Principles of Heredity
... *Although there are multiple R alleles, R1, R2, R3, etc. all are completely dominant over all of the r alleles, r1, r2, r3, etc. ABO Blood Type and Rh Factor are controlled by separate genes. They are inherited independently. ...
... *Although there are multiple R alleles, R1, R2, R3, etc. all are completely dominant over all of the r alleles, r1, r2, r3, etc. ABO Blood Type and Rh Factor are controlled by separate genes. They are inherited independently. ...
BIO SOL Review 16
... a. makes a protein b. codes for RNA molecules c. divides into two cells d. modifies lysosome enzymes ...
... a. makes a protein b. codes for RNA molecules c. divides into two cells d. modifies lysosome enzymes ...
Appendix F - WordPress.com
... There are two methods to test for foods containing GMOs. The ELISA test is used to see if particular proteins are in a sample. PCR is used to amplify regions of GMO genomes. 2. In what organelles is plant DNA located? ...
... There are two methods to test for foods containing GMOs. The ELISA test is used to see if particular proteins are in a sample. PCR is used to amplify regions of GMO genomes. 2. In what organelles is plant DNA located? ...
chapter 19_updates
... DNA at specific nucleotide sequences • Type II restriction enzyme: most useful enzyme • By adding methyl groups to the recognition sequence to protect itself from being digested by its own enzyme in bacteria ...
... DNA at specific nucleotide sequences • Type II restriction enzyme: most useful enzyme • By adding methyl groups to the recognition sequence to protect itself from being digested by its own enzyme in bacteria ...
Forensic DNA Analysis
... Two young women raped and murdered in Narborough, England 5,000 local men are asked to provide blood/saliva samples 1st exoneration and conviction on forensic DNA evidence ...
... Two young women raped and murdered in Narborough, England 5,000 local men are asked to provide blood/saliva samples 1st exoneration and conviction on forensic DNA evidence ...
One label, one tube, Sanger DNA sequencing in one and two lanes
... compressions, where the error rate is below 1%. Direct sequencing with this protocol of plasmid or cosmid DNA, where the background may often be quite noisy, would result in higher error rate. As shown (4, 5), in these cases the four lanes method gives higher accuracy, since it is possible to follow ...
... compressions, where the error rate is below 1%. Direct sequencing with this protocol of plasmid or cosmid DNA, where the background may often be quite noisy, would result in higher error rate. As shown (4, 5), in these cases the four lanes method gives higher accuracy, since it is possible to follow ...
PCR-technique Applications
... - group specific sequences in 16S rRNA as probes (species, ….domains) - different fluorescent dyes attached to the probe - the cells are fixated and made permeable to the probe/s - hybridization direct to the ribosomes ...
... - group specific sequences in 16S rRNA as probes (species, ….domains) - different fluorescent dyes attached to the probe - the cells are fixated and made permeable to the probe/s - hybridization direct to the ribosomes ...
Cells - Troup County High School
... • The Law of Dominance: a recessive trait will only be expressed when the organism’s genotype is recessive homozygous (bb) • The Law of Segregation: during fertilization, new alleles are randomly formed; one can only predict offspring (using Punnett squares) • The Law of Independent Assortment: each ...
... • The Law of Dominance: a recessive trait will only be expressed when the organism’s genotype is recessive homozygous (bb) • The Law of Segregation: during fertilization, new alleles are randomly formed; one can only predict offspring (using Punnett squares) • The Law of Independent Assortment: each ...
4. The diagram below shows a segment of DNA with a total length of
... __ CAP model: catabolite induction: with decrease in glucose -> increase in cAMP cAMP-CAP binds to promoter site therefore, transcription -> lactose metabolism = 3 points (above require explanation & ...
... __ CAP model: catabolite induction: with decrease in glucose -> increase in cAMP cAMP-CAP binds to promoter site therefore, transcription -> lactose metabolism = 3 points (above require explanation & ...
NoLimits 250 bp DNA Fragment
... It is produced using specifically designed plasmid DNA purified by a patented technology. Plasmid DNA is digested with restriction endonucleases and the individual DNA fragment is chromatography-purified from the digestion mixture. ...
... It is produced using specifically designed plasmid DNA purified by a patented technology. Plasmid DNA is digested with restriction endonucleases and the individual DNA fragment is chromatography-purified from the digestion mixture. ...
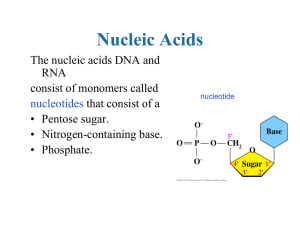
A. Nucleic Acid = polymer of nucleotides 1. nucleotide = molecule
... B. Restriction Enzymes digest DNA by “cutting” DNA between specific nucleotides (a disruption of the bond between a phosphate group and the next sugar molecule), at locations identified as recognition sequences which are approximately 6 base pairs long and enzyme specific! C. In a mixture of DNA and ...
... B. Restriction Enzymes digest DNA by “cutting” DNA between specific nucleotides (a disruption of the bond between a phosphate group and the next sugar molecule), at locations identified as recognition sequences which are approximately 6 base pairs long and enzyme specific! C. In a mixture of DNA and ...
DNA versus RNA Notes File
... • Finally, both DNA and RNA can contain four nitrogenous bases, BUT RNA does not have Thymine. • Thymine is replaced by a similar base called uracil (U). ...
... • Finally, both DNA and RNA can contain four nitrogenous bases, BUT RNA does not have Thymine. • Thymine is replaced by a similar base called uracil (U). ...
Method of localizing, either mRNA within the cytoplasm or DNA
... • Alternative method for the identification of chromosomes in metaphase spreads or interphase nuclei. • Denatured DNA is hybridized to short DNA fragments, or oligonucleotides followed by primer extension with ...
... • Alternative method for the identification of chromosomes in metaphase spreads or interphase nuclei. • Denatured DNA is hybridized to short DNA fragments, or oligonucleotides followed by primer extension with ...
Ch 13 Genetic Engineering
... • Cutting DNA with restriction enzymes • Separate DNA using gel electrophoresis • Identify the sequence using different dyes that attach to nitrogen bases • Make copies using polymerase chain reaction ...
... • Cutting DNA with restriction enzymes • Separate DNA using gel electrophoresis • Identify the sequence using different dyes that attach to nitrogen bases • Make copies using polymerase chain reaction ...
Human Genetics and Genetic Technology Test Review Jeopardy
... season ended. DNA from this blood was compared to meat and blood found in the suspect’s freezer. Was the suspect guilty? Why or why not? ...
... season ended. DNA from this blood was compared to meat and blood found in the suspect’s freezer. Was the suspect guilty? Why or why not? ...
1) Semiconservative DNA replication means that A) each daughter
... B) nucleotides are constantly being recycled as cells make DNA. C) the cell can proofread its newly synthesized DNA only part of the time. D) each strand of a double-stranded DNA molecule is replicated differently 2) DNA helicases A) break hydrogen bonds between complementary nucleotides. B) synthes ...
... B) nucleotides are constantly being recycled as cells make DNA. C) the cell can proofread its newly synthesized DNA only part of the time. D) each strand of a double-stranded DNA molecule is replicated differently 2) DNA helicases A) break hydrogen bonds between complementary nucleotides. B) synthes ...
Techniques
... - Green spot: only expressed in no O2 Red spot: expressed only in plus O2 Yellow: Expressed in both condition ...
... - Green spot: only expressed in no O2 Red spot: expressed only in plus O2 Yellow: Expressed in both condition ...
SNP genotyping

SNP genotyping is the measurement of genetic variations of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between members of a species. It is a form of genotyping, which is the measurement of more general genetic variation. SNPs are one of the most common types of genetic variation. An SNP is a single base pair mutation at a specific locus, usually consisting of two alleles (where the rare allele frequency is >1%). SNPs are found to be involved in the etiology of many human diseases and are becoming of particular interest in pharmacogenetics. Because SNPs are conserved during evolution, they have been proposed as markers for use in quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis and in association studies in place of microsatellites. The use of SNPs is being extended in the HapMap project, which aims to provide the minimal set of SNPs needed to genotype the human genome. SNPs can also provide a genetic fingerprint for use in identity testing. The increase in interest in SNPs has been reflected by the furious development of a diverse range of SNP genotyping methods.