Lab 6: Electrophoresis
... helix at the same position on both strands to produce fragments with blunt ends (Figure 1). Other endonucleses cleave each strand off-center at specific nucleotides to produce fragments with “overhangs” or sticky ends. By using the same restriction enzyme to “cut” DNA from two different organisms, c ...
... helix at the same position on both strands to produce fragments with blunt ends (Figure 1). Other endonucleses cleave each strand off-center at specific nucleotides to produce fragments with “overhangs” or sticky ends. By using the same restriction enzyme to “cut” DNA from two different organisms, c ...
Notes
... cause every codon to change after the mutation. This means that almost every amino acid will be different, causing the polypeptide and protein to have an entirely new shape and function. Oftentimes, a codon will change from an amino acid to a TERM command, cutting the amino acid chain short. ...
... cause every codon to change after the mutation. This means that almost every amino acid will be different, causing the polypeptide and protein to have an entirely new shape and function. Oftentimes, a codon will change from an amino acid to a TERM command, cutting the amino acid chain short. ...
From Genes to Proteins
... than the sugar deoxyribose, which is found in DNA nucleotides. significance of the genetic Ribose contains one more oxygen atom than deoxyribose contains. code. 6A TAKS 2 And third, in addition to the A, G, and C nitrogen bases found in DNA, RNA nucleotides can have a nitrogen base called uracil (YU ...
... than the sugar deoxyribose, which is found in DNA nucleotides. significance of the genetic Ribose contains one more oxygen atom than deoxyribose contains. code. 6A TAKS 2 And third, in addition to the A, G, and C nitrogen bases found in DNA, RNA nucleotides can have a nitrogen base called uracil (YU ...
... of four subunits but contains no carbohydrate; its p1 is 5-6. Streptavidin is widely used in place of avidin because of its lower nonspecific binding. This protein is isolated from the culture broth of S. avidinii by ammonium sulfate precipitation, ion-exchange chromatography, and crystallization. A ...
Lab 1 Artificial Selection The purpose of a particular investigation
... 1. If no new mutations occur, it would be most reasonable to expect bacterial growth on which of the following plates and be sure to justify your answer ____________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ...
... 1. If no new mutations occur, it would be most reasonable to expect bacterial growth on which of the following plates and be sure to justify your answer ____________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ...
Curriculum for UG
... (c) Summarize the basic and clinical aspects of enzymology and regulation of ...
... (c) Summarize the basic and clinical aspects of enzymology and regulation of ...
... This exam has 14 pages and contains 220 points. Allot 1 min/2 pts. Part A: Multiple Choice. Please circle the best answer. 1.5 pts/question 18 pts total. 1. TM refers to: a) the temperature at which 50% of a DNA molecule is denatured. b) the temperature at which 50% of a protein molecule is denature ...
- Biological Sciences
... gene (Janke and Pääbo 1993) seen in the marsupial Didelphis virginiana. Furthermore, the tRNA gene for serine (UCN), which in placentals and marsupials differs from other vertebrates in having six instead of five base pairs in the anticodon stem and only one base between the acceptor stem and the ...
... gene (Janke and Pääbo 1993) seen in the marsupial Didelphis virginiana. Furthermore, the tRNA gene for serine (UCN), which in placentals and marsupials differs from other vertebrates in having six instead of five base pairs in the anticodon stem and only one base between the acceptor stem and the ...
Decoding DNA
... Use your knowledge of transcription and translation to decode this secret message! STEP 1: “Build” a mRNA molecule that is complimentary to the DNA molecule, base pair by base pair. (REMEMBER: in RNA, adenine pairs with uracil) STEP 2: Determine the tRNA codons that would compliment with the mRNA st ...
... Use your knowledge of transcription and translation to decode this secret message! STEP 1: “Build” a mRNA molecule that is complimentary to the DNA molecule, base pair by base pair. (REMEMBER: in RNA, adenine pairs with uracil) STEP 2: Determine the tRNA codons that would compliment with the mRNA st ...
Mechanisms of hormonal regulation and pathologies of protein
... •The others are classed as "essential" amino acids and must be obtained in the diet ...
... •The others are classed as "essential" amino acids and must be obtained in the diet ...
The making of the Fittest: Natural Selection and Adaptation
... 7. Using the information on the Mc1r gene in the introduction and your knowledge of proteins, develop a hypothesis to explain how the change in MC1R protein function might directly affect a rock pocket mouse’s coat color. Be specific and consider both the light-colored and dark-colored phenotypes. S ...
... 7. Using the information on the Mc1r gene in the introduction and your knowledge of proteins, develop a hypothesis to explain how the change in MC1R protein function might directly affect a rock pocket mouse’s coat color. Be specific and consider both the light-colored and dark-colored phenotypes. S ...
File - Ms. Kuiper`s Website
... 15. _______________ is the act of dispersing one liquid in another, as fat in water. 16. Inorganic compounds are compound that do not contain _______________ atoms. 17. There are a total of _______________ amino acids that the human body can't manufacture, and so must be obtained from food. These a ...
... 15. _______________ is the act of dispersing one liquid in another, as fat in water. 16. Inorganic compounds are compound that do not contain _______________ atoms. 17. There are a total of _______________ amino acids that the human body can't manufacture, and so must be obtained from food. These a ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... Magnesium metal can be used to remove tarnish from silver items. Silver tarnish is the corrosion that occurs when silver metal reacts with substances in the environment, especially those containing sulfur. Why would magnesium remove tarnish from silver? ...
... Magnesium metal can be used to remove tarnish from silver items. Silver tarnish is the corrosion that occurs when silver metal reacts with substances in the environment, especially those containing sulfur. Why would magnesium remove tarnish from silver? ...
m5zn_14bea598b5b7901
... acid is attached to four different groups and is, therefore, a chiral or optically active carbon atom. Glycine is exception because its α carbon has two H atoms, so it is optically inactive. • The α carbon can exist in two forms which are mirror image of each other, L form and D form. They are calle ...
... acid is attached to four different groups and is, therefore, a chiral or optically active carbon atom. Glycine is exception because its α carbon has two H atoms, so it is optically inactive. • The α carbon can exist in two forms which are mirror image of each other, L form and D form. They are calle ...
калориметрическое исследование взаимодействия анионитов с
... for all interval of concentration of anions of amino acids varies in following sequence: ΔНi(Gly–) < ΔНi(Tyr2–) < ΔНi(Glu2–). At research of interaction of ion exchangers with organic ions it is necessary to consider coexistence of strong and weak intermolecular interactions which affect on magnitud ...
... for all interval of concentration of anions of amino acids varies in following sequence: ΔНi(Gly–) < ΔНi(Tyr2–) < ΔНi(Glu2–). At research of interaction of ion exchangers with organic ions it is necessary to consider coexistence of strong and weak intermolecular interactions which affect on magnitud ...
Epigenetic effects of the Krüppel-like Transcription
... DNA methylation is the process of the addition of methyl groups to 5 carbon group of the cytosine in a CpG region of DNA. These methyl groups can affect the transcription of genes. KLF1, as a transcription factor also affects the transcription of genes. Therefore, there is a good chance that KLF1 ha ...
... DNA methylation is the process of the addition of methyl groups to 5 carbon group of the cytosine in a CpG region of DNA. These methyl groups can affect the transcription of genes. KLF1, as a transcription factor also affects the transcription of genes. Therefore, there is a good chance that KLF1 ha ...
AP Biology
... When tryptophan is present, it binds to the trp repressor protein, which turns the operon off ...
... When tryptophan is present, it binds to the trp repressor protein, which turns the operon off ...
Principles of BIOCHEMISTRY
... 2. Nitrogen can be transported as glutamine. Glutamine synthetase catalyzes the synthesis of glutamine from glutamate and NH4+ in an ATPdependent reaction: ...
... 2. Nitrogen can be transported as glutamine. Glutamine synthetase catalyzes the synthesis of glutamine from glutamate and NH4+ in an ATPdependent reaction: ...
VEN124 Section I
... Lecture 2: Grape Composition and Ripening: Viticulture from the Plant’s Perspective ...
... Lecture 2: Grape Composition and Ripening: Viticulture from the Plant’s Perspective ...
carbonyl carbons
... • How are they made? – Thermodynamic strategy • Peptide bond formation is coupled to the breakdown of a high energy phosphate bond in a protein factory known as the ribosome. ...
... • How are they made? – Thermodynamic strategy • Peptide bond formation is coupled to the breakdown of a high energy phosphate bond in a protein factory known as the ribosome. ...
the genetics of viruses and bacteria
... Viruses and bacteria are the simplest biological systems—microbial models in which scientists find life’s fundamental molecular mechanisms in their most basic, accessible forms. ...
... Viruses and bacteria are the simplest biological systems—microbial models in which scientists find life’s fundamental molecular mechanisms in their most basic, accessible forms. ...
inducers - Navin Pokala
... RNA polymerase unblocked à genes ac8ve No repressor (lacI-): cannot block RNA polymerase à cons8tu8ve expression Muta8ons (lacOc) in operator region that are unable to bind ...
... RNA polymerase unblocked à genes ac8ve No repressor (lacI-): cannot block RNA polymerase à cons8tu8ve expression Muta8ons (lacOc) in operator region that are unable to bind ...
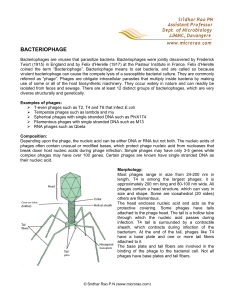
bacteriophage - Micro-Rao
... ¾ Filamentous phages with single stranded DNA such as M13 ¾ RNA phages such as Qbeta Composition: Depending upon the phage, the nucleic acid can be either DNA or RNA but not both. The nucleic acids of phages often contain unusual or modified bases, which protect phage nucleic acid from nucleases tha ...
... ¾ Filamentous phages with single stranded DNA such as M13 ¾ RNA phages such as Qbeta Composition: Depending upon the phage, the nucleic acid can be either DNA or RNA but not both. The nucleic acids of phages often contain unusual or modified bases, which protect phage nucleic acid from nucleases tha ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.