CHEMISTRY (HONOURS) Part
... (b) Explain the terms isoelectric point for an amino acid R-CH.'NH-COOH. (c) Explain, with example, denaturation of proteins. (d) Give an-account of nucleic acids. 10. (a) Explain the terms diamagnetic anisotropy. (b) What is meant by 'splitting of a signal' in NMR spectroscopy? How many splittings ...
... (b) Explain the terms isoelectric point for an amino acid R-CH.'NH-COOH. (c) Explain, with example, denaturation of proteins. (d) Give an-account of nucleic acids. 10. (a) Explain the terms diamagnetic anisotropy. (b) What is meant by 'splitting of a signal' in NMR spectroscopy? How many splittings ...
Cellular Respiration
... Cellular Respiration Simulation Activity Activity Overview: This is a role-playing simulation where the students act as the enzymes of cellular respiration to break down a glucose "molecule." The purpose of the activity is to review the "big picture" of metabolism, aiding students in understanding t ...
... Cellular Respiration Simulation Activity Activity Overview: This is a role-playing simulation where the students act as the enzymes of cellular respiration to break down a glucose "molecule." The purpose of the activity is to review the "big picture" of metabolism, aiding students in understanding t ...
Secondary Structures and Properties of Fibrous Proteins
... how the amino acid side chains tightly fill in the surface clefts. ...
... how the amino acid side chains tightly fill in the surface clefts. ...
Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5/e
... In neuronal signal, electrical signals (nerve impulses) originate in the cell body of a neuron and travel very rapidly over long distances to the axon tip, where neurotransmitters are released and diffuse to the target cell. The target cell (another neuron, a myocyte, or a secretory cell) is only a ...
... In neuronal signal, electrical signals (nerve impulses) originate in the cell body of a neuron and travel very rapidly over long distances to the axon tip, where neurotransmitters are released and diffuse to the target cell. The target cell (another neuron, a myocyte, or a secretory cell) is only a ...
Slide 1
... Fermentation enables cells to produce ATP without oxygen The baking and winemaking industry have used alcohol fermentation for thousands of years – Yeasts are single-celled fungi that not only can use respiration for energy but can ferment under anaerobic conditions – They convert pyruvate to CO2 ...
... Fermentation enables cells to produce ATP without oxygen The baking and winemaking industry have used alcohol fermentation for thousands of years – Yeasts are single-celled fungi that not only can use respiration for energy but can ferment under anaerobic conditions – They convert pyruvate to CO2 ...
... The study evaluated the performance and carcass composition index of Nile tilapia ( Oreochromis niloticus ) fed with diets containing increasing levels of spray-dried blood meal (SDBM) and vat-dried blood meal (VDBM) and formulated based on digestible amino acids. Two hundred and fifty-two fingerlin ...
Carbon Interrupted
... (Lexile 1140L) 1 The element carbon is one of the most important elements for biological life because it is so versatile. Carbon can form up to four chemical bonds by the nature of the way that it bonds to other elements. This large number of bonding possibilities makes carbon able to form varied, ...
... (Lexile 1140L) 1 The element carbon is one of the most important elements for biological life because it is so versatile. Carbon can form up to four chemical bonds by the nature of the way that it bonds to other elements. This large number of bonding possibilities makes carbon able to form varied, ...
use of tobacco plants as bioreactors for the production of human
... mannose 6-phosphate pathway, whereas in plants vacuolar α-mannosidase is targeted to its final destination via the classic secretory pathway involving the ER-Golgi system. MAN2B1 in tobacco tissues is localised in vacuolar compartments. Due to the absence of a plant counterpart of the mannose 6-phos ...
... mannose 6-phosphate pathway, whereas in plants vacuolar α-mannosidase is targeted to its final destination via the classic secretory pathway involving the ER-Golgi system. MAN2B1 in tobacco tissues is localised in vacuolar compartments. Due to the absence of a plant counterpart of the mannose 6-phos ...
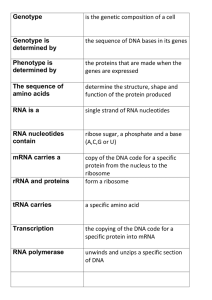
The sequence of amino acids
... multiple translation on the same mRNA strand may be required to enable a protein to perform its specific function ...
... multiple translation on the same mRNA strand may be required to enable a protein to perform its specific function ...
CH 17 PPT
... • For ex: the mRNA codon UUU is translated as the amino acid phenylalanine. The tRNA that transfers phenylalanine to the ribosome has an anticodon of AAA. • As tRNAs deposit amino acids in the correct order, ribosomal enzymes link them into a chain. ...
... • For ex: the mRNA codon UUU is translated as the amino acid phenylalanine. The tRNA that transfers phenylalanine to the ribosome has an anticodon of AAA. • As tRNAs deposit amino acids in the correct order, ribosomal enzymes link them into a chain. ...
Part I. Transcription
... enzyme which does this is called _____________________. The other function of this enzyme is to bring in nucleotides to form the new mRNA molecule. In mRNA, the nitrogenous base ____________(____) is ...
... enzyme which does this is called _____________________. The other function of this enzyme is to bring in nucleotides to form the new mRNA molecule. In mRNA, the nitrogenous base ____________(____) is ...
Balancing Chemical Equations
... Introduction: Chemical equations show how compounds and elements react with one another. An element is a substance consisting of one kind of atom, such as aluminum (Al) or oxygen gas (O2). A compound is a substance made of more than one kind of atom, such as water (H2O) or table salt (NaCl). Questio ...
... Introduction: Chemical equations show how compounds and elements react with one another. An element is a substance consisting of one kind of atom, such as aluminum (Al) or oxygen gas (O2). A compound is a substance made of more than one kind of atom, such as water (H2O) or table salt (NaCl). Questio ...
Chapt 2-9 Practice Problem Answers
... c. Refer to the summary formula for photosynthesis. If you know the number of molecules or moles of any of the reactants used (or products produced), how would you calculate the number of molecules or moles of all of the other reactants needed and products produced? If the formula is balanced and i ...
... c. Refer to the summary formula for photosynthesis. If you know the number of molecules or moles of any of the reactants used (or products produced), how would you calculate the number of molecules or moles of all of the other reactants needed and products produced? If the formula is balanced and i ...
1 - M*W
... d) Have the same number of electrons 23) To draw a Lewis structure you do not need to know a) The number of valence electrons for each atom b) The types of atoms in the molecule c) The number of atoms in the molecule d) Bond energies 24) Neils Bohr’s contribution to modern atomic theory was the prop ...
... d) Have the same number of electrons 23) To draw a Lewis structure you do not need to know a) The number of valence electrons for each atom b) The types of atoms in the molecule c) The number of atoms in the molecule d) Bond energies 24) Neils Bohr’s contribution to modern atomic theory was the prop ...
stage 1 – desired results
... Transfer Goal(s): Understand the relationship of the macromolecules in their body. Understand how proper nutrition helps your body assemble the macromolecules for life. Understand that all life shares common structures and processes. ...
... Transfer Goal(s): Understand the relationship of the macromolecules in their body. Understand how proper nutrition helps your body assemble the macromolecules for life. Understand that all life shares common structures and processes. ...
Introduction to Chemistry for Coach Keith`s Biology
... Elements are pure substances which cannot be chemically broken down into simpler kinds of matter More than 100 elements have been identified, but only about 30 are important in living things All of the Elements are arranged on a chart known as the Periodic Table Periodic charts tell the atomic numbe ...
... Elements are pure substances which cannot be chemically broken down into simpler kinds of matter More than 100 elements have been identified, but only about 30 are important in living things All of the Elements are arranged on a chart known as the Periodic Table Periodic charts tell the atomic numbe ...
CHAPTER 6
... Brain has two remarkable metabolic features 1. very high respiratory metabolism 20 % of oxygen consumed is used by the brain ...
... Brain has two remarkable metabolic features 1. very high respiratory metabolism 20 % of oxygen consumed is used by the brain ...
41. Testing for enzymes
... It may be useful to discuss how to decide which reaction is fastest. Teachers should be sensitive to the needs of vegetarian students. Manganese dioxide, copper oxide and calcium carbonate can also be tested as catalysts to illustrate biological and chemical catalysts. Cooked liver (well done) can a ...
... It may be useful to discuss how to decide which reaction is fastest. Teachers should be sensitive to the needs of vegetarian students. Manganese dioxide, copper oxide and calcium carbonate can also be tested as catalysts to illustrate biological and chemical catalysts. Cooked liver (well done) can a ...
Biology Learning Targets Explained
... recent common ancestor are more closely related than those with an older common ancestor. ...
... recent common ancestor are more closely related than those with an older common ancestor. ...
05_GENE_EXPRESSION
... tRNA Short molecule about 25 000 Daltons Soluble At least 61 different forms each has a specific anticodon as part of its structure. tRNA “translates” the message on the mRNA into a polypeptide chain ...
... tRNA Short molecule about 25 000 Daltons Soluble At least 61 different forms each has a specific anticodon as part of its structure. tRNA “translates” the message on the mRNA into a polypeptide chain ...
Energy systems. - CCVI
... - increases the activity of enzymes (Krebs cycle) - preferential use of fats over glycogen during exercise ...
... - increases the activity of enzymes (Krebs cycle) - preferential use of fats over glycogen during exercise ...
Transcription Biology Review
... • All proteins interact weakly with DNA • Proteins with projecting amino acids interact with the DNA major groove • Hydrogen bonds stabilize position of proteins on DNA • Proteins that line up several amino acid contacts bind strongly to specific DNA sequences ...
... • All proteins interact weakly with DNA • Proteins with projecting amino acids interact with the DNA major groove • Hydrogen bonds stabilize position of proteins on DNA • Proteins that line up several amino acid contacts bind strongly to specific DNA sequences ...
3.2.1 What are Action Molecules?
... specific chemical reaction. Substrate: A substrate is a molecule that an enzyme bonds with in a reaction. Importance of Enzymes: Enzymes control the speed of chemical reaction in the body. They allow these react at speeds which are necessary for the body to function properly and stay alive. Also, ...
... specific chemical reaction. Substrate: A substrate is a molecule that an enzyme bonds with in a reaction. Importance of Enzymes: Enzymes control the speed of chemical reaction in the body. They allow these react at speeds which are necessary for the body to function properly and stay alive. Also, ...
ppt - UGA CAES - University of Georgia
... 2 - Amino acid inhibitors • essential building blocks for plant growth and function • unlike animals, plants make their own • amino acids are the primary components of proteins and nucleic acids • proteins are generally storage proteins or enzymes ...
... 2 - Amino acid inhibitors • essential building blocks for plant growth and function • unlike animals, plants make their own • amino acids are the primary components of proteins and nucleic acids • proteins are generally storage proteins or enzymes ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.