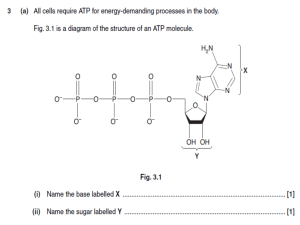
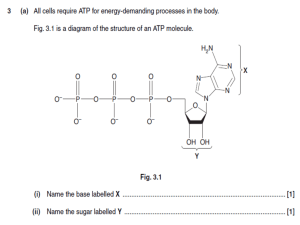
Classification and Nomenclature of Enzymes
... where “a” is the class, “b” is the subclass, “c” is the sub‐subclass, and “d” is the sub‐sub‐subclass. The “b” and “c” digits describe the reaction, while the “d” digit is used to distinguish between different enzymes of the same function based on the actual substrate in the reaction. • Exampl ...
... where “a” is the class, “b” is the subclass, “c” is the sub‐subclass, and “d” is the sub‐sub‐subclass. The “b” and “c” digits describe the reaction, while the “d” digit is used to distinguish between different enzymes of the same function based on the actual substrate in the reaction. • Exampl ...
Big Idea 4 Greco 2015
... a. Structure and function of polymers are derived from the way their monomers are assembled - know each of the following 1. In nucleic acids, biological information is encoded in sequences of nucleotide monomers. Each nucleotide has structural components: a five-carbon sugar (deoxyribose or ribose), ...
... a. Structure and function of polymers are derived from the way their monomers are assembled - know each of the following 1. In nucleic acids, biological information is encoded in sequences of nucleotide monomers. Each nucleotide has structural components: a five-carbon sugar (deoxyribose or ribose), ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... • Sodium hydroxide absorbs all CO2 from the air in the apparatus from the beginning. Potassium hydroxide could be used instead of sodium hydroxide. They both absorb CO2. • As the germinating seeds use oxygen and the pressure reduces in tube A so the manometer level nearest to the seeds rises. • Any ...
... • Sodium hydroxide absorbs all CO2 from the air in the apparatus from the beginning. Potassium hydroxide could be used instead of sodium hydroxide. They both absorb CO2. • As the germinating seeds use oxygen and the pressure reduces in tube A so the manometer level nearest to the seeds rises. • Any ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... • Sodium hydroxide absorbs all CO2 from the air in the apparatus from the beginning. Potassium hydroxide could be used instead of sodium hydroxide. They both absorb CO2. • As the germinating seeds use oxygen and the pressure reduces in tube A so the manometer level nearest to the seeds rises. ...
... • Sodium hydroxide absorbs all CO2 from the air in the apparatus from the beginning. Potassium hydroxide could be used instead of sodium hydroxide. They both absorb CO2. • As the germinating seeds use oxygen and the pressure reduces in tube A so the manometer level nearest to the seeds rises. ...
Cellular Respiration II PPT
... presence of oxygen). However, organisms can also produce small amounts of ATP through anaerobic respiration as well. • Fermentation is a process that is centered around recycling electron carriers so that at least glycolysis can continue. Glycolysis needs NAD+ to function, so by doing this, the orga ...
... presence of oxygen). However, organisms can also produce small amounts of ATP through anaerobic respiration as well. • Fermentation is a process that is centered around recycling electron carriers so that at least glycolysis can continue. Glycolysis needs NAD+ to function, so by doing this, the orga ...
Overview of Metabolism Chapter
... If the muscles contain plenty of available oxygen, pyruvate can undergo complete oxidation to carbon dioxide and water during cellular respiration (Figure 5). Respiration, which consists of three phases, occurs in the mitochondria, the cell’s “powerhouses.” This metabolic pathway traps the maximum a ...
... If the muscles contain plenty of available oxygen, pyruvate can undergo complete oxidation to carbon dioxide and water during cellular respiration (Figure 5). Respiration, which consists of three phases, occurs in the mitochondria, the cell’s “powerhouses.” This metabolic pathway traps the maximum a ...
7.5 Proteins - HS Biology IB
... 7.5.1: Explain the four levels of protein structure, indicating the significance of each level. ...
... 7.5.1: Explain the four levels of protein structure, indicating the significance of each level. ...
Protein and Lipid Catabolism
... – Partial oxidation of substrate • NADH oxidized back to NAD+ • Uses organic compound as terminal electron acceptor – Typically pyruvate or derivative • NO oxidative phosphorylation so ATP yield is low ...
... – Partial oxidation of substrate • NADH oxidized back to NAD+ • Uses organic compound as terminal electron acceptor – Typically pyruvate or derivative • NO oxidative phosphorylation so ATP yield is low ...
Test 2a
... (8 points)Tell me about the different types of catalysis you see occurring in this mechanism. In step 1 His 12 is acting as a general base to remove a proton from the 2' OH of the ribose, and His 119 is acitng as a general acid to donate its proton to the phosphate group between the two ribose sugar ...
... (8 points)Tell me about the different types of catalysis you see occurring in this mechanism. In step 1 His 12 is acting as a general base to remove a proton from the 2' OH of the ribose, and His 119 is acitng as a general acid to donate its proton to the phosphate group between the two ribose sugar ...
bsaa protein digestion by enzyme worksheet
... smaller chains, which are in turn broken down into individual amino acids. These amino acids can then be rearranged into proteins that are found and used in our bodies. ...
... smaller chains, which are in turn broken down into individual amino acids. These amino acids can then be rearranged into proteins that are found and used in our bodies. ...
The Endoplasmic Reticulum Train
... The endoplasmic reticulum is like a train route because it transports the proteins and lipids manufactured in the different parts of the organelle to other parts in the cell. The ribosomes, rough ER, and smooth ER act as the train stops where the product (lipids and proteins) is manufactured. ...
... The endoplasmic reticulum is like a train route because it transports the proteins and lipids manufactured in the different parts of the organelle to other parts in the cell. The ribosomes, rough ER, and smooth ER act as the train stops where the product (lipids and proteins) is manufactured. ...
Protein synthesis
... During the 1950s and 1960s, it became apparent that DNA is essential in the synthesis of proteins. Proteins are used in enzymes and as structural materials in cells. Many specialized proteins function in cellular activities. For example, in humans, the hormone insulin and the muscle cell filaments a ...
... During the 1950s and 1960s, it became apparent that DNA is essential in the synthesis of proteins. Proteins are used in enzymes and as structural materials in cells. Many specialized proteins function in cellular activities. For example, in humans, the hormone insulin and the muscle cell filaments a ...
Lecture 1 Course overview and intro to enzymes
... Web page http;//courses.ucsd.edu/rhampton/bibc102 Ideas in metabolism non-iterated structures but common structural themes metabolic pathway Why study metabolism relevant to all life numerous diseases and conditions catabolism and anabolism we think on many levels from atomic to ecological Proteins ...
... Web page http;//courses.ucsd.edu/rhampton/bibc102 Ideas in metabolism non-iterated structures but common structural themes metabolic pathway Why study metabolism relevant to all life numerous diseases and conditions catabolism and anabolism we think on many levels from atomic to ecological Proteins ...
Document
... 1. Which one of the following nucleotide pair bonds would be found in a DNA molecule? a. adenine-guanine c. adenine-cytosine b. guanine-cytosine d. cytosine-uracil 2. The backbone of a DNA molecule is made of which two components? a. phosphate molecules and ribose sugars b. deoxyphosphate molecules ...
... 1. Which one of the following nucleotide pair bonds would be found in a DNA molecule? a. adenine-guanine c. adenine-cytosine b. guanine-cytosine d. cytosine-uracil 2. The backbone of a DNA molecule is made of which two components? a. phosphate molecules and ribose sugars b. deoxyphosphate molecules ...
Introduction to the Science of Biology The Characteristics
... • Hawaiian Monk seals eat fish • Humans eat fish • What if something happened to the fish? ...
... • Hawaiian Monk seals eat fish • Humans eat fish • What if something happened to the fish? ...
biochemistry-part1
... (ii) Transcription, types of RNAs, their characteristics and function. (iii) Translation leading to functional protein synthesis, colinearity of genes and proteins. 6. Application of Molecular Biology: Concept (i) Recombinant DNA technology – isolation of genes, restriction endonuclease, vectors, cl ...
... (ii) Transcription, types of RNAs, their characteristics and function. (iii) Translation leading to functional protein synthesis, colinearity of genes and proteins. 6. Application of Molecular Biology: Concept (i) Recombinant DNA technology – isolation of genes, restriction endonuclease, vectors, cl ...
SBI4U: Unit 2 Review, Metabolic Processes SAMPLE TEST
... 23. Summarize the key events of Non-cyclic electron flow. Why is it so-called? 24. Explain the similarities and differences between the electron transport chains occurring in the mitochondria with the electron transport chain associated with photosystem II. 25. Summarize cyclic electron flow. When w ...
... 23. Summarize the key events of Non-cyclic electron flow. Why is it so-called? 24. Explain the similarities and differences between the electron transport chains occurring in the mitochondria with the electron transport chain associated with photosystem II. 25. Summarize cyclic electron flow. When w ...
ucla1 - WEHI Bioinformatics
... 84 Puls e fi eld gel electrophoresis 85 Polymerase chain reaction 87 YAC vec tor ...
... 84 Puls e fi eld gel electrophoresis 85 Polymerase chain reaction 87 YAC vec tor ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.