md 2 bbq
... has no other malformations and is otherwise healthy. He has no family history of birth defects. His parents are not related. Which of the following genetic mechanisms is most likely to have caused these congenital abnormalities? • Autosomal dominant inheritance • Autosomal recessive inheritance • Ch ...
... has no other malformations and is otherwise healthy. He has no family history of birth defects. His parents are not related. Which of the following genetic mechanisms is most likely to have caused these congenital abnormalities? • Autosomal dominant inheritance • Autosomal recessive inheritance • Ch ...
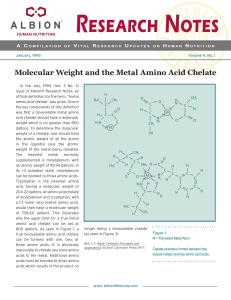
Molecular Weight and the Metal Amino Acid Chelate
... products are formed from metal salts and hydrolyzed protein or amino acids from hydrolyzed protein. The ability to interchange words like hydrolyzed protein or amino acids from hydrolyzed protein has lead to a wide disparity as to what those suppliers call “metal amino acid chelates.” Hydrolyzed pro ...
... products are formed from metal salts and hydrolyzed protein or amino acids from hydrolyzed protein. The ability to interchange words like hydrolyzed protein or amino acids from hydrolyzed protein has lead to a wide disparity as to what those suppliers call “metal amino acid chelates.” Hydrolyzed pro ...
Key Unit 3 (Cell membrane)
... 8. The concentration of a solution outside the cell is the same as inside the cell, thus there is no net movement of molecules. This is known as a _isotonic____ solution. 9. In the cell membrane, where are the fatty acid tails of phospholipid molecules located? Inside (away from the water) 10. How d ...
... 8. The concentration of a solution outside the cell is the same as inside the cell, thus there is no net movement of molecules. This is known as a _isotonic____ solution. 9. In the cell membrane, where are the fatty acid tails of phospholipid molecules located? Inside (away from the water) 10. How d ...
8_3bio
... • Two of the twelve 3-carbon molecules are removed from the cycle. The plant cell uses these molecules to produce sugars, lipids, amino acids, and other compounds needed for plant metabolism and growth. ...
... • Two of the twelve 3-carbon molecules are removed from the cycle. The plant cell uses these molecules to produce sugars, lipids, amino acids, and other compounds needed for plant metabolism and growth. ...
Graph 1: Rabbits Over Time
... Fish might die at some point – living systems cannot handle too much increase in T. 6. Why would it be a bad idea to do this? Death of fish 1.03 Formulate and revise scientific explanations and models of biological phenomena using logic and evidence to: explain observations, make inferences and pred ...
... Fish might die at some point – living systems cannot handle too much increase in T. 6. Why would it be a bad idea to do this? Death of fish 1.03 Formulate and revise scientific explanations and models of biological phenomena using logic and evidence to: explain observations, make inferences and pred ...
Hormones in intermediary metabolism
... Thyroid hormones actions • ↑ protein synthesis, but ↑↑ protein catabolism – result is proteocatabolic • Increased breakdown of muscle proteins • Stimulation of synthesis: Na+/K+ pump, respiratory chain enzymes, ... • The pro-growth importance: T3 and T4 support metabolism, which is necessary for pr ...
... Thyroid hormones actions • ↑ protein synthesis, but ↑↑ protein catabolism – result is proteocatabolic • Increased breakdown of muscle proteins • Stimulation of synthesis: Na+/K+ pump, respiratory chain enzymes, ... • The pro-growth importance: T3 and T4 support metabolism, which is necessary for pr ...
Enzymes
... Several enzymes can work together in a specific order, creating metabolic pathways. In a metabolic pathway, one enzyme takes the product of another enzyme as a substrate. After the catalytic reaction, the product is then passed on to another enzyme. Sometimes more than one enzyme can catalyze the sa ...
... Several enzymes can work together in a specific order, creating metabolic pathways. In a metabolic pathway, one enzyme takes the product of another enzyme as a substrate. After the catalytic reaction, the product is then passed on to another enzyme. Sometimes more than one enzyme can catalyze the sa ...
Cell Transport 2016 - Waterford Public Schools
... a.Phosphate head is polar (water loving)= hydrophilic b.Fatty acid tails non-polar (water fearing)= hydrophobic Fluid Mosaic Model The phospholipids are not attached. They float next to each other ...
... a.Phosphate head is polar (water loving)= hydrophilic b.Fatty acid tails non-polar (water fearing)= hydrophobic Fluid Mosaic Model The phospholipids are not attached. They float next to each other ...
Slides
... from a computational viewpoint They are large molecules (few 100s to several 1000s of atoms) They are made of building blocks (amino acids) drawn from a small “library” of 20 amino-acids They have an unusual kinematic structure: long serial linkage (backbone) with short side-chains ...
... from a computational viewpoint They are large molecules (few 100s to several 1000s of atoms) They are made of building blocks (amino acids) drawn from a small “library” of 20 amino-acids They have an unusual kinematic structure: long serial linkage (backbone) with short side-chains ...
Document
... structure through coaxial stacking of the helices, which is a common RNA Tertiary Structure motif. The 5'terminal phosphate group. The acceptor stem is a 7base pair stem made by the base pairing of the 5'terminal nucleotide with the 3'-terminal nucleotide (which contains the CCA 3'-terminal group us ...
... structure through coaxial stacking of the helices, which is a common RNA Tertiary Structure motif. The 5'terminal phosphate group. The acceptor stem is a 7base pair stem made by the base pairing of the 5'terminal nucleotide with the 3'-terminal nucleotide (which contains the CCA 3'-terminal group us ...
PP - Columbia University
... • So when calulating Go, instead of writing in “55” when water participates in a reaction (e.g., a hydrolysis) we write “1.” • This is not cheating; we are in charge of what is a “standard” condition, and we all agree to this: 55 M H20 is unit (“1”) concentration for the purpose of defining Go. ...
... • So when calulating Go, instead of writing in “55” when water participates in a reaction (e.g., a hydrolysis) we write “1.” • This is not cheating; we are in charge of what is a “standard” condition, and we all agree to this: 55 M H20 is unit (“1”) concentration for the purpose of defining Go. ...
can be determined without changing the identity of matter
... Conservation of mass - During any chemical or physical process, the overall amount of mass remains constant, even if the chemical identity or physical state of the matter involved ...
... Conservation of mass - During any chemical or physical process, the overall amount of mass remains constant, even if the chemical identity or physical state of the matter involved ...
Enzymes
... Enzyme Activity Factors 3) Enzyme concentration – Enzymes are not used up during reactions – Can work effectively at low concentrations ...
... Enzyme Activity Factors 3) Enzyme concentration – Enzymes are not used up during reactions – Can work effectively at low concentrations ...
File - Mr. Downing Science 10
... animal cells. – plants have cells walls – plants store energy as starches and oils, animals as glycogen or fats – plant cells have a large central vacuole – animal cells have more mitochondria because their energy needs are higher – Plant cells have chloroplasts & chlorophyll ...
... animal cells. – plants have cells walls – plants store energy as starches and oils, animals as glycogen or fats – plant cells have a large central vacuole – animal cells have more mitochondria because their energy needs are higher – Plant cells have chloroplasts & chlorophyll ...
Production of Materials by Jimmy Huang
... dissolve polar substances due to the powerful hydrogen bonding. For these properties, ethanol is widely used in cosmetics, food colouring, antiseptics and cleaning agents. Ethanol As A Renewable Resource and a Fuel Ethanol is a liquid and burns readily, and has therefore been proposed as an alternat ...
... dissolve polar substances due to the powerful hydrogen bonding. For these properties, ethanol is widely used in cosmetics, food colouring, antiseptics and cleaning agents. Ethanol As A Renewable Resource and a Fuel Ethanol is a liquid and burns readily, and has therefore been proposed as an alternat ...
2009-10 Chemistry 1st Semester Final Exam Topics and Review
... Metric system Significant Figures Dimensional Analysis Density Physical and Chemical properties, Physical and chemical changes Matter- elements and compounds, mixtures and pure substances Elements, atoms, atomic structure- parts, location, charges, and masses. For any atom, ion, or isotope be able t ...
... Metric system Significant Figures Dimensional Analysis Density Physical and Chemical properties, Physical and chemical changes Matter- elements and compounds, mixtures and pure substances Elements, atoms, atomic structure- parts, location, charges, and masses. For any atom, ion, or isotope be able t ...
Gelatinization of Starch
... enantiomer is one of two stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other, non-superposable. ...
... enantiomer is one of two stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other, non-superposable. ...
Chapter6summaryHO
... Anabolism takes the ATP and precursors to make cell components (also uses nutrients, nitrogen, sulfur, iron, phosphate, to incorporate into the parts of the cell) Precursor metabolites are carbon skeletons used to make other compounds. Example: Glucose to Pyruvate then made into amino acids. There a ...
... Anabolism takes the ATP and precursors to make cell components (also uses nutrients, nitrogen, sulfur, iron, phosphate, to incorporate into the parts of the cell) Precursor metabolites are carbon skeletons used to make other compounds. Example: Glucose to Pyruvate then made into amino acids. There a ...
Setting the stage
... Infrared spectroscopy utilized in chemical simulations of reactions on interstellar ices. Various studies have been performed on amphiphilic vesicle forming molecules. ...
... Infrared spectroscopy utilized in chemical simulations of reactions on interstellar ices. Various studies have been performed on amphiphilic vesicle forming molecules. ...
Conductivity of Solutions
... acid usually ionize less than 5% of the time. Many of these weaker acids are “organic” acids that contain a “carboxyl” group. ...
... acid usually ionize less than 5% of the time. Many of these weaker acids are “organic” acids that contain a “carboxyl” group. ...
Practical Proteins and Amino Acids` Identification
... Biuret’s test Principle: Biuret test is Specific for Proteins – To differentiate between Proteins (+ve) and Amino Acids (-ve). The biuret reagent (copper sulfate in a strong base) reacts with peptide bonds in proteins to form a violet complex known as the “Biuret complex”. Two peptide bonds are at ...
... Biuret’s test Principle: Biuret test is Specific for Proteins – To differentiate between Proteins (+ve) and Amino Acids (-ve). The biuret reagent (copper sulfate in a strong base) reacts with peptide bonds in proteins to form a violet complex known as the “Biuret complex”. Two peptide bonds are at ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.