Notes on Biopolymers
... each other (find the lowest energy way of arranging themselves structurally) • quaternary structure—when neighboring peptides or proteins stack together, as is seen above when the four peptide units in hemoglobin arrange around each other. ...
... each other (find the lowest energy way of arranging themselves structurally) • quaternary structure—when neighboring peptides or proteins stack together, as is seen above when the four peptide units in hemoglobin arrange around each other. ...
Chapter 2: Chemistry Level
... Solutions – homogeneous mixtures of components Solvent – substance present in greatest amount Solute – substance(s) present in smaller amounts ...
... Solutions – homogeneous mixtures of components Solvent – substance present in greatest amount Solute – substance(s) present in smaller amounts ...
Bio Respiration 2009 Yingxin
... O Each NADH generates 3 ATP (10 NADH > 28 ATP. Note: 2 ATP is used up in transporting 2 NADH produced from glycolysis from the cytoplasm to the mitochondria), each FADH2 generates 2 ATP (2 FADH2 > 4 ATP) O Final electron acceptor is oxygen, and is reduced to water O As electron is transported along ...
... O Each NADH generates 3 ATP (10 NADH > 28 ATP. Note: 2 ATP is used up in transporting 2 NADH produced from glycolysis from the cytoplasm to the mitochondria), each FADH2 generates 2 ATP (2 FADH2 > 4 ATP) O Final electron acceptor is oxygen, and is reduced to water O As electron is transported along ...
Codon Bingo - Eduspace
... cards" the small 'D' is the DNA triplet (sense strand) and the small 'R' is the mRNA codon.} They must then transcribe the DNA base pair triplet into the RNA transcript. Then using a codon chart, they translate the mRNA codon into an amino acid. If they have that amino acid on their card somewhere t ...
... cards" the small 'D' is the DNA triplet (sense strand) and the small 'R' is the mRNA codon.} They must then transcribe the DNA base pair triplet into the RNA transcript. Then using a codon chart, they translate the mRNA codon into an amino acid. If they have that amino acid on their card somewhere t ...
AP-Bio-exam-review-outline-may-2
... phosphate, hydroxyl (alcohols), amines) Major classes of organic molecules (carbs, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids) Isomers- same molecular formula/different structures (REMEMBER: structure determines function) ...
... phosphate, hydroxyl (alcohols), amines) Major classes of organic molecules (carbs, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids) Isomers- same molecular formula/different structures (REMEMBER: structure determines function) ...
03_Lecture_Presentation - Cornerstone Charter Academy
... Carbohydrates range from small sugar molecules (monomers) to large polysaccharides – Sugar monomers are monosaccharides, such as glucose and fructose – These can be hooked together to form the polysaccharides ...
... Carbohydrates range from small sugar molecules (monomers) to large polysaccharides – Sugar monomers are monosaccharides, such as glucose and fructose – These can be hooked together to form the polysaccharides ...
Zdroje volných radikál* ROS
... several isoenzymes with different cofactors: Cu, Zn, Mn, Fe Types of superoxide dismutases : mitochondrial (SOD2 = Mn-SOD, Fe-SOD) – tetramer in prokaryotes and in mitochondria matrix ...
... several isoenzymes with different cofactors: Cu, Zn, Mn, Fe Types of superoxide dismutases : mitochondrial (SOD2 = Mn-SOD, Fe-SOD) – tetramer in prokaryotes and in mitochondria matrix ...
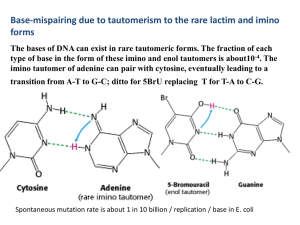
4 . The imino tautomer of adenine can pair with cytosine
... For the family of hexopyranosyl-(4'6') oligonucleotides, whose structures differ from that of homo-DNA by 2 additional OH groups and relate to the natural hexoses in the same way that RNA relates to ribose, none exhibit discernible Watson-Crick base pairing between adenine and uracil Instead, some p ...
... For the family of hexopyranosyl-(4'6') oligonucleotides, whose structures differ from that of homo-DNA by 2 additional OH groups and relate to the natural hexoses in the same way that RNA relates to ribose, none exhibit discernible Watson-Crick base pairing between adenine and uracil Instead, some p ...
Week 5: Macronutrient Jeopardy
... Q: What is a good source of fat? A: Avocados, cheese, dark chocolate, fish, nuts, coconut oil/extra virgin olive oil, or whole eggs. Q: What is the simplest form of a fat? A: Fatty acids -Q: How much of your daily intake should come from fats? A: 20-35% of one’s daily diet Q: What are the three kind ...
... Q: What is a good source of fat? A: Avocados, cheese, dark chocolate, fish, nuts, coconut oil/extra virgin olive oil, or whole eggs. Q: What is the simplest form of a fat? A: Fatty acids -Q: How much of your daily intake should come from fats? A: 20-35% of one’s daily diet Q: What are the three kind ...
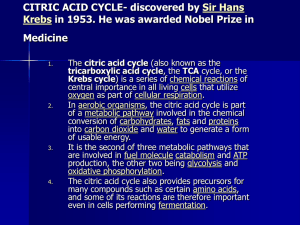
CITRIC ACID CYCLE
... central importance in all living cells that utilize oxygen as part of cellular respiration. In aerobic organisms, the citric acid cycle is part of a metabolic pathway involved in the chemical conversion of carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and water to generate a form of usable en ...
... central importance in all living cells that utilize oxygen as part of cellular respiration. In aerobic organisms, the citric acid cycle is part of a metabolic pathway involved in the chemical conversion of carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and water to generate a form of usable en ...
BIOL 1322 - Victoria College
... energy? Describe marasmus and kwashiorkor. How can the two conditions be distinguished, and in what ways do they overlap? ...
... energy? Describe marasmus and kwashiorkor. How can the two conditions be distinguished, and in what ways do they overlap? ...
Plant Biochemistry, Spring 2012 BOT 6935, section 4264, 4 credits
... 1. The biochemistry of amino acids and proteins, sugars and carbohydrates, and lipids. 2. Quantitative aspects of biochemistry including enzyme kinetics, proteinligand binding, analytical techniques, and bioenergetics 3. Intermediary metabolism, discussed in the context of plant cell structure and f ...
... 1. The biochemistry of amino acids and proteins, sugars and carbohydrates, and lipids. 2. Quantitative aspects of biochemistry including enzyme kinetics, proteinligand binding, analytical techniques, and bioenergetics 3. Intermediary metabolism, discussed in the context of plant cell structure and f ...
UNIVERSITI PENDIOIKAN SULTAN lORIS
... replication of lagging stands is synthesized discontinuously, as series of DNA rragrner1l� known as Okazaki fragment. Describe the synthesis of a lagging strand. The description should begin with reaction by primase and ends with DNA ligase. ...
... replication of lagging stands is synthesized discontinuously, as series of DNA rragrner1l� known as Okazaki fragment. Describe the synthesis of a lagging strand. The description should begin with reaction by primase and ends with DNA ligase. ...
The amino acids
... Glycine is special because it is so flexible, so it can easily make the sharp turns and bends needed in a b-turn. Proline is special because it is so rigid; you could say that it is pre-bent for the turn. Aspartic acid, asparagine, and serine have in common that they have short side chains that can ...
... Glycine is special because it is so flexible, so it can easily make the sharp turns and bends needed in a b-turn. Proline is special because it is so rigid; you could say that it is pre-bent for the turn. Aspartic acid, asparagine, and serine have in common that they have short side chains that can ...
Chemistry for Bio 11
... reactions to form compounds • Molecules- 2 or more atoms combined in a specific way • Compounds- different elements in a molecule, in exact, whole-number ratios, joined by a chemical bond • 2 major means of intramolecular chemical bonding: Covalent (incl. polar and nonpolar) and Ionic ...
... reactions to form compounds • Molecules- 2 or more atoms combined in a specific way • Compounds- different elements in a molecule, in exact, whole-number ratios, joined by a chemical bond • 2 major means of intramolecular chemical bonding: Covalent (incl. polar and nonpolar) and Ionic ...
Lab activity 8 Proteins 2 Alaa S Baraka Islamic university of Gaza
... indicating the presence of proteins. • A light pink color indicates the presence of peptides.. ...
... indicating the presence of proteins. • A light pink color indicates the presence of peptides.. ...
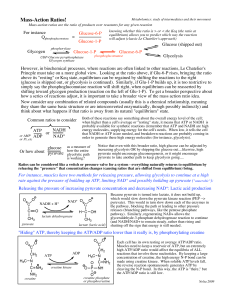
Mass-Action Ratios!
... above its "resting" or Keq state, equilibrium can be regained by shifting the reactions to the right (glucose is shipped out, or glycolysis is continued). Similarly, if Glu-1-P builds up, it is too restrictive to simply say the phosphoglucomutase reaction will shift right, when equilibrium can be re ...
... above its "resting" or Keq state, equilibrium can be regained by shifting the reactions to the right (glucose is shipped out, or glycolysis is continued). Similarly, if Glu-1-P builds up, it is too restrictive to simply say the phosphoglucomutase reaction will shift right, when equilibrium can be re ...
Slide 1
... IV. Cellular Respiration – process by which E of glucose is released in the cell to be used for life processes (movement, breathing, blood circulation, etc…) ...
... IV. Cellular Respiration – process by which E of glucose is released in the cell to be used for life processes (movement, breathing, blood circulation, etc…) ...
The Citric Acid Cycle - Rubin Risto Gulaboski
... • The reactions of metabolism are MANY • In this class we will discuss some of the major reactions: – Glyco - Lysis (glycolysis) – The Citric Acid Cycle – The Electron Transport Chain ...
... • The reactions of metabolism are MANY • In this class we will discuss some of the major reactions: – Glyco - Lysis (glycolysis) – The Citric Acid Cycle – The Electron Transport Chain ...
it_health_summary - Center for Biological Sequence Analysis
... – Alignment and scoring matrices • How does it work & what are the numbers ...
... – Alignment and scoring matrices • How does it work & what are the numbers ...
Intermediate 2 Biology Revision
... What happens to the hydrogen? At this stage Oxygen is termed… What else is some of the light energy used to form? The products of this stage The term given to the second stage The carbon dioxide combines with the hydrogen form the first stage to ...
... What happens to the hydrogen? At this stage Oxygen is termed… What else is some of the light energy used to form? The products of this stage The term given to the second stage The carbon dioxide combines with the hydrogen form the first stage to ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.