CST Review
... functions of DNA, RNA, and protein. BI1. d. Students know the central dogma of molecular biology outlines the flow of information from transcription of ribonucleic acid (RNA) in the nucleus to translation of proteins on ribosomes in the cytoplasm. BI2. a. Students know meiosis is an early step in se ...
... functions of DNA, RNA, and protein. BI1. d. Students know the central dogma of molecular biology outlines the flow of information from transcription of ribonucleic acid (RNA) in the nucleus to translation of proteins on ribosomes in the cytoplasm. BI2. a. Students know meiosis is an early step in se ...
CST Review
... functions of DNA, RNA, and protein. BI1. d. Students know the central dogma of molecular biology outlines the flow of information from transcription of ribonucleic acid (RNA) in the nucleus to translation of proteins on ribosomes in the cytoplasm. BI2. a. Students know meiosis is an early step in se ...
... functions of DNA, RNA, and protein. BI1. d. Students know the central dogma of molecular biology outlines the flow of information from transcription of ribonucleic acid (RNA) in the nucleus to translation of proteins on ribosomes in the cytoplasm. BI2. a. Students know meiosis is an early step in se ...
Study guideCh8
... because we are adding a chemical to create the methylguanine, which then pairs with the wrong base pair, instead of the base substation happening randomly). Base analogs can be introduced into the cells, which bind to the wrong base pair. How is this similar in resulting mutation to the presence of ...
... because we are adding a chemical to create the methylguanine, which then pairs with the wrong base pair, instead of the base substation happening randomly). Base analogs can be introduced into the cells, which bind to the wrong base pair. How is this similar in resulting mutation to the presence of ...
MUTATIONS TAKS QUESTIONS SPRING 2003 – 10: (22) The
... 10 If one nucleotide is omitted or accidentally repeated in the process of DNA duplication, which of the following is most likely to occur? F Gene deletion G* Gene mutation H Gene insertion J Gene segregation JULY 2006 – 11: 32 A deletion of a DNA base from a gene affects an organism by — F causing ...
... 10 If one nucleotide is omitted or accidentally repeated in the process of DNA duplication, which of the following is most likely to occur? F Gene deletion G* Gene mutation H Gene insertion J Gene segregation JULY 2006 – 11: 32 A deletion of a DNA base from a gene affects an organism by — F causing ...
History of Genetics
... • Genes often have several alleles: the same gene in the same chromosomal location, but with minor nucleotide changes that yield slightly different proteins. • For a given gene, many different alleles can exist in a population (members of the same species), but an individual diploid organism can hav ...
... • Genes often have several alleles: the same gene in the same chromosomal location, but with minor nucleotide changes that yield slightly different proteins. • For a given gene, many different alleles can exist in a population (members of the same species), but an individual diploid organism can hav ...
Fathers and Mothers of Genetics
... which were later named after him. The significance of Mendel's work was not recognized until the turn of the 20th century. Its rediscovery in the late 1800’s and early 1900’s prompted the foundation of genetics. ...
... which were later named after him. The significance of Mendel's work was not recognized until the turn of the 20th century. Its rediscovery in the late 1800’s and early 1900’s prompted the foundation of genetics. ...
Genetics practice test
... 8. The most important experimental result that suggested to Watson and Crick that DNA was in the form of a helix was A. the finding of Chargaff that DNA always had equal amounts of A and T and equal amounts of G and C. B. Griffith's results with transformation. C. the discovery that DNA is wound ...
... 8. The most important experimental result that suggested to Watson and Crick that DNA was in the form of a helix was A. the finding of Chargaff that DNA always had equal amounts of A and T and equal amounts of G and C. B. Griffith's results with transformation. C. the discovery that DNA is wound ...
Name:
... organic compounds v. inorganic compounds; 6 elements abundant in living things importance of water for living things – Why is it needed? How is it used? polar molecules v. non-polar molecules o “like dissolved like” cohesion v. adhesion; capillary action Functional groups – identify & desc ...
... organic compounds v. inorganic compounds; 6 elements abundant in living things importance of water for living things – Why is it needed? How is it used? polar molecules v. non-polar molecules o “like dissolved like” cohesion v. adhesion; capillary action Functional groups – identify & desc ...
Biotechnology and its applications - MrsGorukhomework
... genome of yeast in 1992 just for chromosome 3 which consisted of 315 357 nucleotides, took about 10 years.) Thought that DNA → RNA → proteins → control the body, based on that and looking at all the different phenotypes, figured we must have a lot of genes, 100, 000’s. Only about 25, 000. (doesn’t s ...
... genome of yeast in 1992 just for chromosome 3 which consisted of 315 357 nucleotides, took about 10 years.) Thought that DNA → RNA → proteins → control the body, based on that and looking at all the different phenotypes, figured we must have a lot of genes, 100, 000’s. Only about 25, 000. (doesn’t s ...
PositiveTest-DNAevidence
... thousands of people who might be a match for this DNA, the chance that this ...
... thousands of people who might be a match for this DNA, the chance that this ...
Cell Reproduction
... Model a section of a DNA molecule, showing its twisted-ladder structure. Label the the nitrogen bases, sugar, and phosphates. Make sure the nitrogen bases in your drawing are correctly paired. ...
... Model a section of a DNA molecule, showing its twisted-ladder structure. Label the the nitrogen bases, sugar, and phosphates. Make sure the nitrogen bases in your drawing are correctly paired. ...
DNA Barcoding
... plant and species have been identified Rate of extinction has increased from about 1 species per million to 1001000 species per million Most of these species have yet to be identified ...
... plant and species have been identified Rate of extinction has increased from about 1 species per million to 1001000 species per million Most of these species have yet to be identified ...
Organization of Eukaryotic DNA Dr: Hussein abdelaziz
... Nucleosome is formed of a histone core of 8 molecules of histones, 2 H2A, 2 H2B, 2 H3, & 2 H4, around which a segment of DNA double helix is wrapped nearly twice left handed super helical turns Organization of the DNA double strand in nucleosomes make it to look like beads in a string, the 10 nm ...
... Nucleosome is formed of a histone core of 8 molecules of histones, 2 H2A, 2 H2B, 2 H3, & 2 H4, around which a segment of DNA double helix is wrapped nearly twice left handed super helical turns Organization of the DNA double strand in nucleosomes make it to look like beads in a string, the 10 nm ...
DNA
... A always pairs with T and C always pairs with G. This is because of the number of bonds formed between the bases. Two hydrogen bonds form between A and T and three between C and G. Write the compliment for GGCTATTGGCA. ...
... A always pairs with T and C always pairs with G. This is because of the number of bonds formed between the bases. Two hydrogen bonds form between A and T and three between C and G. Write the compliment for GGCTATTGGCA. ...
Biology Chapter 11-1
... -By selecting the most productive plants or animals to produce the next generation, people have found that the productivity d domesticated species can gradually be increased. Restriction Enzymes - Each restriction enzyme is instructed to cut at a presides place in a DNA sequences. -These enzymes mak ...
... -By selecting the most productive plants or animals to produce the next generation, people have found that the productivity d domesticated species can gradually be increased. Restriction Enzymes - Each restriction enzyme is instructed to cut at a presides place in a DNA sequences. -These enzymes mak ...
... 11. Which type of conservation measures – in situ or ex-situ will help the larger number of species to survive? Explain. (2) 12. What is interspecific hybridization. Give an example? (2) 13. What are the advantages of breeding for disease-resistance in plants? (2) 14. Which law of Mendel is universa ...
DNA Replication and recombination
... Is the Genetic Material Protein or DNA? • Many favored proteins until the mid-1940’s. • DNA is simple chemically (4 nucleotides known); how could it then hold complex ...
... Is the Genetic Material Protein or DNA? • Many favored proteins until the mid-1940’s. • DNA is simple chemically (4 nucleotides known); how could it then hold complex ...
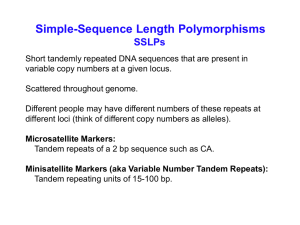
Using microsatellites as molecular markers
... microsatellites to amplify microsatellite-containing region. Depending on number of microsatellite repeats, will get different lengths PCR products (many different possible alleles, not just two) ...
... microsatellites to amplify microsatellite-containing region. Depending on number of microsatellite repeats, will get different lengths PCR products (many different possible alleles, not just two) ...
Okazaki Fragments
... discontinuously against overall direction of replication This strand is made in MANY short segments It is replicated from the replication fork toward the origin Leading Strand ...
... discontinuously against overall direction of replication This strand is made in MANY short segments It is replicated from the replication fork toward the origin Leading Strand ...
Lesson 1 DNA and proteins
... • A genome is the entire sequence of DNA of an organism (about 25000 genes in the human genome). • Each gene occupies a specific locus (position) on a chromosome and each chromosome consists of one molecule of DNA. • The DNA is wrapped around basic histone proteins (Chromatin) • In between genes is ...
... • A genome is the entire sequence of DNA of an organism (about 25000 genes in the human genome). • Each gene occupies a specific locus (position) on a chromosome and each chromosome consists of one molecule of DNA. • The DNA is wrapped around basic histone proteins (Chromatin) • In between genes is ...
PowerPoint Presentation - No Slide Title
... researcher to determine genotype at the most fundamental level - the order of bases along the DNA molecule. This method uses DNA polymerase to synthesize new DNA strands in the presence of dideoxy nucleotides. Since these lack a 3’ OH group, whenever one is incorporated into the growing strand, that ...
... researcher to determine genotype at the most fundamental level - the order of bases along the DNA molecule. This method uses DNA polymerase to synthesize new DNA strands in the presence of dideoxy nucleotides. Since these lack a 3’ OH group, whenever one is incorporated into the growing strand, that ...
Unit 3
... 27. Relate Mendel’s “law of independent assortment” to the behavior of chromosomes during meiosis; describe a situation in which the “law” of independent assortment would be violated. Breeding experiments allowed early geneticists to study and “map” genes, even though there was no way to “see” the g ...
... 27. Relate Mendel’s “law of independent assortment” to the behavior of chromosomes during meiosis; describe a situation in which the “law” of independent assortment would be violated. Breeding experiments allowed early geneticists to study and “map” genes, even though there was no way to “see” the g ...
Clike here - University of Evansville Faculty Web sites
... researcher to determine genotype at the most fundamental level - the order of bases along the DNA molecule. This method uses DNA polymerase to synthesize new DNA strands in the presence of dideoxy nucleotides. Since these lack a 3’ OH group, whenever one is incorporated into the growing strand, that ...
... researcher to determine genotype at the most fundamental level - the order of bases along the DNA molecule. This method uses DNA polymerase to synthesize new DNA strands in the presence of dideoxy nucleotides. Since these lack a 3’ OH group, whenever one is incorporated into the growing strand, that ...
rnalabreport_1
... Links - What links does the site contain? A reliable website will offer links to other reliable websites, not to "junk" sites. ...
... Links - What links does the site contain? A reliable website will offer links to other reliable websites, not to "junk" sites. ...
Nucleic acid double helix

In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, and is a fundamental component in determining its tertiary structure. The term entered popular culture with the publication in 1968 of The Double Helix: A Personal Account of the Discovery of the Structure of DNA, by James Watson.The DNA double helix polymer of nucleic acids, held together by nucleotides which base pair together. In B-DNA, the most common double helical structure, the double helix is right-handed with about 10–10.5 base pairs per turn. This translates into about 20-21 nucleotides per turn. The double helix structure of DNA contains a major groove and minor groove. In B-DNA the major groove is wider than the minor groove. Given the difference in widths of the major groove and minor groove, many proteins which bind to B-DNA do so through the wider major groove.