Cellular_Respiration2011
... passed to coenzymes NAD+ and FAD before reducing or passing them to oxygen. Glucose is oxidized by a series of smaller steps so that smaller packets of energy are released to make ATP, rather than one large explosion of energy. ...
... passed to coenzymes NAD+ and FAD before reducing or passing them to oxygen. Glucose is oxidized by a series of smaller steps so that smaller packets of energy are released to make ATP, rather than one large explosion of energy. ...
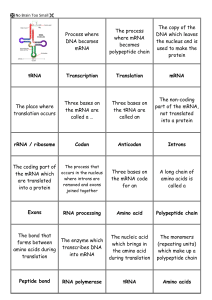
Transcription and Translation
... (m)DNA T A C G C A *Notice two amino acids will still be coded – Frameshift Mutation= a single nucleotide is inserted or deleted into the DNA strand; when this occurs, the reading of the amino acids will shift to the right or left respectively by one base DNA T A G G C A - Italicized G is deleted (m ...
... (m)DNA T A C G C A *Notice two amino acids will still be coded – Frameshift Mutation= a single nucleotide is inserted or deleted into the DNA strand; when this occurs, the reading of the amino acids will shift to the right or left respectively by one base DNA T A G G C A - Italicized G is deleted (m ...
3.2.1: Transcription and Translation
... (m)DNA T A C G C A *Notice two amino acids will still be coded – Frameshift Mutation= a single nucleotide is inserted or deleted into the DNA strand; when this occurs, the reading of the amino acids will shift to the right or left respectively by one base DNA T A G G C A - Italicized G is deleted (m ...
... (m)DNA T A C G C A *Notice two amino acids will still be coded – Frameshift Mutation= a single nucleotide is inserted or deleted into the DNA strand; when this occurs, the reading of the amino acids will shift to the right or left respectively by one base DNA T A G G C A - Italicized G is deleted (m ...
Joseph Jez, PhD
... EXROP students can fit into any of the three major projects in the lab, all of which use a combination of biochemical and structural biology approaches. Specific projects can be tailored to fit the background and expertise of a student but typically include molecular cloning, protein expression and ...
... EXROP students can fit into any of the three major projects in the lab, all of which use a combination of biochemical and structural biology approaches. Specific projects can be tailored to fit the background and expertise of a student but typically include molecular cloning, protein expression and ...
The Phenotyping and Pathophysiology Core
... Confocal Z section imaging of selected renal structures for detailed spatial analysis can also be performed by the Core ...
... Confocal Z section imaging of selected renal structures for detailed spatial analysis can also be performed by the Core ...
Document
... 25.2: Stereochemistry of Amino Acids: The natural configuration of the -carbon is L. D-Amino acids are found in the cell walls of bacteria. The D-amino acids are not genetically encoded, but derived from the epimerization of L-isomers (Ch. ...
... 25.2: Stereochemistry of Amino Acids: The natural configuration of the -carbon is L. D-Amino acids are found in the cell walls of bacteria. The D-amino acids are not genetically encoded, but derived from the epimerization of L-isomers (Ch. ...
Polymer Molecules
... All proteins contain the elements C,O,H, N. They are condensation polymers, made by amino acids linking together. An amine group of one molecule links to the carboxyl group of another molecule to form an amide or peptide bond. The body cannot make every type of amino acids that it needs. So our diet ...
... All proteins contain the elements C,O,H, N. They are condensation polymers, made by amino acids linking together. An amine group of one molecule links to the carboxyl group of another molecule to form an amide or peptide bond. The body cannot make every type of amino acids that it needs. So our diet ...
Grand challenges in bioinformatics.
... from its amino acid sequence. It is widely believed that the amino acid sequence contains all the necessary information to make up the correct three-dimensional structure, since the protein folding is apparently thermodynamically determined; namely, given a proper environment, a protein would fold u ...
... from its amino acid sequence. It is widely believed that the amino acid sequence contains all the necessary information to make up the correct three-dimensional structure, since the protein folding is apparently thermodynamically determined; namely, given a proper environment, a protein would fold u ...
Chapter 4 Notes
... • Chargaff’s Rule states that the amount of adenine is always based with and equal to thymine. The amount of cytosine is always based with and equal guanine. • Rosalind Franklin used x-ray diffraction to make images that helped lead to the discovery of the shape of DNA. • Watson and Crick used Fran ...
... • Chargaff’s Rule states that the amount of adenine is always based with and equal to thymine. The amount of cytosine is always based with and equal guanine. • Rosalind Franklin used x-ray diffraction to make images that helped lead to the discovery of the shape of DNA. • Watson and Crick used Fran ...
Advanced Higher Cells and Proteins
... • A ligand is a substance that can bind to a protein. • R groups not involved in protein folding can allow binding to these other molecules. • Binding sites will have complementary shape and chemistry to the ligand. • The ligand can either be a substrate or a molecule that affects the activity of th ...
... • A ligand is a substance that can bind to a protein. • R groups not involved in protein folding can allow binding to these other molecules. • Binding sites will have complementary shape and chemistry to the ligand. • The ligand can either be a substrate or a molecule that affects the activity of th ...
From DNA to Protein synthesis lab
... mRNA then leaves the nucleus and enters the cl.toplasm. In all cells, the mRNA molecule attaches to a ribosome, where IRNA anticodons translate the mRNA into amino acids. The completed amino acid chain, or polypeptide, then folds into its final shape as a protein. In this iab, you will model transcr ...
... mRNA then leaves the nucleus and enters the cl.toplasm. In all cells, the mRNA molecule attaches to a ribosome, where IRNA anticodons translate the mRNA into amino acids. The completed amino acid chain, or polypeptide, then folds into its final shape as a protein. In this iab, you will model transcr ...
Metabolism/Energy
... These plants open their stomata at night and close them during the day (the reverse of other plants). At night these plants take up CO2 and incorporate it into a variety of organic acids. This mode of carbon fixation is called crassulacean acid metabolism or CAM (named after the plant family Crassul ...
... These plants open their stomata at night and close them during the day (the reverse of other plants). At night these plants take up CO2 and incorporate it into a variety of organic acids. This mode of carbon fixation is called crassulacean acid metabolism or CAM (named after the plant family Crassul ...
Lecture 29
... sufficient to translate a protein of 300 amino acid — This is an example of a “holdase” model. The DNAk holds onto the folding protein for sufficiently long time to allow to fold. 4) GrpE interacts with DnaK substrate complex and causes release of ADP, then ATP can rebind and substrate is released. ...
... sufficient to translate a protein of 300 amino acid — This is an example of a “holdase” model. The DNAk holds onto the folding protein for sufficiently long time to allow to fold. 4) GrpE interacts with DnaK substrate complex and causes release of ADP, then ATP can rebind and substrate is released. ...
7 energy for cells
... and urination rids the body of excess water. d. to acquire chemical energy in a form cells can use e. ATP molecules 2. a. glycolysis b. preparatory reaction c. citric acid cycle d. electron transport chain 3. a. 2, 2, 34 b. electron transport chain 4. a. cytoplasm b. no c. glucose d. pyruvate e. two ...
... and urination rids the body of excess water. d. to acquire chemical energy in a form cells can use e. ATP molecules 2. a. glycolysis b. preparatory reaction c. citric acid cycle d. electron transport chain 3. a. 2, 2, 34 b. electron transport chain 4. a. cytoplasm b. no c. glucose d. pyruvate e. two ...
III. - Sugars and Polysaccharides
... rigid guidance of nucleic acid templates. For this reason, glycoproteins tend to have variable carbohydrate composition, a phenomenon known as microheterogeneity. Characterizing the structures of carbohydrates –and their variations– is one goal of the field of glycomics, which complements the studie ...
... rigid guidance of nucleic acid templates. For this reason, glycoproteins tend to have variable carbohydrate composition, a phenomenon known as microheterogeneity. Characterizing the structures of carbohydrates –and their variations– is one goal of the field of glycomics, which complements the studie ...
A1984SY56700001
... acts with epsilon amino sidechains of lysine residues of proteins, showed promise. This had the additional advantage of altering different amino acid residues from tyrosine and histidine substituted in direct oxidative iodination. “There followed a long period of development of the method at the end ...
... acts with epsilon amino sidechains of lysine residues of proteins, showed promise. This had the additional advantage of altering different amino acid residues from tyrosine and histidine substituted in direct oxidative iodination. “There followed a long period of development of the method at the end ...
115 THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW FOR THE LIVING ENVIRONMENT REGENTS EXAM
... 1. Amino acids are the individual units that bond together to form a polypeptide (protein). 2. Monosaccharides are the individual units that bond to together to form a polysaccharide (starch). 3. Enzymes are protein molecules that catalyze (help) chemical reactions. 4. The 3-dimensional shape of a m ...
... 1. Amino acids are the individual units that bond together to form a polypeptide (protein). 2. Monosaccharides are the individual units that bond to together to form a polysaccharide (starch). 3. Enzymes are protein molecules that catalyze (help) chemical reactions. 4. The 3-dimensional shape of a m ...
FREE Sample Here
... 38) Ions in an ionic molecule are held together due to A) the presence of water molecules. B) the sharing of electrons. C) each electron orbiting all of the ions in the molecule. D) the attraction of similar charges of the ions' protons. E) the attraction of opposite electrical charges. ...
... 38) Ions in an ionic molecule are held together due to A) the presence of water molecules. B) the sharing of electrons. C) each electron orbiting all of the ions in the molecule. D) the attraction of similar charges of the ions' protons. E) the attraction of opposite electrical charges. ...
Pyruvate and Energetics of Glycolysis
... close to zero. What does this tell us about those reactions? A) They are near equilibrium reactions. B) They are not control points for pathway regulation. C) They are reversible reactions. D) All of the above. E) None of the above. ...
... close to zero. What does this tell us about those reactions? A) They are near equilibrium reactions. B) They are not control points for pathway regulation. C) They are reversible reactions. D) All of the above. E) None of the above. ...
2. Propensity
... 8. Propensity to form MCI for two state proteins Pmc(i) = fmc(i) / ft(i) fmc(i) = frequency of occurrence of amino acids that form multiple contacts ft(i) = frequency of residues in the whole protein Ref: Gromiha, M.M. Protein bioinformatics: from sequence to function. Academic Press, 2010. 9. Prope ...
... 8. Propensity to form MCI for two state proteins Pmc(i) = fmc(i) / ft(i) fmc(i) = frequency of occurrence of amino acids that form multiple contacts ft(i) = frequency of residues in the whole protein Ref: Gromiha, M.M. Protein bioinformatics: from sequence to function. Academic Press, 2010. 9. Prope ...
Honors Guided Notes
... C. the light-independent reaction D. the Calvin cycle 2. The three stages of cellular respiration are ________. A. Carbon fixation, the Calvin cycle, and the electron transport chain B. glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain C. glycolysis, the electron transport chain, a ...
... C. the light-independent reaction D. the Calvin cycle 2. The three stages of cellular respiration are ________. A. Carbon fixation, the Calvin cycle, and the electron transport chain B. glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain C. glycolysis, the electron transport chain, a ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.