Slide 1
... are transformed into various compounds – Become intermediates in glycolysis or the citric acid cycle ...
... are transformed into various compounds – Become intermediates in glycolysis or the citric acid cycle ...
Fatty Acid Synthesis
... Fatty Acid Synthase complex (but it may produce short chain FAs) Further elongation and insertion of double bonds are carried out by ...
... Fatty Acid Synthase complex (but it may produce short chain FAs) Further elongation and insertion of double bonds are carried out by ...
Cellular Respiration
... with a small yield of ATP. 3.7.3 Explain that, during anaerobic cell respiration, pyruvate can be converted in the cytoplasm into lactate, or ethanol and carbon dioxide, with no further yield of ATP. 3.7.4 Explain that, during aerobic cell respiration, pyruvate can be broken down in the mitochondrio ...
... with a small yield of ATP. 3.7.3 Explain that, during anaerobic cell respiration, pyruvate can be converted in the cytoplasm into lactate, or ethanol and carbon dioxide, with no further yield of ATP. 3.7.4 Explain that, during aerobic cell respiration, pyruvate can be broken down in the mitochondrio ...
The Nucleolus
... Nucleotides – building blocks of nucleic acids Monomer – a chemical subunit that serves as a building block of a polymer Polymer – a large molecule consisting of many identical or similar molecular units (monomers), covalently joined together in a chain. An example of this is DNA Filaments – ...
... Nucleotides – building blocks of nucleic acids Monomer – a chemical subunit that serves as a building block of a polymer Polymer – a large molecule consisting of many identical or similar molecular units (monomers), covalently joined together in a chain. An example of this is DNA Filaments – ...
Final Review
... Identify the storage form of glucose in animals and in plants. Identify the structural form of glucose in plants. Match the monomer to the polymer (monomers can be used more than once): POLYMER: 1. cellulose 3. DNA 5. starch 7. RNA 2. protein 4. lipid 6. peptide 8. Glycogen MONOMER: a) nucleotide b) ...
... Identify the storage form of glucose in animals and in plants. Identify the structural form of glucose in plants. Match the monomer to the polymer (monomers can be used more than once): POLYMER: 1. cellulose 3. DNA 5. starch 7. RNA 2. protein 4. lipid 6. peptide 8. Glycogen MONOMER: a) nucleotide b) ...
What You Absolutely Need to Know To Pass the NYS Living
... cycles in which the product of one reaction causes another to start or stop. D. While organisms are balanced, they are not unchanging. The term used to describe the balanced state is dynamic equilibrium. 1. Dynamic Equilibrium: A balanced state created by many small, opposing changes. ...
... cycles in which the product of one reaction causes another to start or stop. D. While organisms are balanced, they are not unchanging. The term used to describe the balanced state is dynamic equilibrium. 1. Dynamic Equilibrium: A balanced state created by many small, opposing changes. ...
Lecture 10 - Prediction, Engineering, Design of Protein Structures
... Model was based on rules by which evolutionary changes occur in proteins Catalogued 1000’s of proteins, considered which specific amino acid substitutions occurred when 2 homologous proteins aligned Assumes substitution patterns in closely-related proteins can be extrapolated to more distantly-relat ...
... Model was based on rules by which evolutionary changes occur in proteins Catalogued 1000’s of proteins, considered which specific amino acid substitutions occurred when 2 homologous proteins aligned Assumes substitution patterns in closely-related proteins can be extrapolated to more distantly-relat ...
University of - Biochemistry at the University of Maryland, College Park
... (a; 12 points) Listed below are three enzymes from the glycolysis pathway. For any two (your choice) of these enzymes, draw the complete structure (including all H atoms) of the reactants and products for the reaction catalyzed by that enzyme, and write the names of the reactants and products. You m ...
... (a; 12 points) Listed below are three enzymes from the glycolysis pathway. For any two (your choice) of these enzymes, draw the complete structure (including all H atoms) of the reactants and products for the reaction catalyzed by that enzyme, and write the names of the reactants and products. You m ...
Rugby nutrition - Reading Crusade
... and many other processed foods. This type of sugar is a major cause of tooth decay and weight gain. The body breaks down sucrose quickly, a large amount of energy at one time means that there is a surplus, which is converted into fat, rather than converted into glycogen and stored. The natural s ...
... and many other processed foods. This type of sugar is a major cause of tooth decay and weight gain. The body breaks down sucrose quickly, a large amount of energy at one time means that there is a surplus, which is converted into fat, rather than converted into glycogen and stored. The natural s ...
Amino acids
... • The precise amino acid content, and the sequence of those amino acids, of a specific protein, is determined by the sequence of the bases in the gene that encodes that protein. • The chemical properties of the amino acids of proteins determine the biological activity of the protein. • Proteins not ...
... • The precise amino acid content, and the sequence of those amino acids, of a specific protein, is determined by the sequence of the bases in the gene that encodes that protein. • The chemical properties of the amino acids of proteins determine the biological activity of the protein. • Proteins not ...
Mixotrophic and photoheterotrophic metabolism in
... investigated the effect of three carbon sources (glucose, glycerol and pyruvate, as representatives of sugar, lipid derivatives and organic acids from central metabolic pathways, respectively) on Cyanothece 51142 growth and metabolism. Two nitrogen sources other than N2, ammonia and nitrate, were al ...
... investigated the effect of three carbon sources (glucose, glycerol and pyruvate, as representatives of sugar, lipid derivatives and organic acids from central metabolic pathways, respectively) on Cyanothece 51142 growth and metabolism. Two nitrogen sources other than N2, ammonia and nitrate, were al ...
05D-Proteins2
... backbone. • Attached to the backbone are the various R groups. • Polypeptides range in size from a few monomers to thousands. ...
... backbone. • Attached to the backbone are the various R groups. • Polypeptides range in size from a few monomers to thousands. ...
Ch. 17 - Ltcconline.net
... 1. Once initiation is complete, amino acids are added one at a time till translation is complete 2. Each amino acid that is added onto the growing chain does so in 3 steps a. codon recognition b. peptide bond formation c. translocation 3. termination. 4. release factor J. Review 1. typically, severa ...
... 1. Once initiation is complete, amino acids are added one at a time till translation is complete 2. Each amino acid that is added onto the growing chain does so in 3 steps a. codon recognition b. peptide bond formation c. translocation 3. termination. 4. release factor J. Review 1. typically, severa ...
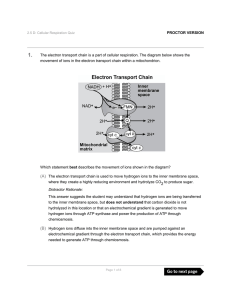
The electron transport chain is a part of cellular respiration. The
... This answer suggests the student may understand that photolysis occurs during the lightdependent reactions in photosynthesis, but does not understand that oxygen is not split and combined with carbon to form carbon dioxide during photosynthesis, and that the plant is undergoing cellular respiration, ...
... This answer suggests the student may understand that photolysis occurs during the lightdependent reactions in photosynthesis, but does not understand that oxygen is not split and combined with carbon to form carbon dioxide during photosynthesis, and that the plant is undergoing cellular respiration, ...
In 1953 Watson and Crick developed a double helix model for DNA
... The two nucleic acid strands are _______________________ to each other. That means that one strand is “_____________________” compared to the other. The 2 nucleic acid strands are held together by ____________ _ _____________ between the nitrogen bases. When the nitrogen bases bond together they fol ...
... The two nucleic acid strands are _______________________ to each other. That means that one strand is “_____________________” compared to the other. The 2 nucleic acid strands are held together by ____________ _ _____________ between the nitrogen bases. When the nitrogen bases bond together they fol ...
Ch 3 Membrane Transports
... Ch 3 Membrane Transports what's so dynamic about cell membranes? living things get nutrients and energy from the envrionment this is true of the entire organism and each cell this requires transport in/out of cells; across cell membrane concepts used: things move from high to low toward equilibrium ...
... Ch 3 Membrane Transports what's so dynamic about cell membranes? living things get nutrients and energy from the envrionment this is true of the entire organism and each cell this requires transport in/out of cells; across cell membrane concepts used: things move from high to low toward equilibrium ...
CHAPTER-IV LIPID METABOLISM BETA
... Beta-oxidation is the process by which fatty acids, in the form of acyl-CoA molecules, are broken down in mitochondria and/or peroxisomes to generate acetyl-CoA, the entry molecule for the citric acid cycle. The beta oxidation of fatty acids involve three stages: 1. Activation of fatty acids in the ...
... Beta-oxidation is the process by which fatty acids, in the form of acyl-CoA molecules, are broken down in mitochondria and/or peroxisomes to generate acetyl-CoA, the entry molecule for the citric acid cycle. The beta oxidation of fatty acids involve three stages: 1. Activation of fatty acids in the ...
15) DIAPHRAGM: A domed shape muscle located beneath the
... remove waste gasses 2) Cellular respiration – the oxidation of food (e.g. glucose/sugar) to release energy and store energy in ATP molecules 3 or more a) Reactants " Products; Questions Sugar + Oxygen " Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy B) Organs of the respiratory system 1) The pharynx – tubelike pas ...
... remove waste gasses 2) Cellular respiration – the oxidation of food (e.g. glucose/sugar) to release energy and store energy in ATP molecules 3 or more a) Reactants " Products; Questions Sugar + Oxygen " Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy B) Organs of the respiratory system 1) The pharynx – tubelike pas ...
Maintaining Life and Homeostasis Vocabulary
... b. Responsiveness or irritability: ability to sense changes in the environment and then react to them Something is hot, you pull away Also amount of carbon dioxide rises too high, breathing rate increases to blow off excess carbon dioxide Nervous system bears major responsibility All cells e ...
... b. Responsiveness or irritability: ability to sense changes in the environment and then react to them Something is hot, you pull away Also amount of carbon dioxide rises too high, breathing rate increases to blow off excess carbon dioxide Nervous system bears major responsibility All cells e ...
EXCRETION
... small intestine where it aids in the breakdown (emulsification) of fats. Most of the bile is eventually eliminated from the body with the digestive wastes. Excess amino acids entering the liver are broken down by a process called deamination. This separates the nonamino portion of the molecule from ...
... small intestine where it aids in the breakdown (emulsification) of fats. Most of the bile is eventually eliminated from the body with the digestive wastes. Excess amino acids entering the liver are broken down by a process called deamination. This separates the nonamino portion of the molecule from ...
Chapter 1: Introduction to Biology Lesson 1.1: Unifying Principles of
... harness and store it is important to the study of biology. So how exactly do cells harness free energy? Let’s briefly examine how photosynthetic organisms harness energy from the photons in sunlight. The reactions which allow the photosynthetic process to occur are endergonic reactions, reactions th ...
... harness and store it is important to the study of biology. So how exactly do cells harness free energy? Let’s briefly examine how photosynthetic organisms harness energy from the photons in sunlight. The reactions which allow the photosynthetic process to occur are endergonic reactions, reactions th ...
9.1 Amino Acids—A Second Look, Continued
... Peptides formed in the condensation of three amino acids are known as tripeptides; ones with four amino acids are tetrapeptides; ones with five amino acids are pentapeptides; etc. ...
... Peptides formed in the condensation of three amino acids are known as tripeptides; ones with four amino acids are tetrapeptides; ones with five amino acids are pentapeptides; etc. ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.