Document
... 5. What happens when an electric current is applied to DNA fragments? ___________________________ 6. The enzyme that copies DNA is called DNA __________________________________________ 7. Dye is added to the unknown sequence of DNA, each base then has a different ___________________ and a different ...
... 5. What happens when an electric current is applied to DNA fragments? ___________________________ 6. The enzyme that copies DNA is called DNA __________________________________________ 7. Dye is added to the unknown sequence of DNA, each base then has a different ___________________ and a different ...
to accompany Holes` Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology
... chain (R group) • Amino acids are linked in a peptide bond joining the amino of one and carboxyl group of another amino acid ...
... chain (R group) • Amino acids are linked in a peptide bond joining the amino of one and carboxyl group of another amino acid ...
BASIC CHEMISTRY
... • The bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G) • adenine (A) always pairs with thymine (T) • cytosine (C) always pairs with Guanine (G) ...
... • The bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G) • adenine (A) always pairs with thymine (T) • cytosine (C) always pairs with Guanine (G) ...
Cockayne syndrome
... o cDNA libraries – complementary DNA libraries are made by reverse transcribing (making DNA from RNA) all of the mRNA in a cell. The DNA copies are replicas of mRNA without introns. These can be used as probes, primers, or many other uses. o PCR-see page 146-biochemistry. o Restriction length fragme ...
... o cDNA libraries – complementary DNA libraries are made by reverse transcribing (making DNA from RNA) all of the mRNA in a cell. The DNA copies are replicas of mRNA without introns. These can be used as probes, primers, or many other uses. o PCR-see page 146-biochemistry. o Restriction length fragme ...
LNA-PNA Comparison4
... Applications of peptide nucleic acid probes 1) PNA fluorescent insitu hybridisationThe PNA-FISH technique was first developed for quantitative telomere analysis. Using a unique fluorescein-labelled PNA probe thus one can map the sequence onto a chromosome. In FISH applications PNA probes have severa ...
... Applications of peptide nucleic acid probes 1) PNA fluorescent insitu hybridisationThe PNA-FISH technique was first developed for quantitative telomere analysis. Using a unique fluorescein-labelled PNA probe thus one can map the sequence onto a chromosome. In FISH applications PNA probes have severa ...
Sequencing the Human Genome
... 2. “Shock” these into the DNA of e-coli bacteria, and let them replicate the BACs to any degree. 3. Take each BAC and cut it into manageable pieces, using restriction enzymes. 4. Clone (artificially replicate) these pieces, so as to have enough to work with. This is known as PCR, or polymerase chain ...
... 2. “Shock” these into the DNA of e-coli bacteria, and let them replicate the BACs to any degree. 3. Take each BAC and cut it into manageable pieces, using restriction enzymes. 4. Clone (artificially replicate) these pieces, so as to have enough to work with. This is known as PCR, or polymerase chain ...
File - Mr. Blaschke`s Science Class
... than those near the ends decreasing probability of protein binding and hence regulating transcriptional activity ...
... than those near the ends decreasing probability of protein binding and hence regulating transcriptional activity ...
Station 6 - Biomolecules
... do a biomolecule’s size and the number of bonds it contains affect the amount of energy that is available? As the molecule size increases, so does the number chemical bonds needed to hold the structure together. These bonds contain energy, which enables the molecule to perform its functions. The mor ...
... do a biomolecule’s size and the number of bonds it contains affect the amount of energy that is available? As the molecule size increases, so does the number chemical bonds needed to hold the structure together. These bonds contain energy, which enables the molecule to perform its functions. The mor ...
DNA Replication and Protein Synthesis
... 3. DNA polymerase slides along the leading strand in the 3’ to 5’ direction synthesizing the matching Okazaki fragments in the 5’ to 3’ direction 4. The RNA primers are degraded by RNase H and replaced with DNA nucleotides by DNA polymerase 5. DNA ligase connects the Okazaki fragments to one another ...
... 3. DNA polymerase slides along the leading strand in the 3’ to 5’ direction synthesizing the matching Okazaki fragments in the 5’ to 3’ direction 4. The RNA primers are degraded by RNase H and replaced with DNA nucleotides by DNA polymerase 5. DNA ligase connects the Okazaki fragments to one another ...
Document
... How many fragments are produced? Are all the fragments the same length? Please organize the fragments from biggest to ...
... How many fragments are produced? Are all the fragments the same length? Please organize the fragments from biggest to ...
Bio1A - Lec 19 slides File
... • Transcription factors mediate the binding of RNA polymerase and the initiation of transcription • The completed assembly of transcription factors and RNA polymerase II bound to a promoter is called a transcription initiation complex • A promoter called a TATA box is crucial in forming the initiati ...
... • Transcription factors mediate the binding of RNA polymerase and the initiation of transcription • The completed assembly of transcription factors and RNA polymerase II bound to a promoter is called a transcription initiation complex • A promoter called a TATA box is crucial in forming the initiati ...
A + U, G + C
... Protein Transcription Translation Remember: in mRNA there is no T! Instead you have U! ...
... Protein Transcription Translation Remember: in mRNA there is no T! Instead you have U! ...
DNA (Gene) Mutations
... Enzymes proofread the DNA and replace incorrect nucleotides with correct nucleotides. The greater the exposure to a mutagen such as UV light, the greater the chance that a mistake will not be corrected. ...
... Enzymes proofread the DNA and replace incorrect nucleotides with correct nucleotides. The greater the exposure to a mutagen such as UV light, the greater the chance that a mistake will not be corrected. ...
Questions - Vanier College
... 8. A principal problem with inserting an unmodified mammalian gene into a BAC, and then getting that gene expressed in bacteria, is that A) bacteria translate polycistronic messages only. B) bacteria cannot remove eukaryotic introns. C) prokaryotes use a different genetic code from that of eukaryote ...
... 8. A principal problem with inserting an unmodified mammalian gene into a BAC, and then getting that gene expressed in bacteria, is that A) bacteria translate polycistronic messages only. B) bacteria cannot remove eukaryotic introns. C) prokaryotes use a different genetic code from that of eukaryote ...
Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria
... inside a viral capsid Crossover occurs between new transduced DNA and new host DNA ...
... inside a viral capsid Crossover occurs between new transduced DNA and new host DNA ...
Unit 2 - Molecular and genetic factors in disease
... inactivation is random , This can have a bearing on the expression of diseases which are due to mutations in genes on the X chromosome as either the normal or the mutant gene may be inactivated. ...
... inactivation is random , This can have a bearing on the expression of diseases which are due to mutations in genes on the X chromosome as either the normal or the mutant gene may be inactivated. ...
Click on Revolution
... other organisms. The plasmid DNA (in red) must first be cut using a protein called a restriction enzyme. This particular enzyme (in blue), EcoR1, cuts DNA at a specific sequence: G A A T T C. When it finds the DNA sequence, the enzyme breaks the sugar-phosphate DNA backbone, leaving overhanging ends ...
... other organisms. The plasmid DNA (in red) must first be cut using a protein called a restriction enzyme. This particular enzyme (in blue), EcoR1, cuts DNA at a specific sequence: G A A T T C. When it finds the DNA sequence, the enzyme breaks the sugar-phosphate DNA backbone, leaving overhanging ends ...
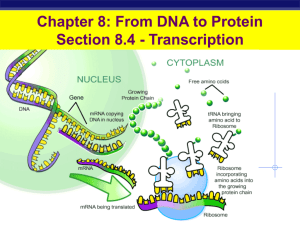
Teacher Guide: From DNA to Proteins - RI
... The focus of this activity is for students to explore the processes of transcription and translation. They determine how DNA’s structure encodes for proteins. The DNA to Proteins unit activity is supported by the Electrostatics activity. To predict why the base pairs (A-T, C-G) bond, students first ...
... The focus of this activity is for students to explore the processes of transcription and translation. They determine how DNA’s structure encodes for proteins. The DNA to Proteins unit activity is supported by the Electrostatics activity. To predict why the base pairs (A-T, C-G) bond, students first ...
Chapter 12: Biotechnology 1. Recombinant DNA What is
... • the PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technique is routinely used to generate huge numbers of identical DNA fragments • involves in vitro DNA replication to amplify desired DNA sequences ...
... • the PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technique is routinely used to generate huge numbers of identical DNA fragments • involves in vitro DNA replication to amplify desired DNA sequences ...
Teacher Guide DNA to Protein FINAL-FR - RI
... The focus of this activity is for students to explore the processes of transcription and translation. They determine how DNA’s structure encodes for proteins. The DNA to Proteins unit activity is supported by the Electrostatics activity. To predict why the base pairs (A-T, C-G) bond, students first ...
... The focus of this activity is for students to explore the processes of transcription and translation. They determine how DNA’s structure encodes for proteins. The DNA to Proteins unit activity is supported by the Electrostatics activity. To predict why the base pairs (A-T, C-G) bond, students first ...
Protein Synthesis Activity
... Transcription: 1. On your answer sheet you have a very small segment of a DNA molecule. Use this segment to transcribe a molecule of mRNA. Start transcribing your mRNA molecule when you find “TAC” and stop when you find “ATT”. Remember, each combination of three nitrogenous bases on mRNA is called a ...
... Transcription: 1. On your answer sheet you have a very small segment of a DNA molecule. Use this segment to transcribe a molecule of mRNA. Start transcribing your mRNA molecule when you find “TAC” and stop when you find “ATT”. Remember, each combination of three nitrogenous bases on mRNA is called a ...
Using Parker Brother`s game CLUE to learn about DNA
... 1. Describe a crime scenario to the students involving some of the characters from the Parker Brother’s game CLUE. Miss Scarlet was found murdered in the library in the middle of the night by Mrs. White (maid). A candlestick lay near the body in a pool of blood. The list of suspects includes wealthy ...
... 1. Describe a crime scenario to the students involving some of the characters from the Parker Brother’s game CLUE. Miss Scarlet was found murdered in the library in the middle of the night by Mrs. White (maid). A candlestick lay near the body in a pool of blood. The list of suspects includes wealthy ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.