DNA Unit Study Guide 2017 - Liberty Union High School District
... DNA T A C T A T T C C T C G T C T C G G C G T A T T mRNA_______________________________________________________________________ tRNA________________________________________________________________________ rRNA/aa______________________________________________________________________ 24. What is a gen ...
... DNA T A C T A T T C C T C G T C T C G G C G T A T T mRNA_______________________________________________________________________ tRNA________________________________________________________________________ rRNA/aa______________________________________________________________________ 24. What is a gen ...
DNA Notes - Firelands Local Schools
... DNA – DNA REGULATES ALL CELLULAR ACTIVITY BY REGULATING PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. – DNA IS A SELF-REPLICATING MOLECULE WHICH GETS PASSED ON FROM ONE GENERATION TO THE NEXT. ...
... DNA – DNA REGULATES ALL CELLULAR ACTIVITY BY REGULATING PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. – DNA IS A SELF-REPLICATING MOLECULE WHICH GETS PASSED ON FROM ONE GENERATION TO THE NEXT. ...
Salmonella typhimurium
... • The genotype is the set of alleles it has for all of its genes (5,000 in bacteria; 40,000 in humans) • The relationship between genotype and phenotype is what genetics is all about • New alleles are created by mutation and their effect the phenotype may be dominant or recessive ...
... • The genotype is the set of alleles it has for all of its genes (5,000 in bacteria; 40,000 in humans) • The relationship between genotype and phenotype is what genetics is all about • New alleles are created by mutation and their effect the phenotype may be dominant or recessive ...
Name - EdWeb
... 1. What is DNA? __________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. What does DNA stand for? ________________________________________________________ 3. Why is DNA called a blueprint? ___________________ ...
... 1. What is DNA? __________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. What does DNA stand for? ________________________________________________________ 3. Why is DNA called a blueprint? ___________________ ...
Study Guide Unit 4 - Mrs. Wolodkowicz`s Biological Realm
... write the definitions for DNA & RNA, transcription & translation, autosome, & sex linkage. the components of DNA the nitrogen bases & their complementary base pairs in DNA & RNA functions of tRNA & mRNA the laws of segregation & independent assortment the terms: dominant, recessive, geno ...
... write the definitions for DNA & RNA, transcription & translation, autosome, & sex linkage. the components of DNA the nitrogen bases & their complementary base pairs in DNA & RNA functions of tRNA & mRNA the laws of segregation & independent assortment the terms: dominant, recessive, geno ...
Human Telomeric Proteins Involved in Cancer and Cellular Aging
... Aging RU 671 Technology Summary Telomeres are repetitive DNA sequences that cap the ends of chromosomes. The primary function of telomeres is to protect chromosome ends from degradation and fusion. Telomeres also appear to play a significant role in cellular aging – each time a cell divides, the mec ...
... Aging RU 671 Technology Summary Telomeres are repetitive DNA sequences that cap the ends of chromosomes. The primary function of telomeres is to protect chromosome ends from degradation and fusion. Telomeres also appear to play a significant role in cellular aging – each time a cell divides, the mec ...
Your genes
... Date _______________________________ Objectives 1. Identify the different structures that make up genetic ...
... Date _______________________________ Objectives 1. Identify the different structures that make up genetic ...
Heredity Picture Vocabulary
... The heredity material of the cell, made up of sequences of four similar chemicals arranged in linear strands, with each strand of DNA called a chromosome. ...
... The heredity material of the cell, made up of sequences of four similar chemicals arranged in linear strands, with each strand of DNA called a chromosome. ...
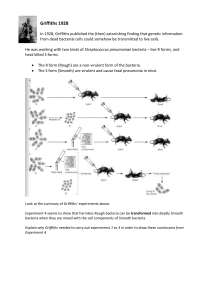
DNA experiments exercise
... Experiment 4 seems to show that harmless Rough bacteria can be transformed into deadly Smooth bacteria when they are mixed with the cell components of Smooth bacteria. Explain why Griffiths needed to carry out experiments 1 to 3 in order to draw these conclusions from Experiment 4. ...
... Experiment 4 seems to show that harmless Rough bacteria can be transformed into deadly Smooth bacteria when they are mixed with the cell components of Smooth bacteria. Explain why Griffiths needed to carry out experiments 1 to 3 in order to draw these conclusions from Experiment 4. ...
Document
... Heterozygote- A person possessing two different forms of a particular gene, one inherited from each parent. Alleles- One member of a pair of series of genes that occupy a specific position on a specific chromosome. Dominant- Exercising the most influence or control. Recessive- Genetics. Of, relatin ...
... Heterozygote- A person possessing two different forms of a particular gene, one inherited from each parent. Alleles- One member of a pair of series of genes that occupy a specific position on a specific chromosome. Dominant- Exercising the most influence or control. Recessive- Genetics. Of, relatin ...
Ch 11 homework
... 6. The feature of "sticky ends" that makes them especially useful in DNA recombination is their ability to (1) A) bind to DNA and thereby activate transcription. B) bind to ribosomes and thereby activate translation. C) form hydrogen-bonded base pairs with complementary single-stranded stretches of ...
... 6. The feature of "sticky ends" that makes them especially useful in DNA recombination is their ability to (1) A) bind to DNA and thereby activate transcription. B) bind to ribosomes and thereby activate translation. C) form hydrogen-bonded base pairs with complementary single-stranded stretches of ...
mutations
... Somatic mutations: mutations that take place in the body cells DNA , but do not affect their offspring. FYI- albinism can be the result of a somatic or germ-line mutation ...
... Somatic mutations: mutations that take place in the body cells DNA , but do not affect their offspring. FYI- albinism can be the result of a somatic or germ-line mutation ...
AZBio Ch 13
... only the largest seeds to be planted in the spring. This practice continued for thousands of years. The original plant is believed to be extinct, but the modern corn plant flourishes. ...
... only the largest seeds to be planted in the spring. This practice continued for thousands of years. The original plant is believed to be extinct, but the modern corn plant flourishes. ...
Genetics Study Guide
... 15. What is it called when cells are copied with half the number of chromosomes? 16. What factors have an influence on your traits? 17. Why do sex-linked disorders occur more often in males? 18. Three bases code for one ______. 19. What determines how tall you grow and whether your hair is curly or ...
... 15. What is it called when cells are copied with half the number of chromosomes? 16. What factors have an influence on your traits? 17. Why do sex-linked disorders occur more often in males? 18. Three bases code for one ______. 19. What determines how tall you grow and whether your hair is curly or ...
ws: DNA Alphabet Activity
... “A Coded Alphabet.” Identify the “start” and “stop” codes on the Coded Alphabet. These codes indicate where each DNA sequence begins and ends. Use the Coded Alphabet to de-code each DNA Sequence and write them in the spaces below. De-Coded Sentences #1: __________________________________________ ...
... “A Coded Alphabet.” Identify the “start” and “stop” codes on the Coded Alphabet. These codes indicate where each DNA sequence begins and ends. Use the Coded Alphabet to de-code each DNA Sequence and write them in the spaces below. De-Coded Sentences #1: __________________________________________ ...
Viruses
... • Use infected cell to produce more viruses • Capsid: protein coat surrounding DNA/RNA core • bacteriophage – virus that infects bacteria ...
... • Use infected cell to produce more viruses • Capsid: protein coat surrounding DNA/RNA core • bacteriophage – virus that infects bacteria ...
BIOLOGY 207 - Dr.McDermid Lecture #1: DNA is the Genetic Material
... Radioisotope 32P to follow DNA; P not found in protein 35S labels protein; S not found in DNA Results 35S protein -> 32P DNA -> Conclusion: If DNA is the hereditary material then: 1) How do cells replicate their DNA? 2) How is genetic information stored? 3) How do mutations occur? 1953 - DNA Structu ...
... Radioisotope 32P to follow DNA; P not found in protein 35S labels protein; S not found in DNA Results 35S protein -> 32P DNA -> Conclusion: If DNA is the hereditary material then: 1) How do cells replicate their DNA? 2) How is genetic information stored? 3) How do mutations occur? 1953 - DNA Structu ...
DNA Extraction Glucose and salt are : added to increase the osmotic
... EDTA protects the DNA from degradative enzymes (called DNAses); EDTA binds divalent cations that are necessary for DNAse activity. NaOH and SDS (a detergent) : The alkaline mixtures ruptures the cells, and the SDS detergent breaks apart the lipid membrane and solubilizes cellular proteins. NaOH also ...
... EDTA protects the DNA from degradative enzymes (called DNAses); EDTA binds divalent cations that are necessary for DNAse activity. NaOH and SDS (a detergent) : The alkaline mixtures ruptures the cells, and the SDS detergent breaks apart the lipid membrane and solubilizes cellular proteins. NaOH also ...