replicate, transcribe, translate
... SUMMARY OF REPLICATION, TRANSCRIPTION & TRANSLATION DNA replication is the process cells use to make new DNA, and is semi-conservative in that each new DNA double-helix formed contains half of the DNA strand replicated. Replication as it occurs within cells requires a DNA template, energy provided b ...
... SUMMARY OF REPLICATION, TRANSCRIPTION & TRANSLATION DNA replication is the process cells use to make new DNA, and is semi-conservative in that each new DNA double-helix formed contains half of the DNA strand replicated. Replication as it occurs within cells requires a DNA template, energy provided b ...
Document
... • Use a table of mRNA codons and their corresponding amino acids to deduce the sequence of amino acids coded by a short mRNA strand of known base sequence ...
... • Use a table of mRNA codons and their corresponding amino acids to deduce the sequence of amino acids coded by a short mRNA strand of known base sequence ...
1_3_nucl_acid_2.ppt
... Image on the exposed film after developing. This tells you which restriction fragments have the gene or region of interest (if you remembered to include size markers!). ...
... Image on the exposed film after developing. This tells you which restriction fragments have the gene or region of interest (if you remembered to include size markers!). ...
In this essay you should have written it as two
... 2 Molecules of ATP are required to start the process Net gain of 2 ATP are produced Diagram can be used to show the above points maximum of 3 Kreb's cycle is an aerobic process / needs oxygen in the cell and occurs in the central liquid matrix of the mitochondrion 3C Pyruvic acid is converted to 2C ...
... 2 Molecules of ATP are required to start the process Net gain of 2 ATP are produced Diagram can be used to show the above points maximum of 3 Kreb's cycle is an aerobic process / needs oxygen in the cell and occurs in the central liquid matrix of the mitochondrion 3C Pyruvic acid is converted to 2C ...
Biological Chemistry
... DNA is a double-stranded _______ (like a twisted ladder) held together by ____________ bonds and is composed of: a. _______________ sugar and phosphate groups form the side rails of the “ladder” b. Nitrogenous ______ held together by ________ bonds form the ladder steps. These bases include: 1) Thym ...
... DNA is a double-stranded _______ (like a twisted ladder) held together by ____________ bonds and is composed of: a. _______________ sugar and phosphate groups form the side rails of the “ladder” b. Nitrogenous ______ held together by ________ bonds form the ladder steps. These bases include: 1) Thym ...
CHAPTER 13 Frontiers of Genetics
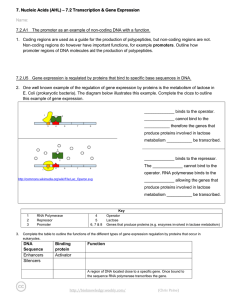
... repressor turns the operator off by binding to it. This process enables prokaryotes to match their cell chemistry to different conditions. Eukaryotic cells have more complicated ways of regulating genes. Gene expression is the transcription and translation of genes into proteins. Some genes have pro ...
... repressor turns the operator off by binding to it. This process enables prokaryotes to match their cell chemistry to different conditions. Eukaryotic cells have more complicated ways of regulating genes. Gene expression is the transcription and translation of genes into proteins. Some genes have pro ...
Chapter 2: Chemical Principles
... • __________ - when a molecule is split into smaller molecules, ions, or atoms. ...
... • __________ - when a molecule is split into smaller molecules, ions, or atoms. ...
Proteins – Amides from Amino Acids
... • They link nucleotides together • Found between the 5’-hydroxyl group (5’ end) on one nucleoside and the 3’-hydroxyl group (3’ end) on the other side ...
... • They link nucleotides together • Found between the 5’-hydroxyl group (5’ end) on one nucleoside and the 3’-hydroxyl group (3’ end) on the other side ...
AP Biology – Evolution Unit
... coordinated precisely for life to exist. This coordination is directed from the nucleus of the cell, by deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA DNA is the hereditary blueprint of the cell. The DNA of a cell is contained in structures called chromosomes. The chromosomes consist of DNA wrapped around proteins c ...
... coordinated precisely for life to exist. This coordination is directed from the nucleus of the cell, by deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA DNA is the hereditary blueprint of the cell. The DNA of a cell is contained in structures called chromosomes. The chromosomes consist of DNA wrapped around proteins c ...
DNA Transcription – A Simulation using Corticon
... 2. Six bases of the mRNA are exposed. 3. A complementary tRNA molecule with its attached amino acid (EG methionine) base pairs via its anticodon UAC with the AUG on the mRNA in the first position P. 4. Another tRNA base pairs with the other three mRNA bases in the ribosome at position A. 5. The enzy ...
... 2. Six bases of the mRNA are exposed. 3. A complementary tRNA molecule with its attached amino acid (EG methionine) base pairs via its anticodon UAC with the AUG on the mRNA in the first position P. 4. Another tRNA base pairs with the other three mRNA bases in the ribosome at position A. 5. The enzy ...
Modern Biology (I) First Midterm (10/24/2007)
... 34. The first evidence that DNA and not protein was the genetic material came from Avery’s experiments showing that ______. a. streptococcal infections are more virulent when the bacteria have a polysaccharide coat b. DNAse, but not protease, prevents dead bacteria from transforming live bacteria c. ...
... 34. The first evidence that DNA and not protein was the genetic material came from Avery’s experiments showing that ______. a. streptococcal infections are more virulent when the bacteria have a polysaccharide coat b. DNAse, but not protease, prevents dead bacteria from transforming live bacteria c. ...
CONFOUNDING PHYLOGENETIC TREES
... -according to rRNA based phylogenies, there are 3 kingdoms of life – bacteria, archaea and eukarya with eukarya derived from archaea -the sequencing of hundreds of genomes has called into question this tree because many proteins in any one organism can be archaeal or bacterial in origin -gene swappi ...
... -according to rRNA based phylogenies, there are 3 kingdoms of life – bacteria, archaea and eukarya with eukarya derived from archaea -the sequencing of hundreds of genomes has called into question this tree because many proteins in any one organism can be archaeal or bacterial in origin -gene swappi ...
Molecular Genetics
... 3. In order to illustrate that transferring genes was possible from one organism to another, scientists used a green fluorescent protein from jellyfish and transferred it to other organisms. The result was that these organisms glowed in the dark. 4. Mammalian genes have the ability to function in ot ...
... 3. In order to illustrate that transferring genes was possible from one organism to another, scientists used a green fluorescent protein from jellyfish and transferred it to other organisms. The result was that these organisms glowed in the dark. 4. Mammalian genes have the ability to function in ot ...
Midterm Practice Test
... the same amino acid as another codon does. (3.) It never codes for more than one amino acid. (4.) It extends from one end of a tRNA molecule (5.) It is the basic unit of the genetic code. 67) What does the term "antiparallel" mean when applied to a DNA double helix? 68) The DNA of all organisms repl ...
... the same amino acid as another codon does. (3.) It never codes for more than one amino acid. (4.) It extends from one end of a tRNA molecule (5.) It is the basic unit of the genetic code. 67) What does the term "antiparallel" mean when applied to a DNA double helix? 68) The DNA of all organisms repl ...
Study Questions – Chapter 1
... estimate to date” by Elie Dolgin in Scientific American, August 2009. “The real cause of obesity: It’s not gluttony. It’s genetics. Why our moralizing misses the point” by Jeffrey Friedman, Newsweek Web Exclusive, September 10, 2009. “Unfortunate drift” by Josie Glausiusz in Discover Magazine, June ...
... estimate to date” by Elie Dolgin in Scientific American, August 2009. “The real cause of obesity: It’s not gluttony. It’s genetics. Why our moralizing misses the point” by Jeffrey Friedman, Newsweek Web Exclusive, September 10, 2009. “Unfortunate drift” by Josie Glausiusz in Discover Magazine, June ...
REVIEW SHEET FOR RNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... Gene: A section of DNA that codes for a protein (polypeptide) Codon (including start and stop): Three sequential bases of mRNA (usually codes for an amino acid)- Start=AUGStop=UAA, UAG, UGA- 64 possibilities -Group of 3 nucleotides in mRNA that specifies an amino acid -Group that can be thought of a ...
... Gene: A section of DNA that codes for a protein (polypeptide) Codon (including start and stop): Three sequential bases of mRNA (usually codes for an amino acid)- Start=AUGStop=UAA, UAG, UGA- 64 possibilities -Group of 3 nucleotides in mRNA that specifies an amino acid -Group that can be thought of a ...
RNA codons and correlant Amino Acids
... other half of your code in the centre of an egg to form a single cell a single code - the zygote. This single cell then multiplied table.jpg with along with its code - through the process of mitosis to form the trillions of cells and hundreds of different cell types found in an adult human being. Th ...
... other half of your code in the centre of an egg to form a single cell a single code - the zygote. This single cell then multiplied table.jpg with along with its code - through the process of mitosis to form the trillions of cells and hundreds of different cell types found in an adult human being. Th ...
長榮管理學院九十學年度二年制技術學系招生考試
... degradative pathways for an organic compound? a. Corresponding biosynthetic and degradative pathways are generally independently regulatable. b. Corresponding biosynthetic and degradative pathways can be compartmentalized in different regions of the cell. c. Corresponding biosynthetic and degradativ ...
... degradative pathways for an organic compound? a. Corresponding biosynthetic and degradative pathways are generally independently regulatable. b. Corresponding biosynthetic and degradative pathways can be compartmentalized in different regions of the cell. c. Corresponding biosynthetic and degradativ ...
Protein Synthesis
... We are always going to assume that the coding side of DNA will be the __________ side. Opposite the coding side is called the __________ side. Two enzymes play a role in transcription: ____________ unzips the DNA molecule and __________________ helps attach the free-floating mRNA nucleotides to the ...
... We are always going to assume that the coding side of DNA will be the __________ side. Opposite the coding side is called the __________ side. Two enzymes play a role in transcription: ____________ unzips the DNA molecule and __________________ helps attach the free-floating mRNA nucleotides to the ...
DNA - Mrs-Lamberts-Biology
... A. Semiconservative replication= the process of copying/doubling the amount of DNA prior to cell division so the daughter cells both get a full set. The next two processes occur back to back, and this is how your genes make your body work. Each gene codes for specific protein(s) each individual cel ...
... A. Semiconservative replication= the process of copying/doubling the amount of DNA prior to cell division so the daughter cells both get a full set. The next two processes occur back to back, and this is how your genes make your body work. Each gene codes for specific protein(s) each individual cel ...
DNA Transcription and Translation
... 3. A mRNA copy is made from the DNA template strand by RNA polymerase 4. A mRNA copy is made until it reaches the termination (stop signal) ...
... 3. A mRNA copy is made from the DNA template strand by RNA polymerase 4. A mRNA copy is made until it reaches the termination (stop signal) ...
Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen
... 25. __________ bonds form when water is removed to hold _________ acids together. ...
... 25. __________ bonds form when water is removed to hold _________ acids together. ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.