Chapter 13 – RNA and Protein Synthesis Study Guide
... 1. What is the genetic code? The relationship between specific sequences of nitrogen bases to amino acids. 2. How is one protein different from another protein? Proteins are different by the sequence and type of amino acids that form the polypeptide. 3. What is translation? Translation is the proces ...
... 1. What is the genetic code? The relationship between specific sequences of nitrogen bases to amino acids. 2. How is one protein different from another protein? Proteins are different by the sequence and type of amino acids that form the polypeptide. 3. What is translation? Translation is the proces ...
File
... Day Three: The Discovery of DNA The Discovery of DNA Frederick Griffith – Discovered a factor that contained information that transformed harmless bacteria into deadly bacteria. Griffith called the process transformation because the harmless strain of bacteria had changed permanently into the disea ...
... Day Three: The Discovery of DNA The Discovery of DNA Frederick Griffith – Discovered a factor that contained information that transformed harmless bacteria into deadly bacteria. Griffith called the process transformation because the harmless strain of bacteria had changed permanently into the disea ...
Nucleic Acid Structures, Energetics, and Dynamics
... used in detecting small changes in sequence, such as singlebase mutations in some genetic diseases. The ultimate goal is to be able to quickly sequence any DNA or RNA from a single molecule without first amplifying it by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR).18 The method will be left as an exercise f ...
... used in detecting small changes in sequence, such as singlebase mutations in some genetic diseases. The ultimate goal is to be able to quickly sequence any DNA or RNA from a single molecule without first amplifying it by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR).18 The method will be left as an exercise f ...
Molecular Genetics - Ursuline High School
... the cytoplasm, waiting for some amino acids to assemble into protein….you already have the instructions, remember the mRNA, …… but you can’t get the amino acids yourself…… you need help…. you need tRNA. The tRNA can pick up specified amino acids.… and bring them to you in the correct order…..but how ...
... the cytoplasm, waiting for some amino acids to assemble into protein….you already have the instructions, remember the mRNA, …… but you can’t get the amino acids yourself…… you need help…. you need tRNA. The tRNA can pick up specified amino acids.… and bring them to you in the correct order…..but how ...
Test # 1. Which of the following is not an electron acceptor or carrier?
... Within the nucleus of a cell, they remove introns from a pre-mRNA, and splice exons together to form mRNA, which is then transported to the cytoplasm. b) Within the nucleus of a cell, they remove exons from a pre-mRNA, and splice introns together to form mRNA, which is then transported to the cytopl ...
... Within the nucleus of a cell, they remove introns from a pre-mRNA, and splice exons together to form mRNA, which is then transported to the cytoplasm. b) Within the nucleus of a cell, they remove exons from a pre-mRNA, and splice introns together to form mRNA, which is then transported to the cytopl ...
Notes Unit 4 Part 8
... Mutation = a change in an organism’s ________ mutations are ____________ and can have unpredictable effects errors in DNA provide the ______________ that is fundamental to the evolution of a species most mutations result in ___________ or the lack of normal development in an organism if the ...
... Mutation = a change in an organism’s ________ mutations are ____________ and can have unpredictable effects errors in DNA provide the ______________ that is fundamental to the evolution of a species most mutations result in ___________ or the lack of normal development in an organism if the ...
Final Review
... ● Both have three components — sugar, phosphate and a nitrogenous base — which form nucleotide units that are connected by covalent bonds to form a linear molecule with 3' and 5' ends, with the nitrogenous bases perpendicular to the sugar-phosphate backbone. ● The basic structural differences includ ...
... ● Both have three components — sugar, phosphate and a nitrogenous base — which form nucleotide units that are connected by covalent bonds to form a linear molecule with 3' and 5' ends, with the nitrogenous bases perpendicular to the sugar-phosphate backbone. ● The basic structural differences includ ...
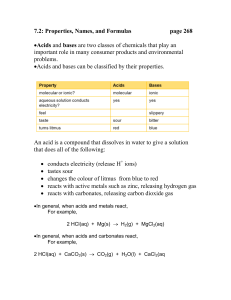
7.2: Properties, Names, and Formulas page 268 •Acids and bases
... 7.2: Properties, Names, and Formulas ...
... 7.2: Properties, Names, and Formulas ...
Chapter 13 Review answers
... will not make you sick Gene Therapy – treat genetic disorders by transferring normal gene into cells that lack them; replacement gene is expressed in person’s cell 98%, therefore 2% codes for proteins Process of altering the genetic material of cells or organisms to allow them to make new substances ...
... will not make you sick Gene Therapy – treat genetic disorders by transferring normal gene into cells that lack them; replacement gene is expressed in person’s cell 98%, therefore 2% codes for proteins Process of altering the genetic material of cells or organisms to allow them to make new substances ...
Mutation: The Source of Genetic Variation
... incorporated into DNA or RNA during synthesis (causes insertion of G rather than A so that an A/T base pair is converted to a G/C in the helix Chemical modifiers directly change the bases in DNA, Nitrous acid changes cytosine into uracil, resulting in a G/C to A/T mutation Intercalating agents g ...
... incorporated into DNA or RNA during synthesis (causes insertion of G rather than A so that an A/T base pair is converted to a G/C in the helix Chemical modifiers directly change the bases in DNA, Nitrous acid changes cytosine into uracil, resulting in a G/C to A/T mutation Intercalating agents g ...
Biochemistry
... •Phospholipids – makes coverings (membranes) water resistant Found in cell membranes •Steroids and Hormones – produce body changes such as puberty Found in cholesterol, testosterone, estrogen ...
... •Phospholipids – makes coverings (membranes) water resistant Found in cell membranes •Steroids and Hormones – produce body changes such as puberty Found in cholesterol, testosterone, estrogen ...
Outline for the Second Part of the Bio Final
... Function of mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA Know how to find the complementary DNA strand Know how to code mRNA from DNA Know how to code for amino acids Types of Mutations o Inversion, Deletion, Insertion, Duplication, Translocation ...
... Function of mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA Know how to find the complementary DNA strand Know how to code mRNA from DNA Know how to code for amino acids Types of Mutations o Inversion, Deletion, Insertion, Duplication, Translocation ...
Do Now: Wednesday, March 19
... for the protein that is needed is unwound Step 2: RNA polymerase (enzyme) uses the DNA to make a complementary strand of mRNA ...
... for the protein that is needed is unwound Step 2: RNA polymerase (enzyme) uses the DNA to make a complementary strand of mRNA ...
Lecture Notes
... Zn fingers are usually modules of larger proteins. Proteins with as many as 37 Zn fingers are known. Their role is to bind specific sequences of DNA or RNA. A number of Zn fingers occur in tandem in a protein. Each finger recognizes 3 consecutive base pairs, so a string of Zn fingers can selectively ...
... Zn fingers are usually modules of larger proteins. Proteins with as many as 37 Zn fingers are known. Their role is to bind specific sequences of DNA or RNA. A number of Zn fingers occur in tandem in a protein. Each finger recognizes 3 consecutive base pairs, so a string of Zn fingers can selectively ...
1 - CSU, Chico
... d. European immigrants flooding in during the early part of this century e. Survivors of a shipwreck (assuming they interbred) 36. Sickle Cell Anemia is an example of a: a. balanced polymorphism b. trait in which heterozygotes have advantages over homozygotes c. trait with no anthropological or evol ...
... d. European immigrants flooding in during the early part of this century e. Survivors of a shipwreck (assuming they interbred) 36. Sickle Cell Anemia is an example of a: a. balanced polymorphism b. trait in which heterozygotes have advantages over homozygotes c. trait with no anthropological or evol ...
Translate your creativity
... 50 µL 5. lncubate the tube at 37° C for 2-4 hours. Please note that overnight incubation increases the amount of the produced protein. ...
... 50 µL 5. lncubate the tube at 37° C for 2-4 hours. Please note that overnight incubation increases the amount of the produced protein. ...
Hotstart Taq DNA Polymerase
... HotStart Taq DNA polymerase is designed for quantitative PCR, a technique that enhances the specificity, sensitivity and yield of DNA amplification. HotStart Taq DNA polymerase is a recombinant Taq DNA polymerase which has been chemical mediated by the addition of heat-labile blocking groups to its ...
... HotStart Taq DNA polymerase is designed for quantitative PCR, a technique that enhances the specificity, sensitivity and yield of DNA amplification. HotStart Taq DNA polymerase is a recombinant Taq DNA polymerase which has been chemical mediated by the addition of heat-labile blocking groups to its ...
DNAandproteinsynthesis
... ‘upstream’ the initiation codon (AUG) where translation will start. The initiator tRNA, carrying methionine, attaches to the initiator codon. The large ribosomal sub-unit binds to complete the protein-synthesizing complex. ...
... ‘upstream’ the initiation codon (AUG) where translation will start. The initiator tRNA, carrying methionine, attaches to the initiator codon. The large ribosomal sub-unit binds to complete the protein-synthesizing complex. ...
Translation
... • The genetic code is a set of rules defining how the code of DNA nucleotides is translated into the code of amino acids. • Genetic code is universal between all ...
... • The genetic code is a set of rules defining how the code of DNA nucleotides is translated into the code of amino acids. • Genetic code is universal between all ...
Nucleotides and Nuclic Acids
... the DNA molecule (equivalent to ~1.5-1.8 supercoils/nucleosome particle theoretically; actual value is ~1), which is relieved by topoisomerases. This results in DNA that is negatively supercoiled once histone proteins are removed. ...
... the DNA molecule (equivalent to ~1.5-1.8 supercoils/nucleosome particle theoretically; actual value is ~1), which is relieved by topoisomerases. This results in DNA that is negatively supercoiled once histone proteins are removed. ...
Notes - marric.us
... 17. Which is the most highly mutagenic? 18. Look at the following figure. Identify the proteins that DNA first coils around. 19. Explain how Hox genes affect an organism. ...
... 17. Which is the most highly mutagenic? 18. Look at the following figure. Identify the proteins that DNA first coils around. 19. Explain how Hox genes affect an organism. ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.