All life is based on the same genetic code
... multiple alleles. • The human ABO blood group is determined by three alleles (IA, IB, and i) of a single gene. ...
... multiple alleles. • The human ABO blood group is determined by three alleles (IA, IB, and i) of a single gene. ...
PreAP Biology Study Guide Unit 4: Molecular Genetics 4.1 What are
... contained the “information” for creating a organism. This experiment which involved the radioactive elements Phosphorus 32 and Sulfur 35 went on to become known as the Hershey-Chase experiment. In no more than four sentences, state the purpose of each radioactive element in the experiment and briefl ...
... contained the “information” for creating a organism. This experiment which involved the radioactive elements Phosphorus 32 and Sulfur 35 went on to become known as the Hershey-Chase experiment. In no more than four sentences, state the purpose of each radioactive element in the experiment and briefl ...
Mutations and DNA Technology Notes
... individuals to bring together the best traits of both. – Mule- cross between a donkey and horse ...
... individuals to bring together the best traits of both. – Mule- cross between a donkey and horse ...
BIOTECHNOLOGY
... Creating organisms containing specific genes or livestock to serve as organ donors or blood donors PCR: polymerase Chain Reaction is used to make large amounts of a specific piece of DNA from a very small sample Recombinant DNA is DNA from 2 or more sources ...
... Creating organisms containing specific genes or livestock to serve as organ donors or blood donors PCR: polymerase Chain Reaction is used to make large amounts of a specific piece of DNA from a very small sample Recombinant DNA is DNA from 2 or more sources ...
File
... series of twenty to thirty-five cycles. Each cycle consists of three steps. Step 1: Denaturing temperature is raised to 94-96°C to break hydrogen bonds Step 2: Annealing temperature is lowered to 56°C to allow primers to attach to the target sequence Step 3: Elongation or Extension temperature is ra ...
... series of twenty to thirty-five cycles. Each cycle consists of three steps. Step 1: Denaturing temperature is raised to 94-96°C to break hydrogen bonds Step 2: Annealing temperature is lowered to 56°C to allow primers to attach to the target sequence Step 3: Elongation or Extension temperature is ra ...
DNA
... the order of the bases in one strand determines the order of the bases in the other strand. ...
... the order of the bases in one strand determines the order of the bases in the other strand. ...
Seeking an Increasingly Explicit Definition of Heredity
... Cracked genetic code- triplet mRNA codons specify each of the twenty amino acids. ...
... Cracked genetic code- triplet mRNA codons specify each of the twenty amino acids. ...
AP Biology
... 8. What is a complementary, short, single stranded nucleic acid that can be either DNA or RNA called? 9. Why do scientists use a radioactive isotope tag for the probes? 10. How is DNA denaturation different than protein denaturation? ...
... 8. What is a complementary, short, single stranded nucleic acid that can be either DNA or RNA called? 9. Why do scientists use a radioactive isotope tag for the probes? 10. How is DNA denaturation different than protein denaturation? ...
Worksheet – DNA and Protein Synthesis Biology 11 Name: DNA
... A. it stays in the nucleus and is copied by DNA B. it carries amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain C. it makes up the ribosomes and provides the site for protein synthesis D. it is transcribed from the DNA and carries the information to the ribosome 6. Read the following DNA sequence left to ...
... A. it stays in the nucleus and is copied by DNA B. it carries amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain C. it makes up the ribosomes and provides the site for protein synthesis D. it is transcribed from the DNA and carries the information to the ribosome 6. Read the following DNA sequence left to ...
76d26f86fc8fd4690d9502156978f6866d36b66a
... Genetic Engineering - faster, more reliable method for_______________ the frequency of a specific allele in a population. B. Recombinant DNA is made by___________ or_____________ fragments of DNA from different ________________ C. Transgenic organisms contain ____________ DNA by a 3 step process. ...
... Genetic Engineering - faster, more reliable method for_______________ the frequency of a specific allele in a population. B. Recombinant DNA is made by___________ or_____________ fragments of DNA from different ________________ C. Transgenic organisms contain ____________ DNA by a 3 step process. ...
DNA and Central Dogma Study Guide
... c) Circle the bases that are purines. Square the bases that are pyrimidines. 2. What are the base paring rules? 3. Draw and label a nucleotide. 4. What term is used to describe the shape of DNA? Why? 5. What is the backbone of DNA made up of? 6. a) Label the sugars, phosphates, and missing bases in ...
... c) Circle the bases that are purines. Square the bases that are pyrimidines. 2. What are the base paring rules? 3. Draw and label a nucleotide. 4. What term is used to describe the shape of DNA? Why? 5. What is the backbone of DNA made up of? 6. a) Label the sugars, phosphates, and missing bases in ...
No Slide Title
... • DNA can vary because of: – Mutation (random copying errors which accrue with time) – Recombination (1/2 of each parent’s DNA mixed to make child) ...
... • DNA can vary because of: – Mutation (random copying errors which accrue with time) – Recombination (1/2 of each parent’s DNA mixed to make child) ...
Marktübersicht PCR-Kits
... concentration of 0.12 μM, 300 μg/ml) in a total reaction volume of 20 μl in 30 minutes at 16 °C in 1x T4 DNA Ligase Reaction Buffer. ...
... concentration of 0.12 μM, 300 μg/ml) in a total reaction volume of 20 μl in 30 minutes at 16 °C in 1x T4 DNA Ligase Reaction Buffer. ...
HapMap PROJECT - Faculty of Science at Bilkent University
... • The correlation between SNPs is mediated by linkage disequilibrium (LD). – LD exists when alleles at distinctive loci occur together more frequently than expected given the known allele frequencies and recombination fraction between the loci. ...
... • The correlation between SNPs is mediated by linkage disequilibrium (LD). – LD exists when alleles at distinctive loci occur together more frequently than expected given the known allele frequencies and recombination fraction between the loci. ...
Gene Therapy
... How are the fragments separated? (by what trait) What is the end result? What are some uses of electrophoresis? ...
... How are the fragments separated? (by what trait) What is the end result? What are some uses of electrophoresis? ...
a copy of the Candy DNA Replication
... Clean all working surfaces and your hands before starting this activity. Your goal is to design a Powerpoint project (or a movie if you know how) that depicts all of the steps of DNA replication. Take photographs of each step and be sure they are easy to see on the Powerpoint. Include labels, arrows ...
... Clean all working surfaces and your hands before starting this activity. Your goal is to design a Powerpoint project (or a movie if you know how) that depicts all of the steps of DNA replication. Take photographs of each step and be sure they are easy to see on the Powerpoint. Include labels, arrows ...
Self-Assembly at nano-Scale Binary Nanoparticles Superlattices
... • Unreacted Au nanoparticle conjugates are removed after magnetic separation, then elevated temperature release the barcode DNA for analysis. • Each Au nanosphere carries hundreds of identical barcode DNA strands, providing substantial amplification. ...
... • Unreacted Au nanoparticle conjugates are removed after magnetic separation, then elevated temperature release the barcode DNA for analysis. • Each Au nanosphere carries hundreds of identical barcode DNA strands, providing substantial amplification. ...
Cell Theory Quiz Study Guide Name
... 17. The order of the nitrogen bases on the DNA molecule is known as the genetic _______. 18. In 1952, Rosalind ____________ discovered DNA is 2 chains of molecules. 19. In 1953, using the above scientist’s research, _____________ and ____________ made a model of DNA. 20. A _____________________ is a ...
... 17. The order of the nitrogen bases on the DNA molecule is known as the genetic _______. 18. In 1952, Rosalind ____________ discovered DNA is 2 chains of molecules. 19. In 1953, using the above scientist’s research, _____________ and ____________ made a model of DNA. 20. A _____________________ is a ...
Molecular Pathology - Fahd Al
... quantity of DNA is insufficient and cannot be used for other methods such as sequencing. • A PCR is performed on an automated cycler, which heats and cools the tubes with the reaction mixture in a very short time. • Performed for 30-40 cycles, in three major steps: 1)denaturation, 2)annealing, and 3 ...
... quantity of DNA is insufficient and cannot be used for other methods such as sequencing. • A PCR is performed on an automated cycler, which heats and cools the tubes with the reaction mixture in a very short time. • Performed for 30-40 cycles, in three major steps: 1)denaturation, 2)annealing, and 3 ...
Restriction Enzymes - Seattle Central College
... • Restriction enzymes are bacterial enzymes that cleave the sugar-phosphate backbone of the DNA at specific nucleotide. • They are member of the class of nucleases. Endonucleases cleave nucleic acid at internal positions, while exonucleases progressively digest from the ends of the nucleic acid mole ...
... • Restriction enzymes are bacterial enzymes that cleave the sugar-phosphate backbone of the DNA at specific nucleotide. • They are member of the class of nucleases. Endonucleases cleave nucleic acid at internal positions, while exonucleases progressively digest from the ends of the nucleic acid mole ...
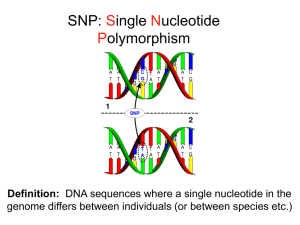
SNP genotyping

SNP genotyping is the measurement of genetic variations of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between members of a species. It is a form of genotyping, which is the measurement of more general genetic variation. SNPs are one of the most common types of genetic variation. An SNP is a single base pair mutation at a specific locus, usually consisting of two alleles (where the rare allele frequency is >1%). SNPs are found to be involved in the etiology of many human diseases and are becoming of particular interest in pharmacogenetics. Because SNPs are conserved during evolution, they have been proposed as markers for use in quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis and in association studies in place of microsatellites. The use of SNPs is being extended in the HapMap project, which aims to provide the minimal set of SNPs needed to genotype the human genome. SNPs can also provide a genetic fingerprint for use in identity testing. The increase in interest in SNPs has been reflected by the furious development of a diverse range of SNP genotyping methods.