Read the passage. (i) Name the substance in cells which carries
... of producing drip dry shirts made from natural fibres. Other cotton plants are being genetically engineered to produce their own insecticides. When they have perfected these new types of cotton plants, the scientists will use cloning techniques to produce large numbers of them. ...
... of producing drip dry shirts made from natural fibres. Other cotton plants are being genetically engineered to produce their own insecticides. When they have perfected these new types of cotton plants, the scientists will use cloning techniques to produce large numbers of them. ...
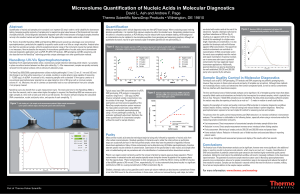
Microvolume Quantification of Nucleic Acids in Molecular Diagnostics
... testing. Assessing quantity and purity of samples prior to analysis has great value because of the financial and time costs of analytical failures. Clinical diagnostic laboratories frequently work with limited amounts of biological samples; therefore not only is the resultant nucleic acid yield ofte ...
... testing. Assessing quantity and purity of samples prior to analysis has great value because of the financial and time costs of analytical failures. Clinical diagnostic laboratories frequently work with limited amounts of biological samples; therefore not only is the resultant nucleic acid yield ofte ...
MUTATIONS
... which changes the genes and how they behave. Factors that cause changes in our DNA: Errors when DNA is copied for new cells Environmental factors change DNA (nicotine, sunlight, x-rays, chemicals Mutations are inherited from the parents ...
... which changes the genes and how they behave. Factors that cause changes in our DNA: Errors when DNA is copied for new cells Environmental factors change DNA (nicotine, sunlight, x-rays, chemicals Mutations are inherited from the parents ...
3 MoleculesCells
... monomers are they made of? What types of glycosidic bonds do they have? What is the structural differences between the storage polysaccharides? Where are each found in nature? 4. Which polysaccharides are used for structural support in living things? How are they constructed with regards to monosacc ...
... monomers are they made of? What types of glycosidic bonds do they have? What is the structural differences between the storage polysaccharides? Where are each found in nature? 4. Which polysaccharides are used for structural support in living things? How are they constructed with regards to monosacc ...
Biotechnology
... Transgenic animals have been used to study genes and to improve the food supply. Mice have been produced with human genes that make their immune systems act similarly to those of humans. This allows scientists to study the effects of diseases on the human immune system. Researchers are trying ...
... Transgenic animals have been used to study genes and to improve the food supply. Mice have been produced with human genes that make their immune systems act similarly to those of humans. This allows scientists to study the effects of diseases on the human immune system. Researchers are trying ...
Biochemistry I INTRO
... The average molecular weight of a nucleotide pair is 660, and each nucleotide pair contributes 0.34 nm to the length of DNA. ...
... The average molecular weight of a nucleotide pair is 660, and each nucleotide pair contributes 0.34 nm to the length of DNA. ...
mcb122 tutorial kit - Covenant University
... 1. The three domains are the Eukarya, the Bacteria, and the Archaea. The separation of life into three domains was originally based on sequence comparisons of rRNA molecules. These comparisons showed that the prokaryotes actually contained two different groups of cells. It also showed that eukaryote ...
... 1. The three domains are the Eukarya, the Bacteria, and the Archaea. The separation of life into three domains was originally based on sequence comparisons of rRNA molecules. These comparisons showed that the prokaryotes actually contained two different groups of cells. It also showed that eukaryote ...
The Genetic Science Glossary - Canadian Council of Churches
... One of the four bases, or building blocks, found in DNA. A d e n i n e Analogy: Adenine is one of the letters in the four-letter DNA alphabet. Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Thymidine (T), and Cytidine (C) are the four different molecules base molecules that compose DNA. The smallest unit of DNA consists ...
... One of the four bases, or building blocks, found in DNA. A d e n i n e Analogy: Adenine is one of the letters in the four-letter DNA alphabet. Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Thymidine (T), and Cytidine (C) are the four different molecules base molecules that compose DNA. The smallest unit of DNA consists ...
Document
... evolution. This has been proven to be particularly true in the case of multicellular eukaryotes to which we, the humans, belong. The reasons for this conceptual change are many. First of all genes have been shown to be “ambiguous” in many ways in the sense that a single sequence may be coding for mo ...
... evolution. This has been proven to be particularly true in the case of multicellular eukaryotes to which we, the humans, belong. The reasons for this conceptual change are many. First of all genes have been shown to be “ambiguous” in many ways in the sense that a single sequence may be coding for mo ...
How does DNA determine the traits of organisms?
... the complimentary mRNA, tRNA, and the amino acid (A.A.) sequence it codes for and the related trait in the chart on the next page. ...
... the complimentary mRNA, tRNA, and the amino acid (A.A.) sequence it codes for and the related trait in the chart on the next page. ...
File
... The Details of Transcription: DNA mRNA RNA polymerase Ribonucleotides: A, U (uracil), G, and C Specificity of base pairing The transcription bubble The template and gene strands The promotor sequence ...
... The Details of Transcription: DNA mRNA RNA polymerase Ribonucleotides: A, U (uracil), G, and C Specificity of base pairing The transcription bubble The template and gene strands The promotor sequence ...
The Four Organic Compounds Notes
... Provide structure for cells, bones, muscles, tissues, organs, hormones, most everything in the body! Special Function: Carries out cell metabolism (via enzymes) ...
... Provide structure for cells, bones, muscles, tissues, organs, hormones, most everything in the body! Special Function: Carries out cell metabolism (via enzymes) ...
Chemistry of Life Chapter 3 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Introduction
... molecules, water (a special type of covalent bond) and pH or hydrogen ion concentration of a solution. This week we will explore four classes macromolecules found in living systems: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. By definition organic compounds are carbon based. These carbon com ...
... molecules, water (a special type of covalent bond) and pH or hydrogen ion concentration of a solution. This week we will explore four classes macromolecules found in living systems: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. By definition organic compounds are carbon based. These carbon com ...
The brain and spinal cord comprise the central nervous system
... • Nondisjunction of autosomes (example Down Syndrome) and Sex Chromosomes • In utero detection methods for genetic defects: Amniocentesis, Chorionic villi sampling • Exceptions to the Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance: Concept of Maternal Inheritance – Mitochondrial and Chloroplast Genes • DNA as Ge ...
... • Nondisjunction of autosomes (example Down Syndrome) and Sex Chromosomes • In utero detection methods for genetic defects: Amniocentesis, Chorionic villi sampling • Exceptions to the Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance: Concept of Maternal Inheritance – Mitochondrial and Chloroplast Genes • DNA as Ge ...
Genetics Review Questions
... 8. A hybrid gene pair is also referred to as heterozygous. 9. Offspring inherit one gene from each parent. 10. Pp has genes that are different and represent a hybrid organism. 11. The likelihood that an event may or may not take place is called probability. 12. What is the probability that a child w ...
... 8. A hybrid gene pair is also referred to as heterozygous. 9. Offspring inherit one gene from each parent. 10. Pp has genes that are different and represent a hybrid organism. 11. The likelihood that an event may or may not take place is called probability. 12. What is the probability that a child w ...
Introduction to Genetical
... – Is the genetic material that is inherited. – Contains the information needed by living cells to specify their structure, function, activity and interaction with other cells and environment. – A DNA molecule can be thought of as a very long sequence of nucleotides or bases. ...
... – Is the genetic material that is inherited. – Contains the information needed by living cells to specify their structure, function, activity and interaction with other cells and environment. – A DNA molecule can be thought of as a very long sequence of nucleotides or bases. ...
DNA Arrays
... …as genes are linked to diseases, quick, inexpensive tests can be performed to determine who carries specific mutations, – gene must be mapped, cloned and sequenced, – DNA chips designed, and data storage and ...
... …as genes are linked to diseases, quick, inexpensive tests can be performed to determine who carries specific mutations, – gene must be mapped, cloned and sequenced, – DNA chips designed, and data storage and ...
From Gene to Protein I.
... Transcription and translation are the two main processes linking gene to protein. A. RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and substitutes the nitrogenous base uracil for thymine. An RNA molecule almost always consists of a single strand. B. The specific seque ...
... Transcription and translation are the two main processes linking gene to protein. A. RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and substitutes the nitrogenous base uracil for thymine. An RNA molecule almost always consists of a single strand. B. The specific seque ...
Biology- Semester 2 Final Exam Review 2012
... Outline the flow of genetic information in cells from DNA to protein. List three ways in which the structure of RNA differs from that of DNA. Summarize the process of transcription. Where does it occur? What is a codon? Describe the importance of the genetic code. Compare the structure and role of m ...
... Outline the flow of genetic information in cells from DNA to protein. List three ways in which the structure of RNA differs from that of DNA. Summarize the process of transcription. Where does it occur? What is a codon? Describe the importance of the genetic code. Compare the structure and role of m ...
The History of DNA WebQuest
... • The discoveries and research that led to the realization that DNA was the genetic material. • The scientists who were involved in discovering the structure of DNA. ...
... • The discoveries and research that led to the realization that DNA was the genetic material. • The scientists who were involved in discovering the structure of DNA. ...
COAS_B1_Ch08 Nucleic acids
... DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. When it was discovered, it was given the name ‘nucleic acid’ because it was mostly found in the nuclei of cells and is slightly acidic. Each nucleotide in a DNA molecule contains: a phosphate group the five-carbon sugar, deoxyribose an organic base. Figure 8.1 s ...
... DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. When it was discovered, it was given the name ‘nucleic acid’ because it was mostly found in the nuclei of cells and is slightly acidic. Each nucleotide in a DNA molecule contains: a phosphate group the five-carbon sugar, deoxyribose an organic base. Figure 8.1 s ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.