B1 - BBS Biology Revision
... B2.5 Proteins – functions and uses Use skills, knowledge and understanding to: evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of using enzymes in the home and in industry. You will need to know: a) Protein molecules are made up of long chains of amino acids. These long chains are folded to produce a spec ...
... B2.5 Proteins – functions and uses Use skills, knowledge and understanding to: evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of using enzymes in the home and in industry. You will need to know: a) Protein molecules are made up of long chains of amino acids. These long chains are folded to produce a spec ...
Appendix - Cengage
... bonded together. The water molecule is a good example of a polar molecule. The oxygen atom pulls the shared electrons more strongly than do the hydrogen atoms within each of the two covalent bonds. Consequently, the electron of each hydrogen atom tends to spend more time away orbiting around the oxy ...
... bonded together. The water molecule is a good example of a polar molecule. The oxygen atom pulls the shared electrons more strongly than do the hydrogen atoms within each of the two covalent bonds. Consequently, the electron of each hydrogen atom tends to spend more time away orbiting around the oxy ...
capitolo 1 - Structural Biology
... relatively bulky, but all have a CH2 group before their ring, which gives a Ramachandran plot comparable for all of them. In Figure 18 the three aromatic amino acids, able to absorb electromagnetic waves in the ultraviolet region, are represented. The aromatic rings give rise to orbitals among which ...
... relatively bulky, but all have a CH2 group before their ring, which gives a Ramachandran plot comparable for all of them. In Figure 18 the three aromatic amino acids, able to absorb electromagnetic waves in the ultraviolet region, are represented. The aromatic rings give rise to orbitals among which ...
AP Biology - gwbiology
... A redox reaction is an electron transfer where one substance loses electons, called oxidation, and is aided by the reducing agent, and another substance gains elects, reduction, and is aided by the oxidizing agent. 3. Why is being “reduced” equivalent to having a greater potential energy? Because in ...
... A redox reaction is an electron transfer where one substance loses electons, called oxidation, and is aided by the reducing agent, and another substance gains elects, reduction, and is aided by the oxidizing agent. 3. Why is being “reduced” equivalent to having a greater potential energy? Because in ...
Molecular Biology Study Guide Powerpoint
... Golgi Body (apparatus): receives and packages products, including proteins, for use in the cell Endoplasmic Reticulum: where chemical reactions take place; a system whose functions include synthesis and transport of lipids and, in regions where ribosomes are attached, of proteins Cell Membrane: form ...
... Golgi Body (apparatus): receives and packages products, including proteins, for use in the cell Endoplasmic Reticulum: where chemical reactions take place; a system whose functions include synthesis and transport of lipids and, in regions where ribosomes are attached, of proteins Cell Membrane: form ...
File - Pomp
... Recycling E Why can’t organisms recycle their E? During transformations, some E becomes unusable energy (heat) Most E from food is lost as heat Heat is only a useable form of E if there is a temperature difference in a ...
... Recycling E Why can’t organisms recycle their E? During transformations, some E becomes unusable energy (heat) Most E from food is lost as heat Heat is only a useable form of E if there is a temperature difference in a ...
Document
... analogy would be that small change (ATP) is often more useful than large bank notes (glucose). What is the energy in ATP used for? The processes in a cell that require energy can be put into three groups: Muscle contraction and other forms of movement, such as cilia, flagella, cytoplasmic streaming, ...
... analogy would be that small change (ATP) is often more useful than large bank notes (glucose). What is the energy in ATP used for? The processes in a cell that require energy can be put into three groups: Muscle contraction and other forms of movement, such as cilia, flagella, cytoplasmic streaming, ...
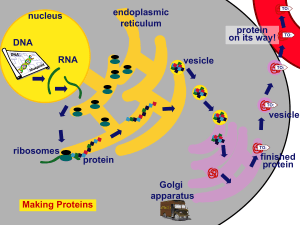
Protein Synthesis
... The ribosome is made of protein and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). All cells need proteins, DNA, and ribosomes. Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes have ribosomes. ...
... The ribosome is made of protein and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). All cells need proteins, DNA, and ribosomes. Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes have ribosomes. ...
protein
... interactions between R groups, rather than interactions between backbone constituents • These interactions between R groups include hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, hydrophobic interactions, and van der Waals interactions • Strong covalent bonds called disulfide bridges may reinforce the protein’s struc ...
... interactions between R groups, rather than interactions between backbone constituents • These interactions between R groups include hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, hydrophobic interactions, and van der Waals interactions • Strong covalent bonds called disulfide bridges may reinforce the protein’s struc ...
Presentation - science
... To build up sugars, nitrates and other nutrients into amino acids which are then built up into proteins. ...
... To build up sugars, nitrates and other nutrients into amino acids which are then built up into proteins. ...
5` 3` - UTSA CS
... • Besides A, C, G, T, we add some A*, C*, G*, and T* – Very similar to ACGT in all aspects, except that – The extension will stop if used ...
... • Besides A, C, G, T, we add some A*, C*, G*, and T* – Very similar to ACGT in all aspects, except that – The extension will stop if used ...
No Slide Title
... Protein folding is a “grand challenge” problem in biology the deciphering of the second half of the genetic code, of pressing practical significance Problem 1: given a protein’s amino acid sequence, predict its 3D structure, which is related to its function Problem 2: “… use the protein’s known 3D s ...
... Protein folding is a “grand challenge” problem in biology the deciphering of the second half of the genetic code, of pressing practical significance Problem 1: given a protein’s amino acid sequence, predict its 3D structure, which is related to its function Problem 2: “… use the protein’s known 3D s ...
View My Files
... vibrate. This produces sounds on the basis of our speech, song,etc. 5). Trachea is also called wind pipe. It channels air to lungs. 6)Trachea at its lower end divides into two bronchi one leading to each lung. 7) The bronchi further divided into smaller and smaller branches called bronchioles. ...
... vibrate. This produces sounds on the basis of our speech, song,etc. 5). Trachea is also called wind pipe. It channels air to lungs. 6)Trachea at its lower end divides into two bronchi one leading to each lung. 7) The bronchi further divided into smaller and smaller branches called bronchioles. ...
Document
... the initial six-carbon stage, glucose is phosphorylated twice and eventually converted to fructose 1,6- bisphosphate. Other sugars are often fed into the pathway by conversion to glucose 6-phosphate or fructose 6-phosphate. This preliminary stage does not yield energy; in fact, two ATP molecules ar ...
... the initial six-carbon stage, glucose is phosphorylated twice and eventually converted to fructose 1,6- bisphosphate. Other sugars are often fed into the pathway by conversion to glucose 6-phosphate or fructose 6-phosphate. This preliminary stage does not yield energy; in fact, two ATP molecules ar ...
Bio 101 Cumulative FINAL Homework Prof. Fournier
... D) In both plants and animals, the daughter cells are genetically identical to the original cell. 52. The uncontrolled division of certain body cells, which then invade the surrounding tissues and interfere with the normal functioning of the body, is known as A) cancer C) cleavage ...
... D) In both plants and animals, the daughter cells are genetically identical to the original cell. 52. The uncontrolled division of certain body cells, which then invade the surrounding tissues and interfere with the normal functioning of the body, is known as A) cancer C) cleavage ...
Lecture 14: Protein and Fat Synthesis
... fatty acid containing 6-C atoms. This process is repeated till Coenzymes-A derivative of long chain fatty acid (which may contain up to 16-18C atoms) is produced. (As a matter of fact the enzyme fatty acid synthetase is not simple but a complex of many enzymes (multienzyme complex) and an acyl carri ...
... fatty acid containing 6-C atoms. This process is repeated till Coenzymes-A derivative of long chain fatty acid (which may contain up to 16-18C atoms) is produced. (As a matter of fact the enzyme fatty acid synthetase is not simple but a complex of many enzymes (multienzyme complex) and an acyl carri ...
Translation - The Citadel
... How does the mRNA sequence of nucleotides direct a ribosome to connect the proper protein sequence of amino acids??? The genetic code = the way that the 4 bases of RNA encode the amino acid sequence of protein. Proteins are made of monomers called amino acids. There are 20 different amino acids. Eac ...
... How does the mRNA sequence of nucleotides direct a ribosome to connect the proper protein sequence of amino acids??? The genetic code = the way that the 4 bases of RNA encode the amino acid sequence of protein. Proteins are made of monomers called amino acids. There are 20 different amino acids. Eac ...
Document
... Oxidized coenzymes go back to glycolysis (step #6) and Krebs cycle to allow them to continue! ...
... Oxidized coenzymes go back to glycolysis (step #6) and Krebs cycle to allow them to continue! ...
16-17 membrane notes
... (remain fluid @ colder temps) CHOLESTEROL (in animal cells only) makes membranes less fluid at higher temps (keep phospholipids from moving around) makes membranes more fluid at lower temps (keep phospholipids from packing closely together) ...
... (remain fluid @ colder temps) CHOLESTEROL (in animal cells only) makes membranes less fluid at higher temps (keep phospholipids from moving around) makes membranes more fluid at lower temps (keep phospholipids from packing closely together) ...
Answers - AP BIOLOGY!
... environments, phospholipid molecules will form bilayers where their polar heads shield their polar tails from the environment. This bilayer is what composes cell membranes. The largely nonpolar/hydrophobic interior of cell membranes keeps even small polar/hydrophilic molecules from diffusing rapidly ...
... environments, phospholipid molecules will form bilayers where their polar heads shield their polar tails from the environment. This bilayer is what composes cell membranes. The largely nonpolar/hydrophobic interior of cell membranes keeps even small polar/hydrophilic molecules from diffusing rapidly ...
BIOL 246 - Marine Biology - American University of Beirut
... biological systems will be illustrated by examples from the literature. Emphasis will be on roles in which nucleic acids are not mere vessels of protein coding sequence, but rather in which their structures function in regulation and catalysis. Experimental methods will be discussed as appropriate, ...
... biological systems will be illustrated by examples from the literature. Emphasis will be on roles in which nucleic acids are not mere vessels of protein coding sequence, but rather in which their structures function in regulation and catalysis. Experimental methods will be discussed as appropriate, ...
microbial nutrition
... found in organic molecules such as proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids ◦ K, Ca, Mg, and Fe cations and serve in variety of roles ...
... found in organic molecules such as proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids ◦ K, Ca, Mg, and Fe cations and serve in variety of roles ...
chapter review questions
... deposit it in cells To convert fat to protein To maintain blood glucose at around 70–110 mg/100 ml of blood To elevate blood glucose to the highest possible level to ensure adequate delivery to the brain ...
... deposit it in cells To convert fat to protein To maintain blood glucose at around 70–110 mg/100 ml of blood To elevate blood glucose to the highest possible level to ensure adequate delivery to the brain ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.