Chlorophyll – Protein complex + H* _ OH – (Ground state)
... even though the excreting microbe is no longer alive. If microbes have an abundance of energy-rich carbon foods, and plenty oxygen, they will rapidly oxidize toxic ammonia to harmless nitrates. These nitrates become available for plant or microbe metabolism or if in excess, decomposition to molecula ...
... even though the excreting microbe is no longer alive. If microbes have an abundance of energy-rich carbon foods, and plenty oxygen, they will rapidly oxidize toxic ammonia to harmless nitrates. These nitrates become available for plant or microbe metabolism or if in excess, decomposition to molecula ...
Ch14
... carbon molecules: DHAP and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. So both the 3 and 4 carbons on glucose become the aldehyde carbon (carbon 1) of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. ...
... carbon molecules: DHAP and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. So both the 3 and 4 carbons on glucose become the aldehyde carbon (carbon 1) of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. ...
Protein Folding and Quality Control
... Protein Folding and Quality Control Folding Function: making specific functional domains critical for function (occurs following or coincident with synthesis) Sequence dependence: Final structure of protein is dependent on amino acid sequence and properties of amino acids that make up polypeptide be ...
... Protein Folding and Quality Control Folding Function: making specific functional domains critical for function (occurs following or coincident with synthesis) Sequence dependence: Final structure of protein is dependent on amino acid sequence and properties of amino acids that make up polypeptide be ...
1 acetyl CoA - WordPress.com
... Citric Acid Cycle/Krebs Cycle The citric acid cycle may seem like an elaborate way to oxidize acetate into carbon dioxide, but there is chemical logic to the cycle. In order to directly oxidize acetate into two molecules of CO2 a C—C bond must be broken. ...
... Citric Acid Cycle/Krebs Cycle The citric acid cycle may seem like an elaborate way to oxidize acetate into carbon dioxide, but there is chemical logic to the cycle. In order to directly oxidize acetate into two molecules of CO2 a C—C bond must be broken. ...
Harvesting Chemical Energy
... Describe the relationship between form and function Relate the caloric requirements of humans to the energy requirements for cellular reactions Describe the workings of each phase of cellular respiration with emphasis on the reactants, the products, the net production of ATP and the cellular ...
... Describe the relationship between form and function Relate the caloric requirements of humans to the energy requirements for cellular reactions Describe the workings of each phase of cellular respiration with emphasis on the reactants, the products, the net production of ATP and the cellular ...
Introduction - Northern Illinois University
... • The 3-dimensional structure of each protein is unique. ...
... • The 3-dimensional structure of each protein is unique. ...
Ninety-nine Point Nine Percent of the Time, Nature Uses the... Acids, and We Don’t Know Exactly Why
... against random mutation. The result would have been a system that was not so much “frozen” in a coincidental arrangement, as it was optimally adapted. Optimal adaptation may sufficiently explain the particulars of the genetic code, and may provide a general context for understanding the universality ...
... against random mutation. The result would have been a system that was not so much “frozen” in a coincidental arrangement, as it was optimally adapted. Optimal adaptation may sufficiently explain the particulars of the genetic code, and may provide a general context for understanding the universality ...
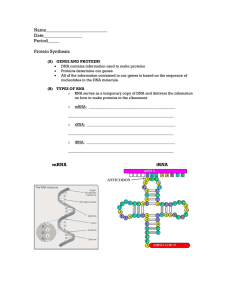
Name___________________________ Date_________________ Period_____
... RNA Polymerase knows where to bind on the DNA due to spots on the DNA called promoters, which act as start point signals for transcription. ...
... RNA Polymerase knows where to bind on the DNA due to spots on the DNA called promoters, which act as start point signals for transcription. ...
Solutions - MIT OpenCourseWare
... BPG is at a higher energy level than 3PG. You can infer this because BPG has two phosphate groups as compare to 3PG, which has one phosphate group. Also, the conversion of BPG into 3PG drives the synthesis of ATP. d) The enzyme triose phosphate isomerase, catalyzes step 5. In this step Dihydroxyacet ...
... BPG is at a higher energy level than 3PG. You can infer this because BPG has two phosphate groups as compare to 3PG, which has one phosphate group. Also, the conversion of BPG into 3PG drives the synthesis of ATP. d) The enzyme triose phosphate isomerase, catalyzes step 5. In this step Dihydroxyacet ...
2/12 Daily Catalyst Pg. 82 Fermentation
... Occurs in nearly all organisms Probably evolved in ancient prokaryotes before there was oxygen in the atmosphere ...
... Occurs in nearly all organisms Probably evolved in ancient prokaryotes before there was oxygen in the atmosphere ...
HPLC is a precise tool Lactose fermentation Lactose is disaccharide
... chromatography determination of organic acids in dairy products. Journal of Food Science, 46, ...
... chromatography determination of organic acids in dairy products. Journal of Food Science, 46, ...
Lecture 1
... Law 1-‐ naturally occurring (spontaneous) processes will always proceed towards the state with the least poten5al energy (releases energy) Law 2-‐ naturally occurring (spontaneous) processes mu ...
... Law 1-‐ naturally occurring (spontaneous) processes will always proceed towards the state with the least poten5al energy (releases energy) Law 2-‐ naturally occurring (spontaneous) processes mu ...
Part (II) Nitrogenous molecules metabolism
... Serve as a reducing agent for glutaredoxin in deoxyribonucleotide synthesis. (Fig 22-37) ...
... Serve as a reducing agent for glutaredoxin in deoxyribonucleotide synthesis. (Fig 22-37) ...
Biochemistry 3020 1. The consumption of
... The antenna chlorophyll molecule passes the energy of the photon, via exciton transfer, to neighboring chlorophyll molecules and ultimately to reaction center chlorophyll molecules. This excites P700 to P700*, which donates an electron to A0. From A0, electrons pass to phylloquinone (A1), through an ...
... The antenna chlorophyll molecule passes the energy of the photon, via exciton transfer, to neighboring chlorophyll molecules and ultimately to reaction center chlorophyll molecules. This excites P700 to P700*, which donates an electron to A0. From A0, electrons pass to phylloquinone (A1), through an ...
Protein Conformation and Function
... • Optimum temperature for most proteins is 37C. • Very few proteins remain biologically active above 50 C. (Some bacteria have protein that remains stable up to 70 C and higher) – Increased Thermal activity (heat or UV) disrupts some of the hydrogen bonds and attractions between non-polar side group ...
... • Optimum temperature for most proteins is 37C. • Very few proteins remain biologically active above 50 C. (Some bacteria have protein that remains stable up to 70 C and higher) – Increased Thermal activity (heat or UV) disrupts some of the hydrogen bonds and attractions between non-polar side group ...
7 CellRespiration
... 15. How does fermentation solve the problems imposed by anaerobic conditions? Does fermentation create the same results? What is the difference between alcoholic fermentation and lactic acid fermentation, and what types of cells do which? How is the rising of bread, the making of beer and yogurt, an ...
... 15. How does fermentation solve the problems imposed by anaerobic conditions? Does fermentation create the same results? What is the difference between alcoholic fermentation and lactic acid fermentation, and what types of cells do which? How is the rising of bread, the making of beer and yogurt, an ...
Chemical Equation Interpretations – Match the chemical equation
... D. When octane and oxygen gas are burned in our cards, carbon dioxide and water come out in the exhaust. E. Methanol , if ingested, reacts with oxygen to form formaldehyde, which is toxic. Water is also formed in this reaction. F. Liquid mercury evaporates to produce mercury vapor. G. Saturated fatt ...
... D. When octane and oxygen gas are burned in our cards, carbon dioxide and water come out in the exhaust. E. Methanol , if ingested, reacts with oxygen to form formaldehyde, which is toxic. Water is also formed in this reaction. F. Liquid mercury evaporates to produce mercury vapor. G. Saturated fatt ...
CHAPTER 3
... - Contains carbon and hydrogen and are usually associated with living things or things that were once alive; four groups of organic substances make up all living things. 1. Carbohydrates-supply energy for cell processes 2. Lipids- store and release large amounts of energy 3. Proteins- the building b ...
... - Contains carbon and hydrogen and are usually associated with living things or things that were once alive; four groups of organic substances make up all living things. 1. Carbohydrates-supply energy for cell processes 2. Lipids- store and release large amounts of energy 3. Proteins- the building b ...
et al
... Figure 3.13. The general structure of an amino acid. All amino acids have the same general structure, comprising a central α-carbon attached to a hydrogen atom, a carboxyl group, an amino group and an R group. The R group is different for each amino acid (see Figure 3.17 ). ...
... Figure 3.13. The general structure of an amino acid. All amino acids have the same general structure, comprising a central α-carbon attached to a hydrogen atom, a carboxyl group, an amino group and an R group. The R group is different for each amino acid (see Figure 3.17 ). ...
File - Mr. Shanks` Class
... a) decreasing the temperature by 5C and keeping the pH at 8. b) increasing the temperature by 5C and keeping the pH at 8. c) maintaining the temperature at 30C and increasing the pH to 9. d) maintaining the temperature at 30C and decreasing the pH to 7. 9. What is the function of the allosteric ...
... a) decreasing the temperature by 5C and keeping the pH at 8. b) increasing the temperature by 5C and keeping the pH at 8. c) maintaining the temperature at 30C and increasing the pH to 9. d) maintaining the temperature at 30C and decreasing the pH to 7. 9. What is the function of the allosteric ...
The Origin of Life - The University of Texas at Dallas
... living thing? One way would be to look closely at the metabolic chart shown earlier, the diagram that maps the basic chemical reactions in all living systems. ...
... living thing? One way would be to look closely at the metabolic chart shown earlier, the diagram that maps the basic chemical reactions in all living systems. ...
Lecture 13 - 14 Conformation of proteins Conformation of a protein
... polypeptide chain lacking regular secondary structure. In enzymes with more than one substrate or allosteric effector sites the different binding sites are often located in different domains. In multifunctional proteins, the different domains perform different tasks. Quaternary structure Prote ...
... polypeptide chain lacking regular secondary structure. In enzymes with more than one substrate or allosteric effector sites the different binding sites are often located in different domains. In multifunctional proteins, the different domains perform different tasks. Quaternary structure Prote ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.