai ...
Organic Molecule Worksheet
... 12. What are the subunits called that make up carbohydrates? 13. What is the ratio of C, H, and O in monosaccharides? 14. Name 3 monosaccharides. 15. Monosaccharides are ___ sugars. 16. What are disaccharides & give an example? 17. Long chains of sugars are ___. Name three. Part 3 Questions: Color ...
... 12. What are the subunits called that make up carbohydrates? 13. What is the ratio of C, H, and O in monosaccharides? 14. Name 3 monosaccharides. 15. Monosaccharides are ___ sugars. 16. What are disaccharides & give an example? 17. Long chains of sugars are ___. Name three. Part 3 Questions: Color ...
Mutation
... Mutations can causes change in the gene sequence that can cause a different amino acid to be made into protein to make it defective (does not work anymore). An example of a mutation (substitution of a nitrogen base) is sickle cell disease (sickle cell anemia). A red blood cell is normally round, but ...
... Mutations can causes change in the gene sequence that can cause a different amino acid to be made into protein to make it defective (does not work anymore). An example of a mutation (substitution of a nitrogen base) is sickle cell disease (sickle cell anemia). A red blood cell is normally round, but ...
2014
... 4. [2 points] Which of the following compounds directly provide atoms to form the purine ring? A) Aspartate B) Carbamoyl phosphate C) Glutamine D) Histidine E) Tryptophan F) Lysine G) Glycine H) Ornithine Circle all correct answer(s) More than one answer may be correct. 5. [4 points] Draw the struct ...
... 4. [2 points] Which of the following compounds directly provide atoms to form the purine ring? A) Aspartate B) Carbamoyl phosphate C) Glutamine D) Histidine E) Tryptophan F) Lysine G) Glycine H) Ornithine Circle all correct answer(s) More than one answer may be correct. 5. [4 points] Draw the struct ...
Recitation 8 Solutions
... What would happen to the encoded protein if the underlined nucleotide C were mutated to a T? N-met-arg-asp-C (This creates a premature stop codon resulting in a truncated protein). 2. Drawn below is part of a wild-type gene. The DNA sequence shown encodes the last amino acids of a protein that is no ...
... What would happen to the encoded protein if the underlined nucleotide C were mutated to a T? N-met-arg-asp-C (This creates a premature stop codon resulting in a truncated protein). 2. Drawn below is part of a wild-type gene. The DNA sequence shown encodes the last amino acids of a protein that is no ...
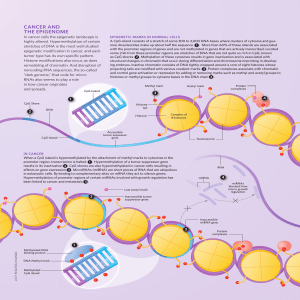
CaNCer aND THe ePIGeNOMe
... epigenetic modification in cancer, and each tumor type has its own specific pattern. Histone modifications also occur, as does remodeling of chromatin. And disruption of noncoding RNA sequences, the so-called “dark genome,” that code for microRNAs also seems to play a role in how cancer originates a ...
... epigenetic modification in cancer, and each tumor type has its own specific pattern. Histone modifications also occur, as does remodeling of chromatin. And disruption of noncoding RNA sequences, the so-called “dark genome,” that code for microRNAs also seems to play a role in how cancer originates a ...
Year Long Biology EOC Review PPT
... • Single stranded • Four base pairs: AUCG • Sugar is Ribose ...
... • Single stranded • Four base pairs: AUCG • Sugar is Ribose ...
Genes and Inheritance
... up of DNA coiled tightly around proteins called histones. Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) carries the code that tells cells what to do. ...
... up of DNA coiled tightly around proteins called histones. Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) carries the code that tells cells what to do. ...
LCHS Biology Quizdom Review
... 5. During protein synthesis, how much DNA is unzipped in order to code for the mRNA strand? A) Only one gene B) Several genes C) The entire DNA strand D) All of the above ...
... 5. During protein synthesis, how much DNA is unzipped in order to code for the mRNA strand? A) Only one gene B) Several genes C) The entire DNA strand D) All of the above ...
Transformation Lab
... Transformation Lab What are plasmids? Circular sequences of DNA that can be incorporated into a bacterial host genome. ...
... Transformation Lab What are plasmids? Circular sequences of DNA that can be incorporated into a bacterial host genome. ...
Carbon Compounds
... 1. All organic compounds contain carbon! 2. Examples: carbohydrates, lipids (fats), proteins, nucleic acids (DNA, RNA) ...
... 1. All organic compounds contain carbon! 2. Examples: carbohydrates, lipids (fats), proteins, nucleic acids (DNA, RNA) ...
UNIT 4 PART 2 APPLIED GENETICS
... small circular pieces of DNA they have the ability to replicate in another cell ...
... small circular pieces of DNA they have the ability to replicate in another cell ...
RevShtFinalBio160
... Review Topics for Bio 160 Final Exam A cell which has a diploid (2n) number of 6 undergoes either mitosis or meiosis. Use the pictures below to answer questions about the stages of division for this cell. (Note: if the correct answer below is more than one letter long, like “ae.”, mark both a AND e ...
... Review Topics for Bio 160 Final Exam A cell which has a diploid (2n) number of 6 undergoes either mitosis or meiosis. Use the pictures below to answer questions about the stages of division for this cell. (Note: if the correct answer below is more than one letter long, like “ae.”, mark both a AND e ...
CHNOPS Lab
... place. The code, in DNA or mRNA, specifies the order in which the amino acids are joined together to form a polypeptide. As the code carried by mRNA is “read” on a ribosome, the amino acids are added to the growing polypeptide chain (protein) . The process by which the information from DNA is transf ...
... place. The code, in DNA or mRNA, specifies the order in which the amino acids are joined together to form a polypeptide. As the code carried by mRNA is “read” on a ribosome, the amino acids are added to the growing polypeptide chain (protein) . The process by which the information from DNA is transf ...
Viruses, Jumping Genes and Other Unusual Genes
... • Usually replicated when DNA is copied, but some can reproduce at other times – autonomous replication ...
... • Usually replicated when DNA is copied, but some can reproduce at other times – autonomous replication ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.