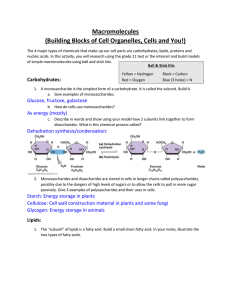
Macromolecules
... break down, and help the body deal with extra cholesterol compared to saturated fats (mostly found in meat, chicken and dairy products) in our bodies. Cholesterol is type of fat that can build up in blood vessels and cause atherosclerosis (plaques that harden and narrow vessels), which can lead to h ...
... break down, and help the body deal with extra cholesterol compared to saturated fats (mostly found in meat, chicken and dairy products) in our bodies. Cholesterol is type of fat that can build up in blood vessels and cause atherosclerosis (plaques that harden and narrow vessels), which can lead to h ...
III. Biotechnology
... fragments and mutations are identified by an abnormal number of fragments ...
... fragments and mutations are identified by an abnormal number of fragments ...
Biology Name: Directions: Read Section 13.3(pgs. 372
... C. roughly once in every million bases. D. roughly once in every 10 million bases. 11. Small changes in genes A. disappear quickly. B. gradually accumulate over time. C. prevent the next generation from developing. D. do not affect future generations. 12. A possible mutagen is A. an anticodon. B. tr ...
... C. roughly once in every million bases. D. roughly once in every 10 million bases. 11. Small changes in genes A. disappear quickly. B. gradually accumulate over time. C. prevent the next generation from developing. D. do not affect future generations. 12. A possible mutagen is A. an anticodon. B. tr ...
Protein Synthesis SG
... Protein synthesis occurs in two stages: transcription and translation. State the purpose of each. Why must the genetic code be written in triplets of nucleotides? From where do ribosomes orginate? Describe the relationship between a DNA triplet, a codon, and an anticodon. What is the evolutionary si ...
... Protein synthesis occurs in two stages: transcription and translation. State the purpose of each. Why must the genetic code be written in triplets of nucleotides? From where do ribosomes orginate? Describe the relationship between a DNA triplet, a codon, and an anticodon. What is the evolutionary si ...
Principles of Genetics, A BRIEF INTRODUCTION
... material that occurs between adjacent chromatids during meiosis. Deme: An independent subpopulation. Diploid: In diploid organisms, each body cell carries two sets of chromosomes; each chromosome exists in two homolohous forms, one of which is phenotypically realized. DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid, a d ...
... material that occurs between adjacent chromatids during meiosis. Deme: An independent subpopulation. Diploid: In diploid organisms, each body cell carries two sets of chromosomes; each chromosome exists in two homolohous forms, one of which is phenotypically realized. DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid, a d ...
File
... • Somatic cell mutations occur in body cells • Germ cell mutations occur in reproductive cells • These are passed on from one generation to the next ...
... • Somatic cell mutations occur in body cells • Germ cell mutations occur in reproductive cells • These are passed on from one generation to the next ...
X-Sheet 2 Protein Synthesis and DNA Fingerprinting
... DNA to specialized sites of the ribosomes where the information is translated for protein synthesis. Transfer RNA (tRNA): carries specific amino acids to the mRNA codon in the production of proteins. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): form the ribosomes and produce the proteins based on the information from ...
... DNA to specialized sites of the ribosomes where the information is translated for protein synthesis. Transfer RNA (tRNA): carries specific amino acids to the mRNA codon in the production of proteins. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): form the ribosomes and produce the proteins based on the information from ...
FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE KEY GENETICS Mendel: “father” of
... resistance to insects and herbicides as well as create organisms that can make human genes. Genetically modified tomatoes with arctic flounder DNA to withstand cold temperatures and bacteria cells creating insulin ...
... resistance to insects and herbicides as well as create organisms that can make human genes. Genetically modified tomatoes with arctic flounder DNA to withstand cold temperatures and bacteria cells creating insulin ...
Proteins, Carbohydrates, and Lipids
... increasingly complex task that requires active, continuing maintenance of digital media. This challenge has focused some interest on DNA as an attractive target for information storage1 because of its capacity for high-density information encoding, longevity under easily achieved conditions2–4 and p ...
... increasingly complex task that requires active, continuing maintenance of digital media. This challenge has focused some interest on DNA as an attractive target for information storage1 because of its capacity for high-density information encoding, longevity under easily achieved conditions2–4 and p ...
Name: Date: Period:_____ Midterm Review: Study Guide # 3
... 4. After you have finished, use this sheet as a study tool to quiz yourself. Quiz yourself by trying to answer all the questions aloud. This will probably take you a few times to feel comfortable. You are finished studying when and only when you can answer 100% of the objectives correctly without ha ...
... 4. After you have finished, use this sheet as a study tool to quiz yourself. Quiz yourself by trying to answer all the questions aloud. This will probably take you a few times to feel comfortable. You are finished studying when and only when you can answer 100% of the objectives correctly without ha ...
Unit VII: Genetics
... Matches the codon to an anticodon on tRNA Ribosome reads next codon and brings in next tRNA with matching anticodon Since tRNA is attached to Amino Acids – two amino acids are located next to each other This proximity allows the ____________________ Makes a peptide Repeats until mRNA says stop ...
... Matches the codon to an anticodon on tRNA Ribosome reads next codon and brings in next tRNA with matching anticodon Since tRNA is attached to Amino Acids – two amino acids are located next to each other This proximity allows the ____________________ Makes a peptide Repeats until mRNA says stop ...
File
... How do we make Biomolecules? When we are growing, we need to make new big macromolecules for our body. Monomers join together to form ___________________by removing water. When you pull the water out, it allows the two parts to join together. This process is called: _____________________. When joini ...
... How do we make Biomolecules? When we are growing, we need to make new big macromolecules for our body. Monomers join together to form ___________________by removing water. When you pull the water out, it allows the two parts to join together. This process is called: _____________________. When joini ...
Year 10 Term 3: Genetics
... LW3 Advances in scientific understanding often rely on developments in technology, and technological advances are often linked to scientific discoveries. (ACSHE158, ACSHE192) 5LW3c. identify that genetic information is transferred as genes in the DNA of chromosomes ...
... LW3 Advances in scientific understanding often rely on developments in technology, and technological advances are often linked to scientific discoveries. (ACSHE158, ACSHE192) 5LW3c. identify that genetic information is transferred as genes in the DNA of chromosomes ...
Biochemistry of Cells
... There are 20 amino acids that combine in different numbers, orders, and arrangements to form proteins. ...
... There are 20 amino acids that combine in different numbers, orders, and arrangements to form proteins. ...
DNA History: A Timeline Activity
... 2. Once you feel comfortable with their contribution and their experiments, fill in the month and year of the scientist(s) main contribution below their picture and cut out the squares. Glue each cut-out in chronological order across the top of a piece of paper. 3. Cut out the pictures below of the ...
... 2. Once you feel comfortable with their contribution and their experiments, fill in the month and year of the scientist(s) main contribution below their picture and cut out the squares. Glue each cut-out in chronological order across the top of a piece of paper. 3. Cut out the pictures below of the ...
2.5 Genetics - Elaine Galvin
... (Matching) RNA production (notion of both DNA and RNA must be given) The process of making a protein using the mRNA code a template A haploid sex cell which is capable of fusion The fusion of 2[haploid] gametes to form a [diploid] zygote An alternative form of a gene Has identical alleles [for a tra ...
... (Matching) RNA production (notion of both DNA and RNA must be given) The process of making a protein using the mRNA code a template A haploid sex cell which is capable of fusion The fusion of 2[haploid] gametes to form a [diploid] zygote An alternative form of a gene Has identical alleles [for a tra ...
Structure of a protein - Campus
... As a result of the special structure of the bases, the 2 DNA molecules can only bind to each other in a single manner, with 2 hydrogen bonds allowing only the union of adenine with thymine (AT), while 3 hydrogen bonds only allow guanine to bind with cytosine (GC). ...
... As a result of the special structure of the bases, the 2 DNA molecules can only bind to each other in a single manner, with 2 hydrogen bonds allowing only the union of adenine with thymine (AT), while 3 hydrogen bonds only allow guanine to bind with cytosine (GC). ...
Terms - Cuny
... Organic Molecule: The types of chain molecules, which make up living things. Carbohydrate: The type of organic molecule that animals use to make energy. It is composed of many sugar molecules strung together. Plants make carbohydrates to store the sugar they make during photosynthesis. Animals get c ...
... Organic Molecule: The types of chain molecules, which make up living things. Carbohydrate: The type of organic molecule that animals use to make energy. It is composed of many sugar molecules strung together. Plants make carbohydrates to store the sugar they make during photosynthesis. Animals get c ...
DNA–DNA hybridisation
... muscle blocks during early embryonic life. This is best explained by common ancestry—that they are all descendants of a common ...
... muscle blocks during early embryonic life. This is best explained by common ancestry—that they are all descendants of a common ...
4.4.1 Evidence to support the theory of evolution
... muscle blocks during early embryonic life. This is best explained by common ancestry—that they are all descendants of a common ...
... muscle blocks during early embryonic life. This is best explained by common ancestry—that they are all descendants of a common ...
The Genetic Code of Genes and Genomes
... strand consists of deoxyribose sugars alternating with phosphate groups that link 5 ' carbon of one sugar to the 3' carbon of the next sugar in line ...
... strand consists of deoxyribose sugars alternating with phosphate groups that link 5 ' carbon of one sugar to the 3' carbon of the next sugar in line ...
Biochem notes
... They occur naturally in plants, animals, and fungi, with the most familiar type of animal sterol being cholesterol. Cholesterol is vital to cellular function, and a precursor to fat-soluble vitamins and steroid hormones. 3-six sided rings and one 5-sided ring + alcohol ...
... They occur naturally in plants, animals, and fungi, with the most familiar type of animal sterol being cholesterol. Cholesterol is vital to cellular function, and a precursor to fat-soluble vitamins and steroid hormones. 3-six sided rings and one 5-sided ring + alcohol ...
D - Cloudfront.net
... a. forest that was replaced by a freshwater lake b. freshwater lake that was replaced by a desert c. saltwater sea that was replaced by a forest d. freshwater lake that was replaced by a forest ...
... a. forest that was replaced by a freshwater lake b. freshwater lake that was replaced by a desert c. saltwater sea that was replaced by a forest d. freshwater lake that was replaced by a forest ...
Microbes in nutrition Digestion vast majority of GI tract bacteria are
... (1) not reproducible in laboratory (2) oil deposits have characteristics that make biological origin likely b. oil deposits rich in anaerobic bacteria (1) particularly SRB (2) cultures that produce oil-like compounds are mixed cultures including SRB c. crude oil often contains porphyrins (chemicals ...
... (1) not reproducible in laboratory (2) oil deposits have characteristics that make biological origin likely b. oil deposits rich in anaerobic bacteria (1) particularly SRB (2) cultures that produce oil-like compounds are mixed cultures including SRB c. crude oil often contains porphyrins (chemicals ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.