in Power-Point Format
... from DNA-containing materials (Jeffreys et al., 1986) • Minisatellite DNA - sequence of bases repeated several times, also called DNA fingerprint – Individuals differ in repeats of basic sequence – – Difference large enough that 2 people have only remote chance of exactly same pattern • Other repeat ...
... from DNA-containing materials (Jeffreys et al., 1986) • Minisatellite DNA - sequence of bases repeated several times, also called DNA fingerprint – Individuals differ in repeats of basic sequence – – Difference large enough that 2 people have only remote chance of exactly same pattern • Other repeat ...
Monomer polymer2011
... Monomer A small repeating unit that can make larger more complex molecules. ...
... Monomer A small repeating unit that can make larger more complex molecules. ...
MCB 110 Problem set 2. DNA replication - Answers
... In the figure, the pol δ holoenzymes are not coupled at the replication fork. This is likely an oversimplification in the figure. In eukaryotes, the replicative helicase is made up of six different homologous subunits (as shown), and there is a hand-off of the lagging strand from primase to pol α to ...
... In the figure, the pol δ holoenzymes are not coupled at the replication fork. This is likely an oversimplification in the figure. In eukaryotes, the replicative helicase is made up of six different homologous subunits (as shown), and there is a hand-off of the lagging strand from primase to pol α to ...
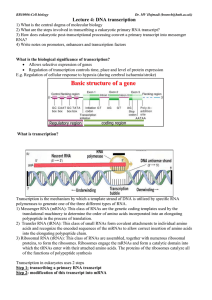
Lecture 4: DNA transcription
... Allows selective expression of genes Regulation of transcription controls time, place and level of protein expression E.g. Regulation of cellular response to hypoxia (during cerebral ischaemia/stroke) ...
... Allows selective expression of genes Regulation of transcription controls time, place and level of protein expression E.g. Regulation of cellular response to hypoxia (during cerebral ischaemia/stroke) ...
CH 15 PowerPoint
... – only one of two DNA strands (template or antisense strand) is transcribed – non-transcribed strand is termed coding strand or sense strand – In both bacteria and eukaryotes, the polymerase adds ribonucleotides to the growing 3’ end of an RNA chain. synthesis proceeds in 5’3’ direction ...
... – only one of two DNA strands (template or antisense strand) is transcribed – non-transcribed strand is termed coding strand or sense strand – In both bacteria and eukaryotes, the polymerase adds ribonucleotides to the growing 3’ end of an RNA chain. synthesis proceeds in 5’3’ direction ...
DNA Lab Techniques
... Steps in DNA Sequencing • Many copies of a single strand of DNA are placed in a test tube • DNA polymerase is added • A mixture of nucleotides is added some of which have dye molecules attached • Each base (A,T,C,G) has a different color dye ...
... Steps in DNA Sequencing • Many copies of a single strand of DNA are placed in a test tube • DNA polymerase is added • A mixture of nucleotides is added some of which have dye molecules attached • Each base (A,T,C,G) has a different color dye ...
A-DNA
... The 2 strands are twisted about each other, coiled around a common axis, forming a righthanded double helix. The hydrophilic sugar- phosphate backbone of each chain lies on the outside of the molecule. The hydrophobic nitrogenous bases project inwards from the outer sugar-phosphate framework, perpen ...
... The 2 strands are twisted about each other, coiled around a common axis, forming a righthanded double helix. The hydrophilic sugar- phosphate backbone of each chain lies on the outside of the molecule. The hydrophobic nitrogenous bases project inwards from the outer sugar-phosphate framework, perpen ...
UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT (Abstract)
... DR PG/Tabulation section/GAI ‘F’ ‘G’ sections/ GAII/GAIII/SF/FC ...
... DR PG/Tabulation section/GAI ‘F’ ‘G’ sections/ GAII/GAIII/SF/FC ...
DNA Replication
... Recall that your body cells each contain 46 chromosomes made up of DNA. The DNA is copied once during the cell cycle, in the S phase. After a cell divides, the resulting cells each have a complete set of DNA. ...
... Recall that your body cells each contain 46 chromosomes made up of DNA. The DNA is copied once during the cell cycle, in the S phase. After a cell divides, the resulting cells each have a complete set of DNA. ...
Intro to Biology review - Brookings School District
... Kind of chemical reaction used by cells to join molecules together by removing an H and OH to make a water molecule Dehydration synthesis ...
... Kind of chemical reaction used by cells to join molecules together by removing an H and OH to make a water molecule Dehydration synthesis ...
pGLO TM Bacterial Transformation
... vector: a DNA molecule used to insert foreign DNA into a host cell A circular piece of autonomously replicating DNA Plasmids are like minichromosomes Originally evolved by bacteria May express antibiotic resistance gene or be modified to express proteins of interest ...
... vector: a DNA molecule used to insert foreign DNA into a host cell A circular piece of autonomously replicating DNA Plasmids are like minichromosomes Originally evolved by bacteria May express antibiotic resistance gene or be modified to express proteins of interest ...
Ch 8 Genetic Technology and Diagnostics
... transformation •Bacteriophages: have the natural ability to inject DNA into bacterial hosts through transduction •Vectors typically contain a gene that confers drug resistance to their cloning host - cells can be grown on drug containing media ...
... transformation •Bacteriophages: have the natural ability to inject DNA into bacterial hosts through transduction •Vectors typically contain a gene that confers drug resistance to their cloning host - cells can be grown on drug containing media ...
The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... Nucleic Acids • Nucleotides are linked together by phosphodiester linkages – Covalent bond between a phosphate group and a sugar • This creates the sugarphosphate backbone • One end will have a phosphate attached to a 5’ carbon; the other will have a hydroxyl group on a 3’ carbon (these are the end ...
... Nucleic Acids • Nucleotides are linked together by phosphodiester linkages – Covalent bond between a phosphate group and a sugar • This creates the sugarphosphate backbone • One end will have a phosphate attached to a 5’ carbon; the other will have a hydroxyl group on a 3’ carbon (these are the end ...
Ch 2-- Matter
... 4. buffers – weak acids or bases that can react with strong acids or bases to prevent sharp, sudden changes in pH for maintaining homeostasis a. fluids within most body cells must be kept between 6.5-7.5 III. Carbon Compounds organic chemistry – study of all compounds that contain bonds between ca ...
... 4. buffers – weak acids or bases that can react with strong acids or bases to prevent sharp, sudden changes in pH for maintaining homeostasis a. fluids within most body cells must be kept between 6.5-7.5 III. Carbon Compounds organic chemistry – study of all compounds that contain bonds between ca ...
DNA – Deoxyribonucleic Acid
... copies made and distributed to new cells. – Chromosome # is retained (stays the same). ...
... copies made and distributed to new cells. – Chromosome # is retained (stays the same). ...
DNA Extraction from Human Cheek Cells
... DNA Extraction from Human Cheek Cells (20 points) Introduction: DNA molecules of humans are very long and contain about 30,000,000 base pairs in a single string of DNA. How is so much DNA packed into such a tiny cell nucleus? DNA is wrapped around proteins called histones. When the DNA is curled aro ...
... DNA Extraction from Human Cheek Cells (20 points) Introduction: DNA molecules of humans are very long and contain about 30,000,000 base pairs in a single string of DNA. How is so much DNA packed into such a tiny cell nucleus? DNA is wrapped around proteins called histones. When the DNA is curled aro ...
Zoo/Bot 3333
... were used to amplify DNA isolated from Sperm number one man's somatic cells, and from 20 ...
... were used to amplify DNA isolated from Sperm number one man's somatic cells, and from 20 ...
Cloning and PCR File
... Gene cloning is the process of isolating and making copies of a gene. This is useful for many purposes. For example, gene cloning might be used to isolate and make copies of a normal gene for gene therapy. Gene cloning involves four steps: isolation, ligation, transformation, and selection. You can ...
... Gene cloning is the process of isolating and making copies of a gene. This is useful for many purposes. For example, gene cloning might be used to isolate and make copies of a normal gene for gene therapy. Gene cloning involves four steps: isolation, ligation, transformation, and selection. You can ...
RNA & Protein Synthesis
... 1) mRNA attaches to ribosome 2) tRNA brings amino acids (a.acids) to ribosome 3) A. acids attached along “assembly line” 4) Continues until a “stop” codon is reached ...
... 1) mRNA attaches to ribosome 2) tRNA brings amino acids (a.acids) to ribosome 3) A. acids attached along “assembly line” 4) Continues until a “stop” codon is reached ...
DNA Webquest - Fredericksburg City Schools
... 3. What was Erwin Chargaff’s contribution to the DNA puzzle? ...
... 3. What was Erwin Chargaff’s contribution to the DNA puzzle? ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.