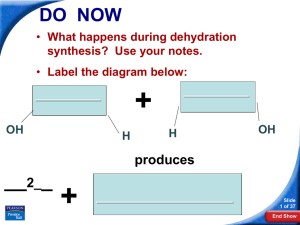
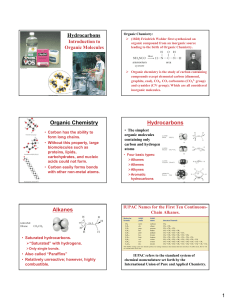
Overview of the Origin of Life
... swirling mass of gas and dust • The planets are thought to have formed from violent collisions of space debris. • The age of earth is approx. 4 billion years ...
... swirling mass of gas and dust • The planets are thought to have formed from violent collisions of space debris. • The age of earth is approx. 4 billion years ...
Nadine Noelting
... Eukaryotic phenylalanine-4-hydroxylase (eu_PheOH); a member of the biopterindependent aromatic amino acid hydroxylase family of non-heme, iron(II)-dependent enzymes that also includes prokaryotic phenylalanine-4-hydroxylase (pro_PheOH), eukaryotic tyrosine hydroxylase (TyrOH) and eukaryotic tryptoph ...
... Eukaryotic phenylalanine-4-hydroxylase (eu_PheOH); a member of the biopterindependent aromatic amino acid hydroxylase family of non-heme, iron(II)-dependent enzymes that also includes prokaryotic phenylalanine-4-hydroxylase (pro_PheOH), eukaryotic tyrosine hydroxylase (TyrOH) and eukaryotic tryptoph ...
Cellular Respiration
... In a general sense, fermentation is the conversion of a carbohydrate such as sugar into an acid or an alcohol. More specifically, fermentation can refer to the use of yeast to change sugar into alcohol or the use of bacteria to create lactic acid in certain foods. Fermentation occurs naturally in ma ...
... In a general sense, fermentation is the conversion of a carbohydrate such as sugar into an acid or an alcohol. More specifically, fermentation can refer to the use of yeast to change sugar into alcohol or the use of bacteria to create lactic acid in certain foods. Fermentation occurs naturally in ma ...
Biology Top 101 - Magnolia High School
... Proteins • Monomer- amino acids • Function- building and repairing cells, communication, transport, and regulation • Tests- Biurets • Examples: enzymes, ...
... Proteins • Monomer- amino acids • Function- building and repairing cells, communication, transport, and regulation • Tests- Biurets • Examples: enzymes, ...
Respiratory Levels of Organization
... capillary and red blood cell membrane some carbon dioxide is picked up hemoglobin by molecules inside the red blood cell. Inside the cells of the body tissues, oxygen will be used during the process of aerobic cellular respiration. Cellular respiration is a process used by our cells to convert nutri ...
... capillary and red blood cell membrane some carbon dioxide is picked up hemoglobin by molecules inside the red blood cell. Inside the cells of the body tissues, oxygen will be used during the process of aerobic cellular respiration. Cellular respiration is a process used by our cells to convert nutri ...
Life Processes - 1
... converts it into maltose. Lipase acts on fat and converts it into fatty acids and glycerol. Pancreatic lipase is the main fat digesting enzyme in our body. Q2. Write the importance of photosynthesis to the biosphere. Ans2. Photosynthesis is the only process through which energy enters the biosphere ...
... converts it into maltose. Lipase acts on fat and converts it into fatty acids and glycerol. Pancreatic lipase is the main fat digesting enzyme in our body. Q2. Write the importance of photosynthesis to the biosphere. Ans2. Photosynthesis is the only process through which energy enters the biosphere ...
Cell Communication
... Within multicellular organisms, cells must communicate with one another to coordinate their activities A signal transduction pathway is a series of steps by which a signal on a cell’s surface is converted into a specific cellular response Signal transduction pathways are very similar in all or ...
... Within multicellular organisms, cells must communicate with one another to coordinate their activities A signal transduction pathway is a series of steps by which a signal on a cell’s surface is converted into a specific cellular response Signal transduction pathways are very similar in all or ...
CH 11 Study Guide: DNA, RNA, and Proteins
... mRNA: carries the DNA message from the nucleus to the cytoplasm (to the ribosome) rRNA: forms the ribosome tRNA: carries amino acids to the ribosome so that proteins can be made 5. Who discovered the structure of DNA? Watson & Crick 6. IF a sequence of codons on a DNA strand is AAC TAG GGT, what is ...
... mRNA: carries the DNA message from the nucleus to the cytoplasm (to the ribosome) rRNA: forms the ribosome tRNA: carries amino acids to the ribosome so that proteins can be made 5. Who discovered the structure of DNA? Watson & Crick 6. IF a sequence of codons on a DNA strand is AAC TAG GGT, what is ...
Document
... system because it occurs universally d. Glycolysis is considered to be an ancient metabolic system because it is the most efficient metabolic pathway for ATP synthesis ...
... system because it occurs universally d. Glycolysis is considered to be an ancient metabolic system because it is the most efficient metabolic pathway for ATP synthesis ...
WHAT IS PHOTOSYNTHESIS?
... WHAT IS PHOTOSYNTHESIS? Life on Earth is held primarily by the energy from the sun that is harnessed through photosynthesis that takes place in the chloroplasts of algae in the aquatic environment, primarily in the ocean and in terrestrial plants. ...
... WHAT IS PHOTOSYNTHESIS? Life on Earth is held primarily by the energy from the sun that is harnessed through photosynthesis that takes place in the chloroplasts of algae in the aquatic environment, primarily in the ocean and in terrestrial plants. ...
PART 1: TRUE OR FALSE (1 point each)
... 1. Both amino acids and sugars are linked into macromolecules via condensation reactions, in which a molecule of water is generated. 2. In living organisms, the majority of proteins found exist in only one isomeric form. 3. Within a single protein, both alpha helices and beta sheets can be present. ...
... 1. Both amino acids and sugars are linked into macromolecules via condensation reactions, in which a molecule of water is generated. 2. In living organisms, the majority of proteins found exist in only one isomeric form. 3. Within a single protein, both alpha helices and beta sheets can be present. ...
Carbohydrate Metabolism Glucose Metabolism Oxidation of Glucose
... 1. Hexokinase has high affinity for glucose ( Km ≈ 0.04 mM ) . Since the resting level for blood glucose is about 5mM , therefore hexokinase would be expected to be fully active for all body cells at the resting level and the liver would not be competing with other cells for glucose . On the other h ...
... 1. Hexokinase has high affinity for glucose ( Km ≈ 0.04 mM ) . Since the resting level for blood glucose is about 5mM , therefore hexokinase would be expected to be fully active for all body cells at the resting level and the liver would not be competing with other cells for glucose . On the other h ...
File
... Many lipids are formed from glycerol and a. fatty acids. b. monosaccharides. c. amino acids. ...
... Many lipids are formed from glycerol and a. fatty acids. b. monosaccharides. c. amino acids. ...
Replication, Transcription, and Translation
... instructions as the cells that preceded it. This also insures that every new generation of individuals has the same ...
... instructions as the cells that preceded it. This also insures that every new generation of individuals has the same ...
Advanced Biology
... process of conducting science and the scientific method. Students will develop and understanding of the basic principles of biochemistry, cell structure and function, cell metabolism (photosynthesis and respiration), and genetics. Students are expected to be able to apply concepts to solve problems. ...
... process of conducting science and the scientific method. Students will develop and understanding of the basic principles of biochemistry, cell structure and function, cell metabolism (photosynthesis and respiration), and genetics. Students are expected to be able to apply concepts to solve problems. ...
D. E. Shaw Research is seeking postdoctoral fellows of exceptional... Postdoctoral Fellowships at D. E. Shaw Research
... physics, or in a relevant area of computer science or applied mathematics. Relevant areas of experience might include the study of allosteric interactions or other functionally important conformational changes in biological molecules, structure prediction or design for proteins or RNA, the study of ...
... physics, or in a relevant area of computer science or applied mathematics. Relevant areas of experience might include the study of allosteric interactions or other functionally important conformational changes in biological molecules, structure prediction or design for proteins or RNA, the study of ...
3+4 - Using Other Fuels
... • Small stores in muscle cells • Large stores in subcutaneous adipose tissue (body fat) • Triglycerides are broken down into FAs and Glycerol • These go through process of Beta-Oxidation • This produces a molecule that can enter Krebs Cycle. 5 mins to find out why Fats provide more enrgy than Glycog ...
... • Small stores in muscle cells • Large stores in subcutaneous adipose tissue (body fat) • Triglycerides are broken down into FAs and Glycerol • These go through process of Beta-Oxidation • This produces a molecule that can enter Krebs Cycle. 5 mins to find out why Fats provide more enrgy than Glycog ...
Protein Synthesis
... (Transcription) • Then, decode those DNA instructions (now in the form of mRNA) to construct correct amino acids into a protein. (Translation) ...
... (Transcription) • Then, decode those DNA instructions (now in the form of mRNA) to construct correct amino acids into a protein. (Translation) ...
Biology
... a. plants make polysaccharides, while animals make proteins. b. proteins are made of monomers, while polysaccharides are not. c. polysaccharides are made of monosaccharides, while proteins are made of amino acids. ...
... a. plants make polysaccharides, while animals make proteins. b. proteins are made of monomers, while polysaccharides are not. c. polysaccharides are made of monosaccharides, while proteins are made of amino acids. ...
CAÑIHUA (Chenopodium pallidicaule) Origin Highlands
... Highlands of Peru and Bolivia. History It was domesticated by the settlers of Tiahuanaco (pre-Incan culture). Nutrients/Main compounds High content of protein. Essential amino acids (lysine, isoleucine and tryptophan). Source of vitamin Bcomplex and essential minerals: iron, magnesium, zinc, seleniu ...
... Highlands of Peru and Bolivia. History It was domesticated by the settlers of Tiahuanaco (pre-Incan culture). Nutrients/Main compounds High content of protein. Essential amino acids (lysine, isoleucine and tryptophan). Source of vitamin Bcomplex and essential minerals: iron, magnesium, zinc, seleniu ...
Kevin Ahern's Biochemistry (BB 450/550) at Oregon State University
... UDP-glucose), are ACTIVATED. Activated carriers contain a high energy between themselves (such as CoA) and the molecule they are carrying (acetyl group). The high energy of their bond is used to make possible the reaction where the molecule being carried is donated to a larger molecule. 2. There are ...
... UDP-glucose), are ACTIVATED. Activated carriers contain a high energy between themselves (such as CoA) and the molecule they are carrying (acetyl group). The high energy of their bond is used to make possible the reaction where the molecule being carried is donated to a larger molecule. 2. There are ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.