1 - JustAnswer
... 4. The process of breaking a complex substance down into smaller components is called A. neutralization. C. anabolism. B. metabolism. D. catabolism. 5. Amino acids that you obtain from eating foods are classified as A. essential. C. extracellular. B. facilitated. D. inorganic. 6. Combining a base an ...
... 4. The process of breaking a complex substance down into smaller components is called A. neutralization. C. anabolism. B. metabolism. D. catabolism. 5. Amino acids that you obtain from eating foods are classified as A. essential. C. extracellular. B. facilitated. D. inorganic. 6. Combining a base an ...
Krebs Cycle - 2008 BIOCHEM 201
... • Function of citric acid cycle is to oxidize organic molecules under aerobic conditions. • 8 reactions in the Krebs cycle • Pyruvate is degraded to CO2. • 1 GTP (ATP in bacteria) and 1 FADH2 are produced during one turn of the cycle. • 3 NADH are produced during one turn of the cycle. • NADH and FA ...
... • Function of citric acid cycle is to oxidize organic molecules under aerobic conditions. • 8 reactions in the Krebs cycle • Pyruvate is degraded to CO2. • 1 GTP (ATP in bacteria) and 1 FADH2 are produced during one turn of the cycle. • 3 NADH are produced during one turn of the cycle. • NADH and FA ...
Protein Structure Predictions 2
... Statistics – composition of amino acids Neural networks – patterns of amino acids ...
... Statistics – composition of amino acids Neural networks – patterns of amino acids ...
SCIENCE REVIEW Your task is to make a flashcard for
... 55. This type of tree has leaves that change colors in the fall: deciduous trees 56. This type of tree produces seeds in cones and do not lose their leaves in autumn: coniferous trees 57. Deciduous trees are able to conserve water in winter by: losing their leaves 58. Coniferous trees are able to co ...
... 55. This type of tree has leaves that change colors in the fall: deciduous trees 56. This type of tree produces seeds in cones and do not lose their leaves in autumn: coniferous trees 57. Deciduous trees are able to conserve water in winter by: losing their leaves 58. Coniferous trees are able to co ...
A sweet trick for fighting infection
... “tremendous success” but notes there could be room to improve further too. In some cases where the native bacterial structure can’t be used a synthetic structure produced in a chemistry lab is an attractive alternative. And it’s not just bacteria he has in his sights: he is also looking at how cleve ...
... “tremendous success” but notes there could be room to improve further too. In some cases where the native bacterial structure can’t be used a synthetic structure produced in a chemistry lab is an attractive alternative. And it’s not just bacteria he has in his sights: he is also looking at how cleve ...
Introduction to Protein Folding and Molecular Simulation
... If 100 psec (10-10 sec) were required to convert from a conformation to another one, a random search of all conformations would require 5 x 1047 x 10-10 sec ≒ 1.6 x 1030 years. However, folding of proteins takes place in msec to sec order. Therefore, proteins fold not via a random search but a more ...
... If 100 psec (10-10 sec) were required to convert from a conformation to another one, a random search of all conformations would require 5 x 1047 x 10-10 sec ≒ 1.6 x 1030 years. However, folding of proteins takes place in msec to sec order. Therefore, proteins fold not via a random search but a more ...
Microbiology
... Group translocation of substances requires a transporter protein and PEP (phosphoenol pyruvate) as an energy source. ...
... Group translocation of substances requires a transporter protein and PEP (phosphoenol pyruvate) as an energy source. ...
Lab 11
... – State a hypothesis (an “if then” statement, may require multiple sentences) that is clear and appropriately addresses the purpose of this laboratory exercise. ...
... – State a hypothesis (an “if then” statement, may require multiple sentences) that is clear and appropriately addresses the purpose of this laboratory exercise. ...
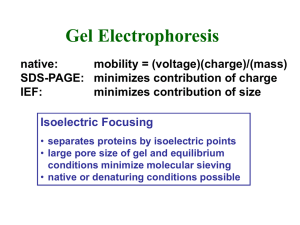
No Slide Title
... • separates proteins by isoelectric points • large pore size of gel and equilibrium conditions minimize molecular sieving • native or denaturing conditions possible ...
... • separates proteins by isoelectric points • large pore size of gel and equilibrium conditions minimize molecular sieving • native or denaturing conditions possible ...
Use of Amino Acid-Nucleotide Base Pair Potentials in Screening
... processes involving gene expression, DNA replication and repair [1]. Since DNA play very important roles in cells, they are molecular targets of many clinically used drugs, such as anticancer drugs and antibiotics [2]. Study on the protein-DNA interactions would be meaningful for drugs design on the ...
... processes involving gene expression, DNA replication and repair [1]. Since DNA play very important roles in cells, they are molecular targets of many clinically used drugs, such as anticancer drugs and antibiotics [2]. Study on the protein-DNA interactions would be meaningful for drugs design on the ...
Name three amino acids that are typically found at the
... result in a higher number of correctly modified clones after transformation of the host cell than a plasmid constructed with only EcoR1, although both plasmids are positively selected by ampicillin and the reporter gene? ...
... result in a higher number of correctly modified clones after transformation of the host cell than a plasmid constructed with only EcoR1, although both plasmids are positively selected by ampicillin and the reporter gene? ...
ch9 ppt outline
... In Cellular Respiration, cells turn C6H12O6 + O2 into CO2 + H20 molecules and produce energy in the form of _________ . ATP (Adenosine TriPhosphate),is the main energy source for cell processes. Q4. GIVE A SPECIFIC EXAMPLE OF A CELLULAR PROCESS THAT USE ATP. TRANSFERING ENERGY -How is energy release ...
... In Cellular Respiration, cells turn C6H12O6 + O2 into CO2 + H20 molecules and produce energy in the form of _________ . ATP (Adenosine TriPhosphate),is the main energy source for cell processes. Q4. GIVE A SPECIFIC EXAMPLE OF A CELLULAR PROCESS THAT USE ATP. TRANSFERING ENERGY -How is energy release ...
Energy systems.
... - increases the activity of enzymes (Krebs cycle) - preferential use of fats over glycogen during exercise ...
... - increases the activity of enzymes (Krebs cycle) - preferential use of fats over glycogen during exercise ...
BI0 120 cell and tissues
... E. All of these. 59. Saturated fatty acids store more energy than unsaturated fatty acids. Based on your knowledge of aerobic respiration, you draw this conclusion because saturated fatty acids: A. are more highly reduced. B. are deaminated. C. lack phosphate. D. contain more ester linkages. E. cont ...
... E. All of these. 59. Saturated fatty acids store more energy than unsaturated fatty acids. Based on your knowledge of aerobic respiration, you draw this conclusion because saturated fatty acids: A. are more highly reduced. B. are deaminated. C. lack phosphate. D. contain more ester linkages. E. cont ...
Distance
... A specific subclass is the -turn, a region of the polypeptide of 4 amino acids (i, i+1, i+2, i+3) having a hydrogen bond from O(i) to N(i+3). -turns can be classified into several subclasses based on the and angles of residues i+1 and i+2. Most common turn types: Type I and Type II. ...
... A specific subclass is the -turn, a region of the polypeptide of 4 amino acids (i, i+1, i+2, i+3) having a hydrogen bond from O(i) to N(i+3). -turns can be classified into several subclasses based on the and angles of residues i+1 and i+2. Most common turn types: Type I and Type II. ...
Tyrocidine Biosynthesis by Three Complementary Fractions from
... where the second and third phenylalanines may be replaced by a corresponding tryptophan, and tyrosine by phenylalanine or tryptophan. An enzyme system prepared from Bacillus brevis (ATCC 8185), active in tyrocidine biosynthesis, was resolved into three complementary fractions ...
... where the second and third phenylalanines may be replaced by a corresponding tryptophan, and tyrosine by phenylalanine or tryptophan. An enzyme system prepared from Bacillus brevis (ATCC 8185), active in tyrocidine biosynthesis, was resolved into three complementary fractions ...
Name Date__________________ DNA and Protein Synthesis
... 3-If instead of ACT, the first DNA triplet was ACG, which amino acid would be coded for? 4-What amino acid is carried by a tRNA with the anticodon, GUA? 5-Sickle cell anemia is a disease of red blood cells in which a genetic mutation in DNA leads to a mutation in hemoglobin. A single base change alt ...
... 3-If instead of ACT, the first DNA triplet was ACG, which amino acid would be coded for? 4-What amino acid is carried by a tRNA with the anticodon, GUA? 5-Sickle cell anemia is a disease of red blood cells in which a genetic mutation in DNA leads to a mutation in hemoglobin. A single base change alt ...
Exam 4 key fall 2010
... Without oxygen electron transport would shut down and NADH and FADH2 could not be reoxidized and all of metabolism would halt. ...
... Without oxygen electron transport would shut down and NADH and FADH2 could not be reoxidized and all of metabolism would halt. ...
LB145-lecture1
... Integrating Questions (set #4) 8. Table 1.1 highlights the nitrogen to phosphorous ratio (N/P) of the transforming material. Determine the N/P ratios for the five amino acids and four nucleotides shown in Figure 1.5. Why was the N/P ratio so important to Avery’s interpretation of their data? 9. Add ...
... Integrating Questions (set #4) 8. Table 1.1 highlights the nitrogen to phosphorous ratio (N/P) of the transforming material. Determine the N/P ratios for the five amino acids and four nucleotides shown in Figure 1.5. Why was the N/P ratio so important to Avery’s interpretation of their data? 9. Add ...
50695_1 - Griffith Research Online
... protein folding problem has been heavily sought after is due to their importance. Proteins carry out all of the main functionality within an organism on a cellular level. For example, red blood cells contain a protein known as the hemoglobin. This protein carries out the functionality of carrying ox ...
... protein folding problem has been heavily sought after is due to their importance. Proteins carry out all of the main functionality within an organism on a cellular level. For example, red blood cells contain a protein known as the hemoglobin. This protein carries out the functionality of carrying ox ...
Secondary Structures and Properties of Fibrous Proteins
... how the amino acid side chains tightly fill in the surface clefts. ...
... how the amino acid side chains tightly fill in the surface clefts. ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.