Recap: structure of ATP
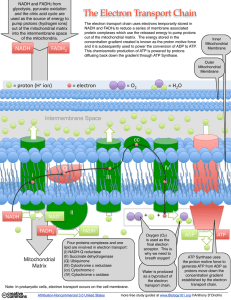
... matrix via ATP synthase 6. Movement of protons drives synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate 7. Protons, electrons and oxygen combine to form water, the final electron acceptor ...
... matrix via ATP synthase 6. Movement of protons drives synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate 7. Protons, electrons and oxygen combine to form water, the final electron acceptor ...
Biology paper 2 ms MBOONI EAST SUB – COUNTY JOINT
... Such seeds and fruits enclose air in them to lower their density for buoyancy; They have fibrous/spongy to lower the density for buoyancy; Have impermeable seed coat or epicarp to prevent water from entering during floatation so as to avoid rotting; The seeds can remain viable while in water ...
... Such seeds and fruits enclose air in them to lower their density for buoyancy; They have fibrous/spongy to lower the density for buoyancy; Have impermeable seed coat or epicarp to prevent water from entering during floatation so as to avoid rotting; The seeds can remain viable while in water ...
capitolo 1 - Structural Biology
... Main properties of the lateral chains We recall briefly some features of the amino acids. Amino acids can be distinguished into different classes in view of their polarità. By varying the criterion for classification it changes the class to which the amino acids belong. Tryptophan and arginine for ...
... Main properties of the lateral chains We recall briefly some features of the amino acids. Amino acids can be distinguished into different classes in view of their polarità. By varying the criterion for classification it changes the class to which the amino acids belong. Tryptophan and arginine for ...
PHOTOSYNTHESIS HOW PLANTS MAKE THEIR
... • OCCURS IN THE CYTOPLASM OF ALL CELLS • No O2 is required, anaerobic respiration • 1. THROUGH A SERIES OF REACTIONS, IT WILL PRODUCE: • 4 ATPS, AND 2 NADH+ & 2 PYRUVATES ...
... • OCCURS IN THE CYTOPLASM OF ALL CELLS • No O2 is required, anaerobic respiration • 1. THROUGH A SERIES OF REACTIONS, IT WILL PRODUCE: • 4 ATPS, AND 2 NADH+ & 2 PYRUVATES ...
Studies on some essential amino acids: Synthesis of methyl esters
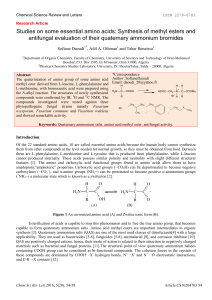
... capable to form quaternary ammonium salts. Amino acid methyl esters are important intermediates in organic synthesis [3]. Quaternary ammonium salts (QAS) are one of the most used classes of disinfectants[4] with a large applicability. They are used as bactericides [5-6], fungicides [5-8], antimalari ...
... capable to form quaternary ammonium salts. Amino acid methyl esters are important intermediates in organic synthesis [3]. Quaternary ammonium salts (QAS) are one of the most used classes of disinfectants[4] with a large applicability. They are used as bactericides [5-6], fungicides [5-8], antimalari ...
Midterm Review Student Requested
... polymers, and types of bonds. – Carbs: monosaccharides, polysaccharides, glycosidic linkage – Lipids: fatty acids and glycerol, triglycerides, ester linkage – Proteins: amino acids, polypeptides, peptide bonds – Nucleic Acids: nucleotides, nucleic acids, phosphodiester bonds ...
... polymers, and types of bonds. – Carbs: monosaccharides, polysaccharides, glycosidic linkage – Lipids: fatty acids and glycerol, triglycerides, ester linkage – Proteins: amino acids, polypeptides, peptide bonds – Nucleic Acids: nucleotides, nucleic acids, phosphodiester bonds ...
corrected version for study guide
... glycolysis- the breakdown of sugar into pyruvate – takes place in the cytoplasm Krebs cycle(citric acid cycle)- finishes the breakdown of pyruvic acid to carbon dioxide and releasing more ATP and also NADH and FADH2 ATP synthase—The enzyme embedded in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion where H+ ...
... glycolysis- the breakdown of sugar into pyruvate – takes place in the cytoplasm Krebs cycle(citric acid cycle)- finishes the breakdown of pyruvic acid to carbon dioxide and releasing more ATP and also NADH and FADH2 ATP synthase—The enzyme embedded in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion where H+ ...
Practice Questions
... 16. C - The Nuclear Localization Sequence (II) and start transfer (III) sequence are both part of the primary sequence of a polypeptide and are therefore incorporated during translation. Targeting to the lysosome or for extracellular export require the addition of carbohydrate tags which are added p ...
... 16. C - The Nuclear Localization Sequence (II) and start transfer (III) sequence are both part of the primary sequence of a polypeptide and are therefore incorporated during translation. Targeting to the lysosome or for extracellular export require the addition of carbohydrate tags which are added p ...
Ch18.doc
... 5. Both alanine and lactate have to be converted to pyruvate. From lactate, it is the lactate dehydrogenase reaction (1 NADH), then pyruvate gets oxidized by pyruvate dehydrogenase (1 NADH) and one turn of the CAC: yielding 3NADH, 1FADH2 and 1 GTP. Converting NADH and FADH2 to ATPs we use 1 NADH = 2 ...
... 5. Both alanine and lactate have to be converted to pyruvate. From lactate, it is the lactate dehydrogenase reaction (1 NADH), then pyruvate gets oxidized by pyruvate dehydrogenase (1 NADH) and one turn of the CAC: yielding 3NADH, 1FADH2 and 1 GTP. Converting NADH and FADH2 to ATPs we use 1 NADH = 2 ...
The Importance of Non-Coding DNA
... DNA- the material that transfers genetic characteristics in all life forms, constructed of two nucleotide strands coiled around each other in a double helix with the sidepieces composed of alternating phosphate and deoxyribose units and the rungs composed of the purine and pyrimidine bases adenine, ...
... DNA- the material that transfers genetic characteristics in all life forms, constructed of two nucleotide strands coiled around each other in a double helix with the sidepieces composed of alternating phosphate and deoxyribose units and the rungs composed of the purine and pyrimidine bases adenine, ...
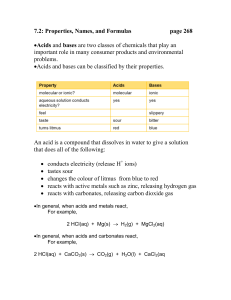
7.2: Properties, Names, and Formulas page 268 •Acids and bases
... 7.2: Properties, Names, and Formulas ...
... 7.2: Properties, Names, and Formulas ...
Modeling DNA Structure and Function
... to the mRNA sequence, draw the amino acid sequence that would be produced during translation. (To do this, you'll have to be able to interpret the genetic code as it appears in your text.) 1. How many bases make up one codon? 2. How many codons are present in the mRNA strand you made in lab? 3. On w ...
... to the mRNA sequence, draw the amino acid sequence that would be produced during translation. (To do this, you'll have to be able to interpret the genetic code as it appears in your text.) 1. How many bases make up one codon? 2. How many codons are present in the mRNA strand you made in lab? 3. On w ...
adrenal support plus
... VITAMIN B6 – Pyridoxal-5’-phosphate is vital for conversion of protein and carbohydrate stores into glucose to support blood sugar between meals. It is also essential for the formation of several neurotransmitters, including serotonin (from tryptophan), dopamine, and norepinephrine.* FOLIC ACID – An ...
... VITAMIN B6 – Pyridoxal-5’-phosphate is vital for conversion of protein and carbohydrate stores into glucose to support blood sugar between meals. It is also essential for the formation of several neurotransmitters, including serotonin (from tryptophan), dopamine, and norepinephrine.* FOLIC ACID – An ...
DNA vs. RNA
... RNA molecules are produced by copying part of the nucleotide sequence of DNA into a complementary sequence in RNA required enzyme = RNA polymerase 1. RNA polymerase binds to DNA (in nucleus) 2. separates the DNA strands 3. RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a ...
... RNA molecules are produced by copying part of the nucleotide sequence of DNA into a complementary sequence in RNA required enzyme = RNA polymerase 1. RNA polymerase binds to DNA (in nucleus) 2. separates the DNA strands 3. RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a ...
Translation
... • tRNA: Adaptor molecules that mediate the transfer of information from nucleic acids to protein • Ribosomes: manufacturing units of a cell; located in the cytoplasm. Contain ribosomal RNA and proteins. • Enzymes: required for the attachment of amino acids to the correct tRNA molecule, and for pepti ...
... • tRNA: Adaptor molecules that mediate the transfer of information from nucleic acids to protein • Ribosomes: manufacturing units of a cell; located in the cytoplasm. Contain ribosomal RNA and proteins. • Enzymes: required for the attachment of amino acids to the correct tRNA molecule, and for pepti ...
“There is grandeur in this view of life”
... Amino acids Amino acids are basic organic chemical compounds. More than 5o0 exist in nature. ...
... Amino acids Amino acids are basic organic chemical compounds. More than 5o0 exist in nature. ...
LECTURE #6: Translation and Mutations
... Not harmful or helpful SILENT MUTATIONS Mutation does not change “end result”…change in DNA still makes the SAME amino acid NO noticeable change occurs ...
... Not harmful or helpful SILENT MUTATIONS Mutation does not change “end result”…change in DNA still makes the SAME amino acid NO noticeable change occurs ...
BSc in Applied Biotechnology 3 BO0045 ‑ MICROBIOLOGY
... dehydrogenase, followed by the oxidation of 6-phosphoglucono-d-lactone to pentose ribulose 5-phosphate and CO2. • NADPH is produced during these oxidations. The capability of this oxidative metabolic system to bypass glycolysis explains the term shunt. • All cyanobacteria, Acetobacter suboxydans, an ...
... dehydrogenase, followed by the oxidation of 6-phosphoglucono-d-lactone to pentose ribulose 5-phosphate and CO2. • NADPH is produced during these oxidations. The capability of this oxidative metabolic system to bypass glycolysis explains the term shunt. • All cyanobacteria, Acetobacter suboxydans, an ...
What is an acid or a base
... ion of the base unite to form water. Acids ___________________________. Even gold, the least active metal, is attacked by an acid, a mixture of acids called 'aqua regia,' or 'royal liquid.' When an acid reacts with a metal, it produces a compound with the cation of the metal and the anion of the aci ...
... ion of the base unite to form water. Acids ___________________________. Even gold, the least active metal, is attacked by an acid, a mixture of acids called 'aqua regia,' or 'royal liquid.' When an acid reacts with a metal, it produces a compound with the cation of the metal and the anion of the aci ...
CELL PHYSIOLOGY Cell: are the basic structural and functional
... comprises 60 - 90% of most living organisms (and cells) important because it serves as an excellent solvent & enters into many metabolic reactions found in both intra- & extracellular fluid ...
... comprises 60 - 90% of most living organisms (and cells) important because it serves as an excellent solvent & enters into many metabolic reactions found in both intra- & extracellular fluid ...
Understanding conserved amino acids in proteins
... and Rossman fold (R). We compute correlation coe>cient [19] between values of SMF (k), obtained at Tsel , and Sacr (k) for all three folds. The results are summarized in Table 1. The plots of SMF (k) and Sacr (k) versus k as well as their scatter plots are shown in Figs. 1–3(a,b). The correlation be ...
... and Rossman fold (R). We compute correlation coe>cient [19] between values of SMF (k), obtained at Tsel , and Sacr (k) for all three folds. The results are summarized in Table 1. The plots of SMF (k) and Sacr (k) versus k as well as their scatter plots are shown in Figs. 1–3(a,b). The correlation be ...
What is the Electron Transport Chain?
... NADH and FADH2 from glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation and the citric acid cycle are used as the source of energy to pump protons (hydrogen ions) out of the mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane space of the mitochondria. ...
... NADH and FADH2 from glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation and the citric acid cycle are used as the source of energy to pump protons (hydrogen ions) out of the mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane space of the mitochondria. ...
Kate Buckman Modified session plan: Fermentation: one part in a
... However in the absence of oxygen this pathway is not an option. As NADH is only present in small amounts, it must be oxidized back to NAD+ in order for ATP production to continue through glycolysis. Anaerobic organisms (like yeast) or cells functioning under insufficient oxygen conditions (such as h ...
... However in the absence of oxygen this pathway is not an option. As NADH is only present in small amounts, it must be oxidized back to NAD+ in order for ATP production to continue through glycolysis. Anaerobic organisms (like yeast) or cells functioning under insufficient oxygen conditions (such as h ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.