Course Content Form - Pima Community College
... concentrations from initial concentrations, apply Le Chatelier's principle to a chemical reaction and predict how changes in concentration, temperature, pressure, and volume influence the equilibrium system. Distinguish between Arrhenius and Bronsted acids and bases, identify conjugate acid/base pai ...
... concentrations from initial concentrations, apply Le Chatelier's principle to a chemical reaction and predict how changes in concentration, temperature, pressure, and volume influence the equilibrium system. Distinguish between Arrhenius and Bronsted acids and bases, identify conjugate acid/base pai ...
Overview of milestones in genetics and genetic variation Author
... organisms and this material should fulfil three requirements: Replication ability-It should be able to replicate so that parents can pass this material to the offspring Information carrier-It must carry necessary information for the animal development and functioning Prone to changes-It should ...
... organisms and this material should fulfil three requirements: Replication ability-It should be able to replicate so that parents can pass this material to the offspring Information carrier-It must carry necessary information for the animal development and functioning Prone to changes-It should ...
Bacteria Evolving - American Museum of Natural History
... it. At the same time, the virus can pick up DNA from the infected cell, move it over and inject it into another cell. The DNA becomes part of the second organism’s genome. This process is called transduction (Figure 2). • Bacteria can also trade DNA with each other, in a process called conjugation ...
... it. At the same time, the virus can pick up DNA from the infected cell, move it over and inject it into another cell. The DNA becomes part of the second organism’s genome. This process is called transduction (Figure 2). • Bacteria can also trade DNA with each other, in a process called conjugation ...
Bioc 462a Lecture Notes
... In proteins, amino acids are joined together via the peptide bond, which is formed by the reaction of the -carboxyl group of one amino acid with the -amino group of another amino acid. If this process is repeated many times, then a long linear chain of amino acids is produced - a polypeptide. By c ...
... In proteins, amino acids are joined together via the peptide bond, which is formed by the reaction of the -carboxyl group of one amino acid with the -amino group of another amino acid. If this process is repeated many times, then a long linear chain of amino acids is produced - a polypeptide. By c ...
Effects of high magnetic fields on in vitro transcription
... formed the hypothesis that the biomolecules within the plant were either aligned or distorted by the strong magnetic field, due to the molecule’s structural diamagnetic anisotropy. This magnetic effect may be the cause of some disruption in normal plant function, and perhaps produce this stress resp ...
... formed the hypothesis that the biomolecules within the plant were either aligned or distorted by the strong magnetic field, due to the molecule’s structural diamagnetic anisotropy. This magnetic effect may be the cause of some disruption in normal plant function, and perhaps produce this stress resp ...
Chapter 2 : The Chemistry of Life Section 3 : Carbon
... • Organic Chemistry – study of chemistry that contain bonds between carbon atoms • Carbon can bond with many elements, including hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur, and nitrogen to form the molecules of life ...
... • Organic Chemistry – study of chemistry that contain bonds between carbon atoms • Carbon can bond with many elements, including hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur, and nitrogen to form the molecules of life ...
Week 26 Biology
... traits are transferred from one generation to the next via genes. H.B.4: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the specific mechanisms by which characteristics or traits are transferred from one generation to the next via genes. H.B.4: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the ...
... traits are transferred from one generation to the next via genes. H.B.4: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the specific mechanisms by which characteristics or traits are transferred from one generation to the next via genes. H.B.4: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the ...
Activity: Protein Exploration!
... Each protein is made of a specific sequence of amino acids. Twenty different amino acids are found in proteins. Each amino acid consists of two parts – a backbone and a sidechain. The backbone is the same in all 20 amino acids and the sidechain is different in each one. Each sidechain consists of a ...
... Each protein is made of a specific sequence of amino acids. Twenty different amino acids are found in proteins. Each amino acid consists of two parts – a backbone and a sidechain. The backbone is the same in all 20 amino acids and the sidechain is different in each one. Each sidechain consists of a ...
Mutations - WordPress.com
... – Original : The fat cat ate the wee rat. Inversion – Mutation: The fat tar eew eht eta tac. ...
... – Original : The fat cat ate the wee rat. Inversion – Mutation: The fat tar eew eht eta tac. ...
"thinking acids" handout
... also important to consider the relative concentrations of the acid compared to the conjugate base in a variety of situations, and well as when that balance inverts. Moving into future coursework, for example, Biochemistry, we can more easily reason through the complexities of amino acids and which f ...
... also important to consider the relative concentrations of the acid compared to the conjugate base in a variety of situations, and well as when that balance inverts. Moving into future coursework, for example, Biochemistry, we can more easily reason through the complexities of amino acids and which f ...
PPT
... My Algorithm • The population – Bit strings of 0’s and 1’s – 0’s are spaces, 1’s mean a letter is placed there – The number of 1’s stays constant as the number of letters in the smaller search string ...
... My Algorithm • The population – Bit strings of 0’s and 1’s – 0’s are spaces, 1’s mean a letter is placed there – The number of 1’s stays constant as the number of letters in the smaller search string ...
Biology end of the year material review
... 34. The gene for color vision (C) is dominant to the gene for color blindness (c) and is located on the X chromosome. If a color blind man and a woman with homozygous normal color vision have children, what are the chances that they will have a colorblind child? 35. Why do some lethal (deadly) allel ...
... 34. The gene for color vision (C) is dominant to the gene for color blindness (c) and is located on the X chromosome. If a color blind man and a woman with homozygous normal color vision have children, what are the chances that they will have a colorblind child? 35. Why do some lethal (deadly) allel ...
RNA interference - genemol de Jean
... The life cycle and replication of many RNA viruses involves a double-stranded RNA stage, so it is likely that part of the RNA interference machinery evolved as a defense against these viruses. The machinery is however also used by the cell itself to regulate gene activity: certain parts of the genom ...
... The life cycle and replication of many RNA viruses involves a double-stranded RNA stage, so it is likely that part of the RNA interference machinery evolved as a defense against these viruses. The machinery is however also used by the cell itself to regulate gene activity: certain parts of the genom ...
mutation in lac
... cells, the lens cell makes the crystallin protein (not albumin), whereas the liver cell makes albumin (not crystallin). Explain (draw the different situation in each cell). ...
... cells, the lens cell makes the crystallin protein (not albumin), whereas the liver cell makes albumin (not crystallin). Explain (draw the different situation in each cell). ...
Cracking the PPR code: predicting and manipulating protein/RNA
... Where can code mismatches be tolerated along the PPR10/RNA interface? • As mismatches move toward the center, the loss of binding affinity decreases, OR • The cost of a mismatch could be affected by how many stable interactions are surrounding it. ...
... Where can code mismatches be tolerated along the PPR10/RNA interface? • As mismatches move toward the center, the loss of binding affinity decreases, OR • The cost of a mismatch could be affected by how many stable interactions are surrounding it. ...
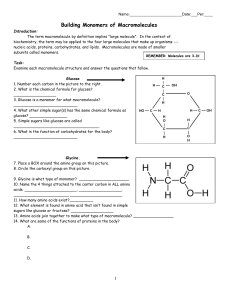
Building Monomers of Macromolecules
... Building Monomers of Macromolecules Introduction: The term macromolecule by definition implies "large molecule". In the context of biochemistry, the term may be applied to the four large molecules that make up organisms --nucleic acids, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. Macromolecules are made of ...
... Building Monomers of Macromolecules Introduction: The term macromolecule by definition implies "large molecule". In the context of biochemistry, the term may be applied to the four large molecules that make up organisms --nucleic acids, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. Macromolecules are made of ...
Lecture Slides
... • The model of DNA is like a rope ladder twisted into a spiral. – The ropes at the sides represent the sugar-phosphate backbones. – Each wooden rung represents a pair of bases connected by hydrogen ...
... • The model of DNA is like a rope ladder twisted into a spiral. – The ropes at the sides represent the sugar-phosphate backbones. – Each wooden rung represents a pair of bases connected by hydrogen ...
Chapter 14 Constant Allele Frequencies
... C. STRs are nonuniformly distributed. D. restrictive enzymes cannot be used to cut short DNA molecules. 25. Principles of population genetics must be applied to determine identity based on DNA profiling because A. VNTRs are not found in all populations. B. individuals are their own populations. C. n ...
... C. STRs are nonuniformly distributed. D. restrictive enzymes cannot be used to cut short DNA molecules. 25. Principles of population genetics must be applied to determine identity based on DNA profiling because A. VNTRs are not found in all populations. B. individuals are their own populations. C. n ...
Week 1 – Cell structure and Function and Cell membranes
... Fibrous proteins form structural elements of the body (e.g. collagen/keratin) Globular proteins can have a variety of functions, for example as enzymes, membrane proteins, some hormones and antibodies Conjugated proteins have a non-protein molecule attached (i.e. the haem group in haemoglobin) ...
... Fibrous proteins form structural elements of the body (e.g. collagen/keratin) Globular proteins can have a variety of functions, for example as enzymes, membrane proteins, some hormones and antibodies Conjugated proteins have a non-protein molecule attached (i.e. the haem group in haemoglobin) ...
Chapter 14 Constant Allele Frequencies
... C. STRs are nonuniformly distributed. D. restrictive enzymes cannot be used to cut short DNA molecules. 25. Principles of population genetics must be applied to determine identity based on DNA profiling because A. VNTRs are not found in all populations. B. individuals are their own populations. C. n ...
... C. STRs are nonuniformly distributed. D. restrictive enzymes cannot be used to cut short DNA molecules. 25. Principles of population genetics must be applied to determine identity based on DNA profiling because A. VNTRs are not found in all populations. B. individuals are their own populations. C. n ...
genetics and heredity notes student version
... chromosomes that are loosely opened when it’s being copied into a protein. ______________________ describes when areas of the chromosome that are tightly compacted and not being used. Some areas of DNA are even able to move to new location in the chromsome- these are called _________________ or ju ...
... chromosomes that are loosely opened when it’s being copied into a protein. ______________________ describes when areas of the chromosome that are tightly compacted and not being used. Some areas of DNA are even able to move to new location in the chromsome- these are called _________________ or ju ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.