File
... at high copy number. • all employ markers that can be selected readily in yeast and which will often complement the corresponding mutations in E. coli as well. • The four most widely used markers are His3, Leu2, Trp1, and Ura3. ...
... at high copy number. • all employ markers that can be selected readily in yeast and which will often complement the corresponding mutations in E. coli as well. • The four most widely used markers are His3, Leu2, Trp1, and Ura3. ...
CHAPTER 18
... same basic strategy except the secondary plates would contain the antibiotic instead of T1 phage. If the antibiotic resistance arose as a result of random mutation on the master plate, one would expect the antibiotic-resistant colonies to appear at the same locations on two different secondary plate ...
... same basic strategy except the secondary plates would contain the antibiotic instead of T1 phage. If the antibiotic resistance arose as a result of random mutation on the master plate, one would expect the antibiotic-resistant colonies to appear at the same locations on two different secondary plate ...
brief talk
... Cons – Does not allow parallelism – Inefficient and fairly slow – Requires large number of promoter -transcription factor pairs ...
... Cons – Does not allow parallelism – Inefficient and fairly slow – Requires large number of promoter -transcription factor pairs ...
Supplementary Information
... reactions of ~1.5 kb each. Nested RT-PCR was carried out as described above for generating QRT-PCR standards. Instead of cloning, the resulting PCR products were sequenced directly using BigDye Terminator v3.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit (Applied Biosystems, Inc.) and BetterBuffer (Microzone Ltd) according ...
... reactions of ~1.5 kb each. Nested RT-PCR was carried out as described above for generating QRT-PCR standards. Instead of cloning, the resulting PCR products were sequenced directly using BigDye Terminator v3.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit (Applied Biosystems, Inc.) and BetterBuffer (Microzone Ltd) according ...
Unraveling the mechanisms of RNA
... Kinetic analyses of both protein and RNA mutations designed to study U1A/U1hpII complex stability were also performed. The co-crystal structure identified a particular base (A6) in the RNA loop that stacks with U1A residue Phe56. This requires a rearrangement from the free protein, however, suggestin ...
... Kinetic analyses of both protein and RNA mutations designed to study U1A/U1hpII complex stability were also performed. The co-crystal structure identified a particular base (A6) in the RNA loop that stacks with U1A residue Phe56. This requires a rearrangement from the free protein, however, suggestin ...
Document
... • Carboxypeptidases that use active site serine residues are called "serine carboxypeptidases". • Carboxypeptidases that use an active site cysteine are called "cysteine carboxypeptidase" (or "thiol carboxypeptidases"). – By substrate preference: • In this classification system, carboxypeptidases th ...
... • Carboxypeptidases that use active site serine residues are called "serine carboxypeptidases". • Carboxypeptidases that use an active site cysteine are called "cysteine carboxypeptidase" (or "thiol carboxypeptidases"). – By substrate preference: • In this classification system, carboxypeptidases th ...
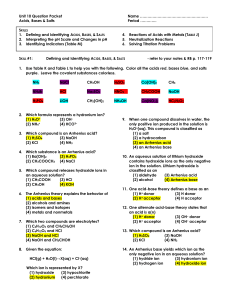
KEY - Unit 10 - Practice Questions
... (4) Zn 41. Under standard conditions, which metal will react with 0.1 M HCl to liberate hydrogen gas? (1) Ag (2) Au (3) Cu (4) Mg 42. Because tap water is slightly acidic, water pipes made of iron corrode over time, as shown by the balanced ionic equation below: 2Fe(s) + 6H+(aq) 2Fe3+(aq) + 3H2(g) ...
... (4) Zn 41. Under standard conditions, which metal will react with 0.1 M HCl to liberate hydrogen gas? (1) Ag (2) Au (3) Cu (4) Mg 42. Because tap water is slightly acidic, water pipes made of iron corrode over time, as shown by the balanced ionic equation below: 2Fe(s) + 6H+(aq) 2Fe3+(aq) + 3H2(g) ...
Laboratory of Insect Genetics and Biosciences (IGB) Dept. Biology
... the DNA of mammalian somatic cells”. A recent paper showed the existence of non-CG methylation in mammalian somatic cells (PMID:26030523). In fact, non-CG methylation in mammals seems to be more informative of gene expression than CG methylation. R: It is true that DNA methylation has been detected ...
... the DNA of mammalian somatic cells”. A recent paper showed the existence of non-CG methylation in mammalian somatic cells (PMID:26030523). In fact, non-CG methylation in mammals seems to be more informative of gene expression than CG methylation. R: It is true that DNA methylation has been detected ...
Snímek 1
... decay pathway, and/or produce truncated proteins. These effects result in a dramatic reduction in the number of functional ClC-1 channel. ...
... decay pathway, and/or produce truncated proteins. These effects result in a dramatic reduction in the number of functional ClC-1 channel. ...
Full-Text PDF
... proteins may decrease the ratio λ260/λ280 and phenols as well as carbohydrates have an analog influence on the quotient λ260/λ230. In 18 of 19 samples, a λ260/λ230 ratio below 1 was detected. There might be high amounts of humic substances in the matrices and it was not possible to remove them with ...
... proteins may decrease the ratio λ260/λ280 and phenols as well as carbohydrates have an analog influence on the quotient λ260/λ230. In 18 of 19 samples, a λ260/λ230 ratio below 1 was detected. There might be high amounts of humic substances in the matrices and it was not possible to remove them with ...
Grade 12 Biology: Final Exam
... 11. What is the significance of the different hominids? 12. What was responsible for the evolution of chips and bonobos from their common ancestor? (Include information about the characteristics of each species in your answer) 13. How are new species formed according to evolutionary theory? 14. What ...
... 11. What is the significance of the different hominids? 12. What was responsible for the evolution of chips and bonobos from their common ancestor? (Include information about the characteristics of each species in your answer) 13. How are new species formed according to evolutionary theory? 14. What ...
Transition bias and substitution models
... • Mutation: Transitional mutation occurs more frequently than transversions because – Misincorporation during DNA replication occur more frequently between two purines or between two pyrimidines than between a purine and a pyrimidine – A purine is more likely to mutate chemically to another purine t ...
... • Mutation: Transitional mutation occurs more frequently than transversions because – Misincorporation during DNA replication occur more frequently between two purines or between two pyrimidines than between a purine and a pyrimidine – A purine is more likely to mutate chemically to another purine t ...
State v. Johnson
... occurrence frequency of alleles represented in the autorads are calculated for each racial population. If any allele's frequency in any of the populations is less than ten percent, that allele is assigned the frequency of ten percent. In other words, no allele will be assumed to occur less frequent ...
... occurrence frequency of alleles represented in the autorads are calculated for each racial population. If any allele's frequency in any of the populations is less than ten percent, that allele is assigned the frequency of ten percent. In other words, no allele will be assumed to occur less frequent ...
TRANSLATION Protein synthesis is the final step in the decoding
... The mechanism of translation Proteins are synthesized starting with their N termini, corresponding to translation of the mRNA in the 5’ to 3’ direction. Translation of mRNA may be conveniently divided into three stages: initiation, where the correct site on the mRNA for commencing translation is ide ...
... The mechanism of translation Proteins are synthesized starting with their N termini, corresponding to translation of the mRNA in the 5’ to 3’ direction. Translation of mRNA may be conveniently divided into three stages: initiation, where the correct site on the mRNA for commencing translation is ide ...
C2005/F2401 Key to Exam #3
... Explanation: You had to draw the stop codons (that end translation of hap) and show how they could overlap the start codon (for translation of nar). There is no possible overlap between the stop codon UAG and the start codon AUG. However UAA and UGA can overlap AUG. For UAA, the last A in UAA can ov ...
... Explanation: You had to draw the stop codons (that end translation of hap) and show how they could overlap the start codon (for translation of nar). There is no possible overlap between the stop codon UAG and the start codon AUG. However UAA and UGA can overlap AUG. For UAA, the last A in UAA can ov ...
The purB gene of Escherichia coli K-12 is
... The purine nucleotides AMP and GMP are synthesized through a branched multi-enzyme pathway. In Escberichia coli, the structural genes (pur and gtla) for these enzymes have been mapped on the chromosome (Berlyn e t al., 1996), and occur at various loci either individually (ptlrT, pwL, pztrC, ptlrA) o ...
... The purine nucleotides AMP and GMP are synthesized through a branched multi-enzyme pathway. In Escberichia coli, the structural genes (pur and gtla) for these enzymes have been mapped on the chromosome (Berlyn e t al., 1996), and occur at various loci either individually (ptlrT, pwL, pztrC, ptlrA) o ...
Slides
... 2. Extension causes displacement of strand on other side of nick 3. D-loop is cleaved, invading strand is ligated to newly created 3′-end of the homologous strand 4. 3′-end of newly synthesized strand & the 5′-end of a homologous strand are ligated forming a ...
... 2. Extension causes displacement of strand on other side of nick 3. D-loop is cleaved, invading strand is ligated to newly created 3′-end of the homologous strand 4. 3′-end of newly synthesized strand & the 5′-end of a homologous strand are ligated forming a ...
BCH 101- 5 Amino acids
... centers of enzymatically active proteins. Indeed, it is the very nature of certain amino acid Rgroups that allow enzyme reactions to occur. The imidazole ring of histidine allows it to act as either a proton donor or acceptor at physiological pH. Hence, it is frequently found in the reactive center ...
... centers of enzymatically active proteins. Indeed, it is the very nature of certain amino acid Rgroups that allow enzyme reactions to occur. The imidazole ring of histidine allows it to act as either a proton donor or acceptor at physiological pH. Hence, it is frequently found in the reactive center ...
module 1: introduction to the genome browser: what is a gene?
... Figure 15 The end of the translated region for the A isoform of tra. Genes have directionality As you saw above, the sequence of the codons in the A isoform of tra are read from left to right relative to the orientation of contig1. This also means that the start of the protein is located toward the ...
... Figure 15 The end of the translated region for the A isoform of tra. Genes have directionality As you saw above, the sequence of the codons in the A isoform of tra are read from left to right relative to the orientation of contig1. This also means that the start of the protein is located toward the ...
Gene Section BLM (Bloom) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... Garkavtsev IV, Kley N, Grigorian IA, Gudkov AV. The Bloom syndrome protein interacts and cooperates with p53 in regulation of transcription and cell growth control. Oncogene. 2001 Dec 13;20(57):8276-80 Langland G, Kordich J, Creaney J, Goss KH, Lillard-Wetherell K, Bebenek K, Kunkel TA, Groden J. Th ...
... Garkavtsev IV, Kley N, Grigorian IA, Gudkov AV. The Bloom syndrome protein interacts and cooperates with p53 in regulation of transcription and cell growth control. Oncogene. 2001 Dec 13;20(57):8276-80 Langland G, Kordich J, Creaney J, Goss KH, Lillard-Wetherell K, Bebenek K, Kunkel TA, Groden J. Th ...
Working with ribonucleic acid (RNA)-based biotechnologies)
... molecules, and represent an interesting alternative to the RNAi. Unfortunately ribozyme design has proved difficult. It is likely that further RNA molecules will be identified. ...
... molecules, and represent an interesting alternative to the RNAi. Unfortunately ribozyme design has proved difficult. It is likely that further RNA molecules will be identified. ...
Chapter 17--6 slides per page
... Some introns contain sequences that may regulate gene expression ...
... Some introns contain sequences that may regulate gene expression ...
video slide - Morgan Community College
... • Automation has allowed scientists to measure expression of thousands of genes at one time using DNA microarray assays • DNA microarray assays compare patterns of gene expression in different tissues, at different times, or under different conditions ...
... • Automation has allowed scientists to measure expression of thousands of genes at one time using DNA microarray assays • DNA microarray assays compare patterns of gene expression in different tissues, at different times, or under different conditions ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.