Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation
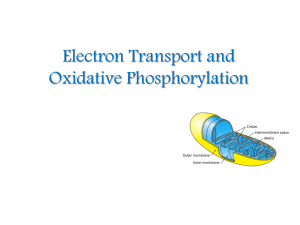
... The inner mitochondrial membrane contains 5 separate enzyme complexes, called compelexes I, II, III, IV and V. Each complex accepts or donates electrons to mobile carrier, such as coenzyme Q and cytochrome c. The electrons ultimately combine with oxygen and protons to form water. ...
... The inner mitochondrial membrane contains 5 separate enzyme complexes, called compelexes I, II, III, IV and V. Each complex accepts or donates electrons to mobile carrier, such as coenzyme Q and cytochrome c. The electrons ultimately combine with oxygen and protons to form water. ...
Alcohol Metabolism
... Acetyl CoA fatty acid synthesis FAs accumulate in the liver Once the liver is congested with fat: Decreased efficiency of hepatocytes Decreased conversion of vitamin D to active form Decreased gluconeogenesis Decreased glu & increased acetyl CoA ketosis (acidic) Accumulation of NADH + ...
... Acetyl CoA fatty acid synthesis FAs accumulate in the liver Once the liver is congested with fat: Decreased efficiency of hepatocytes Decreased conversion of vitamin D to active form Decreased gluconeogenesis Decreased glu & increased acetyl CoA ketosis (acidic) Accumulation of NADH + ...
Measurement of Diabetes-Predictive Amino Acids from Dried Blood
... diabetes could be predicted up to 12 years prior to disease onset by measuring relative levels of 5 amino acids (Ile, Leu, Val, Tyr, and Phe) in plasma. As this method could prove to be a powerful diagnostic screening test for early detection and prevention of diabetes, we determined whether these r ...
... diabetes could be predicted up to 12 years prior to disease onset by measuring relative levels of 5 amino acids (Ile, Leu, Val, Tyr, and Phe) in plasma. As this method could prove to be a powerful diagnostic screening test for early detection and prevention of diabetes, we determined whether these r ...
The Characteristics of Life
... These traits are passed on through DNA. Every organism we know of in the world uses DNA to pass on it’s genetic code. ...
... These traits are passed on through DNA. Every organism we know of in the world uses DNA to pass on it’s genetic code. ...
TCA Cycle
... A dark-colored, mitochondrionrich adipose tissue in many mammals that generates heat (not energy) to regulate body temperature, especially in hibernating animals. ...
... A dark-colored, mitochondrionrich adipose tissue in many mammals that generates heat (not energy) to regulate body temperature, especially in hibernating animals. ...
honors final key
... a. 4.58 mol to particles of Al = 2.76x1024 b. 4.58 mol to grams of Al = 124g c. 901.49 g to particles of Carbon dioxide = 1.23x 1025 d. 901.49 g to L of carbon dioxide = 458.9 18. Define molar mass. The mass of a mole of a substance, equal to the atomic mass in grams 19. Give molar mass of a. Vanadi ...
... a. 4.58 mol to particles of Al = 2.76x1024 b. 4.58 mol to grams of Al = 124g c. 901.49 g to particles of Carbon dioxide = 1.23x 1025 d. 901.49 g to L of carbon dioxide = 458.9 18. Define molar mass. The mass of a mole of a substance, equal to the atomic mass in grams 19. Give molar mass of a. Vanadi ...
Biochemistry_practice_test
... 6. Inhibitory synapses most often involve which of the following channels? A. Cl- channels B. Na+ channels C. Ca2+ channels D. K+ channels E. H+ channels 7. A person deficient in vitamin B12 might also be deficient in which of the following? A. coenzyme B. cofactor C. substrate D. alpha helix 8. The ...
... 6. Inhibitory synapses most often involve which of the following channels? A. Cl- channels B. Na+ channels C. Ca2+ channels D. K+ channels E. H+ channels 7. A person deficient in vitamin B12 might also be deficient in which of the following? A. coenzyme B. cofactor C. substrate D. alpha helix 8. The ...
Slide 1 - pharmaHUB
... Characteristic of functional groups such as -O-H, -CH3, -COCH3, and COOH. Determined empirically by studying the spectra of many related molecules. Always found in the spectrum of a molecule containing that group, and always occurs in the same narrow frequency range. The form of the bands is ...
... Characteristic of functional groups such as -O-H, -CH3, -COCH3, and COOH. Determined empirically by studying the spectra of many related molecules. Always found in the spectrum of a molecule containing that group, and always occurs in the same narrow frequency range. The form of the bands is ...
Directional mutational pressure affects the amino acid composition
... taken away by this approach (Harvey & Pagel, 1991). Therefore, in our study, only one sequence from the same genus is used and the coefficient of correlation is denoted as rg . Furthermore, we will show that deletion of relatively closely related genera has little effect on or may even increase the ...
... taken away by this approach (Harvey & Pagel, 1991). Therefore, in our study, only one sequence from the same genus is used and the coefficient of correlation is denoted as rg . Furthermore, we will show that deletion of relatively closely related genera has little effect on or may even increase the ...
(a) Electrons
... • Water is the only common substance to exist in the natural environment in all three physical states of matter. • The structure of the water molecule allows it to interact with other molecules and this was true in the beginning when other molecules would around and interact. • Water’s unique emerge ...
... • Water is the only common substance to exist in the natural environment in all three physical states of matter. • The structure of the water molecule allows it to interact with other molecules and this was true in the beginning when other molecules would around and interact. • Water’s unique emerge ...
Biology Summary
... the body uses reserves of stem cells to replace worn-out or damaged cells mainly found in bone barrow, blood, muscle tissue, lining of digestive tract, brain, and retina of the eye ...
... the body uses reserves of stem cells to replace worn-out or damaged cells mainly found in bone barrow, blood, muscle tissue, lining of digestive tract, brain, and retina of the eye ...
Biological Themes Biology: the science of living organisms and the
... Development: the process by which an organism grows Unicellular vs. Multicellular Development Structure and Function Morphology: the internal and external appearance of an organism Anatomy = Internal Morphology STRUCTURE DETERMINES FUNCTION Energy Relationships All orga ...
... Development: the process by which an organism grows Unicellular vs. Multicellular Development Structure and Function Morphology: the internal and external appearance of an organism Anatomy = Internal Morphology STRUCTURE DETERMINES FUNCTION Energy Relationships All orga ...
very new glucogen me..
... Glycogen storage disease: there are group of inherited disorder cause deposition of abnormal quantity of glycogen in tissues lead to deficiency of glucose-6-phosphatase like. ...
... Glycogen storage disease: there are group of inherited disorder cause deposition of abnormal quantity of glycogen in tissues lead to deficiency of glucose-6-phosphatase like. ...
Regulation of Glycolysis
... Because the principle function of glycolysis is to produce ATP, it must be regulated so that ATP is generated only when needed. The enzyme which controls the flux of metabolites through the glycolytic pathway is phosphofructokinase (PFK-1). PFK-1 is an allosteric enzyme that occupies the key regulat ...
... Because the principle function of glycolysis is to produce ATP, it must be regulated so that ATP is generated only when needed. The enzyme which controls the flux of metabolites through the glycolytic pathway is phosphofructokinase (PFK-1). PFK-1 is an allosteric enzyme that occupies the key regulat ...
Carbohydrate Catabolism Cellular Respiration
... – Any spoilage of food by microorganisms – Any process that produces alcoholic beverages or acidic dairy products – Scientific definition: – Releases energy from oxidation of organic molecules – Does not require oxygen – Does not use the Krebs cycle or ETC – Uses an organic molecule as the final ele ...
... – Any spoilage of food by microorganisms – Any process that produces alcoholic beverages or acidic dairy products – Scientific definition: – Releases energy from oxidation of organic molecules – Does not require oxygen – Does not use the Krebs cycle or ETC – Uses an organic molecule as the final ele ...
PASS MOCK EXAM
... Facilitators do not bring copies of the mock exam to the session. Please print out and complete the exam before you attend. ...
... Facilitators do not bring copies of the mock exam to the session. Please print out and complete the exam before you attend. ...
Cellular Metabolism - Napa Valley College
... 3. The ETC uses the energy from the electrons to transport H+ against the concentration gradient, transporting them from the lumen of the mitochondria to the intermembrane space. ...
... 3. The ETC uses the energy from the electrons to transport H+ against the concentration gradient, transporting them from the lumen of the mitochondria to the intermembrane space. ...
Cellular Respiration
... • Glycolysis occurs in nearly all organisms • Glycolysis probably evolved in ancient prokaryotes before O2 on planet ...
... • Glycolysis occurs in nearly all organisms • Glycolysis probably evolved in ancient prokaryotes before O2 on planet ...
Cells - Part 2 Nucleus
... Complementary base pairing with anticodons (tRNA) provides the amino acids in the correct sequence! " "A is complementary to U! " "C is complementary to G! ...
... Complementary base pairing with anticodons (tRNA) provides the amino acids in the correct sequence! " "A is complementary to U! " "C is complementary to G! ...
File
... • In protein production there are codons that will indicate to the ribosome when to start and when to end. • Once the chain of up to several hundreds of amino acids is completed, the process stops and the protein gets sent to the endoplasmic reticulum to be packed and released. • The order of amino ...
... • In protein production there are codons that will indicate to the ribosome when to start and when to end. • Once the chain of up to several hundreds of amino acids is completed, the process stops and the protein gets sent to the endoplasmic reticulum to be packed and released. • The order of amino ...
Chapter 6 PowerPoint
... – 200 molecules of carbonic acid per hour made without enzyme – 600,000 molecules formed per second with enzyme ...
... – 200 molecules of carbonic acid per hour made without enzyme – 600,000 molecules formed per second with enzyme ...
Chapter 16 The Citric Acid Cycle
... cycle (TCA) which enzymatically oxidized them to CO2 and the energy released is conserved in NADH and FADH2 ─ These reduced coenzymes are themselves oxidized, giving up protons and electrons (eare transferred to O2) ...
... cycle (TCA) which enzymatically oxidized them to CO2 and the energy released is conserved in NADH and FADH2 ─ These reduced coenzymes are themselves oxidized, giving up protons and electrons (eare transferred to O2) ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.























