Hand Outs B 1 - University of Wisconsin–Madison
... Definitions for Parents-complex concepts in simple language for you to use with your school-aged children ...
... Definitions for Parents-complex concepts in simple language for you to use with your school-aged children ...
First Semester Exam Review (Word Doc)
... Recognize differences in plant and animal cells Explain different roles of vacuoles in plant and animal cells (sometimes vacuoles in animal cells are vesicles) Understand that chloroplasts and cell walls are only found in plant cells because of their functions 2.02c Investigate and Describe th ...
... Recognize differences in plant and animal cells Explain different roles of vacuoles in plant and animal cells (sometimes vacuoles in animal cells are vesicles) Understand that chloroplasts and cell walls are only found in plant cells because of their functions 2.02c Investigate and Describe th ...
Fact Sheet
... Management of Propionic Acidemia and Methylmalonic Acidemia There is no cure for PA or MMA, but they can be managed with a modified diet, medication, and special medical formulas specifically designed for persons with PA or MMA. The modified diet for these disorders is low in propiogenic amino acid ...
... Management of Propionic Acidemia and Methylmalonic Acidemia There is no cure for PA or MMA, but they can be managed with a modified diet, medication, and special medical formulas specifically designed for persons with PA or MMA. The modified diet for these disorders is low in propiogenic amino acid ...
Chapter 9
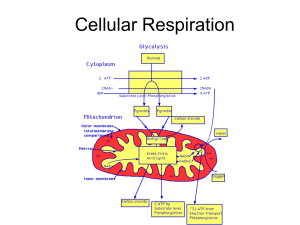
... Step 3: Electron Transport Chainenergy from electrons carried by NADH and FADH2 to the inner mitochondrial membrane is used to make ATP. As e- move down the etc, energy “spillover” is used to pump H+ into inner membrane space. H+ diffuse back through ATP synthase which adds phosphates onto ADP mole ...
... Step 3: Electron Transport Chainenergy from electrons carried by NADH and FADH2 to the inner mitochondrial membrane is used to make ATP. As e- move down the etc, energy “spillover” is used to pump H+ into inner membrane space. H+ diffuse back through ATP synthase which adds phosphates onto ADP mole ...
The tricarboxylic acid cycle In many bacteria, yeasts, filamentous
... The glyoxalate cycle As a consequence of removing intermediate compounds from these amphibolic pathways for biosynthesis, their levels may become depleted. For example, oxaloacetate is taken from the TCA cycle to furnish the demand for carbon skeletons in amino acid biosynthesis. Hence, these interm ...
... The glyoxalate cycle As a consequence of removing intermediate compounds from these amphibolic pathways for biosynthesis, their levels may become depleted. For example, oxaloacetate is taken from the TCA cycle to furnish the demand for carbon skeletons in amino acid biosynthesis. Hence, these interm ...
Chapter 9. Cellular Respiration STAGE 1: Glycolysis
... Break down Easily. 8. For a Molecule of Glucose to undergo Glycolysis, a Cell must First "SPEND" ATP to energize the Glucose Molecule. The ATP provides the Activation Energy needed to begin Glycolysis. 9. Although ATP (ENERGY) is used to begin Glycolysis, the reactions that make up the ...
... Break down Easily. 8. For a Molecule of Glucose to undergo Glycolysis, a Cell must First "SPEND" ATP to energize the Glucose Molecule. The ATP provides the Activation Energy needed to begin Glycolysis. 9. Although ATP (ENERGY) is used to begin Glycolysis, the reactions that make up the ...
Randy Carroll
... Double Helix: The structural shape of DNA. Guanine: Pairs with cytosine. Helicase: The chains made in DNA separated by Enzymes. Mutation: An error in the replication process of DNA. Nitrogen-Containing Base: An atom surround by oxygen that contains nitrogen. Purine: Pyrimidine: Bases that have one r ...
... Double Helix: The structural shape of DNA. Guanine: Pairs with cytosine. Helicase: The chains made in DNA separated by Enzymes. Mutation: An error in the replication process of DNA. Nitrogen-Containing Base: An atom surround by oxygen that contains nitrogen. Purine: Pyrimidine: Bases that have one r ...
genetic code-unit-1.- study mat-2012
... represented by more than one codon. For example, the three amino acids-arginine, serine and leucine-each have six synonymous codons. However, for many of the synonym codons specifying the same amino acid the first two bases of the triplet are constant, whereas the third can vary; for example, all co ...
... represented by more than one codon. For example, the three amino acids-arginine, serine and leucine-each have six synonymous codons. However, for many of the synonym codons specifying the same amino acid the first two bases of the triplet are constant, whereas the third can vary; for example, all co ...
C483 Exam I 2014 Answer Key
... 2) 6pts What are the major differences between a 310 helix and an alpha helix? Why is glycine likely found so often in a 310 helix? Many differences. Most relevant: 310 helix: 3 residues per turn, 10 atoms per H-bond loop. Alpha helix: 3.6 residues per turn, 13 atoms per H-bond loop. Glycine has no ...
... 2) 6pts What are the major differences between a 310 helix and an alpha helix? Why is glycine likely found so often in a 310 helix? Many differences. Most relevant: 310 helix: 3 residues per turn, 10 atoms per H-bond loop. Alpha helix: 3.6 residues per turn, 13 atoms per H-bond loop. Glycine has no ...
Effect of Systemic Fungicide on Nucleic Acid, Amino Acid and
... both control and treated plants. While cystein, proline, tryptophane and valine were observed in appreciable amount in treated samples as compare to control after first and second spray. Reduction in nucleic acid, changes in amino acids and increase in total phenolic contents were significantly incr ...
... both control and treated plants. While cystein, proline, tryptophane and valine were observed in appreciable amount in treated samples as compare to control after first and second spray. Reduction in nucleic acid, changes in amino acids and increase in total phenolic contents were significantly incr ...
3.1 Carbon`s Place in the Living World
... (b) Secondary structure Structural motifs, such as the corkscrew-like alpha helix, beta pleated sheets, and the less organized "random coils" are parts of many polypeptide chains, forming their secondary structure. (c) Tertiary structure These motifs may persist through a set of larger-scale turns t ...
... (b) Secondary structure Structural motifs, such as the corkscrew-like alpha helix, beta pleated sheets, and the less organized "random coils" are parts of many polypeptide chains, forming their secondary structure. (c) Tertiary structure These motifs may persist through a set of larger-scale turns t ...
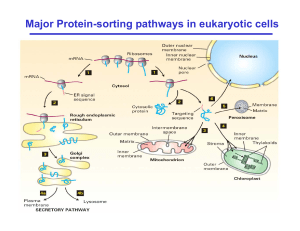
Major Protein-sorting pathways in eukaryotic cells
... Major topological classes of integral membrane proteins synthesized on the rough ER ...
... Major topological classes of integral membrane proteins synthesized on the rough ER ...
Separation of Low Levels of Isoleucine from Leucine Using
... The European Pharmacacopoeia (Ph. Eur.) defines requirements for the qualitative and quantitative composition of amino acids and mixtures of amino acids. The requirements for allowed impurities are also defined. Manufacturers of amino acids are legally bound to prove that their amino acids meet thes ...
... The European Pharmacacopoeia (Ph. Eur.) defines requirements for the qualitative and quantitative composition of amino acids and mixtures of amino acids. The requirements for allowed impurities are also defined. Manufacturers of amino acids are legally bound to prove that their amino acids meet thes ...
Bio 313 worksheet 2 - Iowa State University
... 8. (#21 from chapter 8) DNA molecules of different sizes are often separated with the use of a technique called electrophoresis. With this technique, DNA molecules are placed in a gel, an electrical current is applied to the gel, and the DNA molecules migrate toward the positive pole of the current. ...
... 8. (#21 from chapter 8) DNA molecules of different sizes are often separated with the use of a technique called electrophoresis. With this technique, DNA molecules are placed in a gel, an electrical current is applied to the gel, and the DNA molecules migrate toward the positive pole of the current. ...
The Hiring Process at ARIAD
... Summary ARIAD Pharmaceuticals Inc is seeking an independent and highly motivated scientist with a strong background in molecular biology, protein biochemistry and structural chemistry to join our pre-clinical small molecule oncology drug discovery team. The successful candidate will play a key role ...
... Summary ARIAD Pharmaceuticals Inc is seeking an independent and highly motivated scientist with a strong background in molecular biology, protein biochemistry and structural chemistry to join our pre-clinical small molecule oncology drug discovery team. The successful candidate will play a key role ...
Coarse-Graining of Macromolecules
... The Great Idea of Jacob and Monod: Genes that Control Genes ...
... The Great Idea of Jacob and Monod: Genes that Control Genes ...
Cellular Respiration
... pretty much the opposite of each other! Photosynthesis • Plants • * use sunlight to make glucose • * take in carbon dioxide • * give off oxygen • *carbon dioxide + water + sunlight glucose + oxygen ...
... pretty much the opposite of each other! Photosynthesis • Plants • * use sunlight to make glucose • * take in carbon dioxide • * give off oxygen • *carbon dioxide + water + sunlight glucose + oxygen ...
... 19. The major reason for A pairing with U is: a) complementary hydrogen bonds. b) a purine-pyrimidine pair fits well in the double helix. c) efficient stacking of this arrangement of bases in the helix. d) recognition of non-’Watson-Crick’ hydrogen bonds by DNA polymerases 20. An expression vector o ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.