last of Chapter 11, all of Chapter 12
... toad genome, but more are needed: 4000-fold increase in gene copy number via rolling circle replicating extrachromosomal rRNA genes, over 3 weeks during oogenesis). ...
... toad genome, but more are needed: 4000-fold increase in gene copy number via rolling circle replicating extrachromosomal rRNA genes, over 3 weeks during oogenesis). ...
History of Genetics
... • 1953: James Watson and Francis Crick determine the structure of the DNA molecule, which leads directly to knowledge of how it replicates • 1966: Marshall Nirenberg solves the genetic code, showing that 3 DNA bases code for one amino acid. • 1972: Stanley Cohen and Herbert Boyer combine DNA from tw ...
... • 1953: James Watson and Francis Crick determine the structure of the DNA molecule, which leads directly to knowledge of how it replicates • 1966: Marshall Nirenberg solves the genetic code, showing that 3 DNA bases code for one amino acid. • 1972: Stanley Cohen and Herbert Boyer combine DNA from tw ...
Lecture 10: Nucleic acids (DNA & RNA)
... viruses). 2) Ribonucleic acid (RNA): in some viruses, RNA serves as the genetic material. Nucleic acids store and transmit genetic information المعلومات الوراثية Organisms inherit ترثDNA from their parents. Each DNA molecule is very long and usually consists of hundreds to thousands of ge ...
... viruses). 2) Ribonucleic acid (RNA): in some viruses, RNA serves as the genetic material. Nucleic acids store and transmit genetic information المعلومات الوراثية Organisms inherit ترثDNA from their parents. Each DNA molecule is very long and usually consists of hundreds to thousands of ge ...
Review Questions Chapter 12 Review Sheet
... 3. Name the scientists who helped discover the shape of the DNA molecule using a technique known as X-ray diffraction. Rosie Franklin 4. Name the scientists who figured out the correct arrangement of molecules to build the first correct model of DNA. James Watson and Francis Crick 5. Through the pro ...
... 3. Name the scientists who helped discover the shape of the DNA molecule using a technique known as X-ray diffraction. Rosie Franklin 4. Name the scientists who figured out the correct arrangement of molecules to build the first correct model of DNA. James Watson and Francis Crick 5. Through the pro ...
File - Ms. Wilson`s Biology Class
... Read the text below and answer the following questions: 1. In order to speed up the copying process (replication), DNA replication begins at ___________ locations along each chromosome. 2. The two DNA strands are pulled apart and copied in both directions at the rate of about _________ nucleotides p ...
... Read the text below and answer the following questions: 1. In order to speed up the copying process (replication), DNA replication begins at ___________ locations along each chromosome. 2. The two DNA strands are pulled apart and copied in both directions at the rate of about _________ nucleotides p ...
Instructional Objectives—DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis
... Objective 3: Explain how nucleotides are arranged in DNA and RNA. If DNA is a ladder, where are sugars and phosphates located? Nitrogen bases? DNA is double stranded, but RNA is ___________________________ Objective 4: Relate the structure of DNA to its function in carrying genetic information. ...
... Objective 3: Explain how nucleotides are arranged in DNA and RNA. If DNA is a ladder, where are sugars and phosphates located? Nitrogen bases? DNA is double stranded, but RNA is ___________________________ Objective 4: Relate the structure of DNA to its function in carrying genetic information. ...
Transgenic Organisms
... species; possible because of the universal nature of the genetic code – Fig. 13-12 1. Microorganisms – easy to grow, divide rapidly, can be used to produce human proteins 2. Animals can be used to improve food supply, or to study effect of human diseases 3. Plants – genes can be implanted that provi ...
... species; possible because of the universal nature of the genetic code – Fig. 13-12 1. Microorganisms – easy to grow, divide rapidly, can be used to produce human proteins 2. Animals can be used to improve food supply, or to study effect of human diseases 3. Plants – genes can be implanted that provi ...
4.4 Genetic engineering and biotechnology – summary of mark
... 4.4.10 Discuss the potential benefits and possible harmful effects of one example of genetic modification. ...
... 4.4.10 Discuss the potential benefits and possible harmful effects of one example of genetic modification. ...
File
... • Bacterial genomes are larger than viral genomes, but much smaller than a typical eukaryotic genome • Most DNA in a bacterium is found in a single circular chromosome that is composed of double-stranded DNA found in the nucleiod region. ...
... • Bacterial genomes are larger than viral genomes, but much smaller than a typical eukaryotic genome • Most DNA in a bacterium is found in a single circular chromosome that is composed of double-stranded DNA found in the nucleiod region. ...
Chapter 13 Review answers
... will not make you sick Gene Therapy – treat genetic disorders by transferring normal gene into cells that lack them; replacement gene is expressed in person’s cell 98%, therefore 2% codes for proteins Process of altering the genetic material of cells or organisms to allow them to make new substances ...
... will not make you sick Gene Therapy – treat genetic disorders by transferring normal gene into cells that lack them; replacement gene is expressed in person’s cell 98%, therefore 2% codes for proteins Process of altering the genetic material of cells or organisms to allow them to make new substances ...
Chapter 12 DNA and RNA ANSWER KEY
... acids used in the construction of proteins. 8. Answers may vary. Having a sequence of DNA that could be edited into several different mRNA molecules makes it possible for a single gene to produce several different proteins specifically used in different tissues. This allows a cell to carry less gene ...
... acids used in the construction of proteins. 8. Answers may vary. Having a sequence of DNA that could be edited into several different mRNA molecules makes it possible for a single gene to produce several different proteins specifically used in different tissues. This allows a cell to carry less gene ...
Genetic Engineering
... pancreas of cows and pigs (limited production) • Today, most human insulin comes from human insulin-making genes transferred into simple cells such as bacteria or baker’s yeast (unlimited supply) – Identical to insulin made by the human pancreas ...
... pancreas of cows and pigs (limited production) • Today, most human insulin comes from human insulin-making genes transferred into simple cells such as bacteria or baker’s yeast (unlimited supply) – Identical to insulin made by the human pancreas ...
DNA and RNA - Xavier High School
... • Hershey-Chase are testing to see if DNA is the molecule that carries genetic information. ...
... • Hershey-Chase are testing to see if DNA is the molecule that carries genetic information. ...
Evelyn Section A
... THE STRUCTURE AND SIGNIFICANT OF DNA TO LIFE The DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is "a complex, high-molecular-weight biochemical macromolecule composed of nucleotide chains that convey genetic information’' (1, 4). It is regularly in the form of a double helix, having the hereditary instructions indica ...
... THE STRUCTURE AND SIGNIFICANT OF DNA TO LIFE The DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is "a complex, high-molecular-weight biochemical macromolecule composed of nucleotide chains that convey genetic information’' (1, 4). It is regularly in the form of a double helix, having the hereditary instructions indica ...
HLA typing of renal patients and investigation of disease
... which separates the DNA according to its molecular size. The contents of the plates are loaded into wells in an agarose gel, which provides a solid but porous matrix. The samples are held to the bottom of the well by the glycerol in the PCR mixture. The negatively charged DNA moves through the gel t ...
... which separates the DNA according to its molecular size. The contents of the plates are loaded into wells in an agarose gel, which provides a solid but porous matrix. The samples are held to the bottom of the well by the glycerol in the PCR mixture. The negatively charged DNA moves through the gel t ...
8.2 All Genetic Information Is Encoded in the Structure of DNA
... THE STRUCTURE OF DNA OR RNA • DNA As the Source of Genetic Information • Watson and Crick’s discovery of the three-dimensional structure of DNA • X-ray diffraction image of DNA ...
... THE STRUCTURE OF DNA OR RNA • DNA As the Source of Genetic Information • Watson and Crick’s discovery of the three-dimensional structure of DNA • X-ray diffraction image of DNA ...
7 October 2015 The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences has
... Each day our DNA is damaged by UV radiation, free radicals and other carcinogenic substances, but even without such external attacks, a DNA molecule is inherently unstable. Thousands of spontaneous changes to a cell’s genome occur on a daily basis. Furthermore, defects can also arise when DNA is cop ...
... Each day our DNA is damaged by UV radiation, free radicals and other carcinogenic substances, but even without such external attacks, a DNA molecule is inherently unstable. Thousands of spontaneous changes to a cell’s genome occur on a daily basis. Furthermore, defects can also arise when DNA is cop ...
SBI4U: Molecular Genetics Unit Review
... 4. When new DNA or RNA is synthesized, in which direction does it grow? 5’ -> 3’ because polymerases can only add nucleotides onto the 3’ end 5. What are two different kinds of bonds that hold nucleic acids together? Hydrogen bonds (between nitrogenous bases) and phosphodiester bonds (between nucleo ...
... 4. When new DNA or RNA is synthesized, in which direction does it grow? 5’ -> 3’ because polymerases can only add nucleotides onto the 3’ end 5. What are two different kinds of bonds that hold nucleic acids together? Hydrogen bonds (between nitrogenous bases) and phosphodiester bonds (between nucleo ...
Microbial Genetics
... • Analogs for bases – 5-bromo-uracil for thymine (5BU can pair with G as well as with A) – 2-aminopurine for adenine (2AP can pair with C as well as with T) ...
... • Analogs for bases – 5-bromo-uracil for thymine (5BU can pair with G as well as with A) – 2-aminopurine for adenine (2AP can pair with C as well as with T) ...
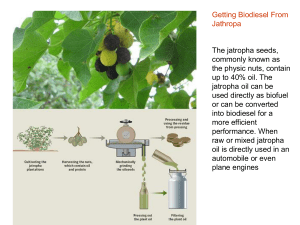
Jatropha genotyping In Gh Pu QR In Gh Pu QR 13 primer pairs
... commonly known as the physic nuts, contain up to 40% oil. The jatropha oil can be used directly as biofuel or can be converted into biodiesel for a more efficient performance. When raw or mixed jatropha oil is directly used in an automobile or even plane engines ...
... commonly known as the physic nuts, contain up to 40% oil. The jatropha oil can be used directly as biofuel or can be converted into biodiesel for a more efficient performance. When raw or mixed jatropha oil is directly used in an automobile or even plane engines ...
Nucleic acid double helix

In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, and is a fundamental component in determining its tertiary structure. The term entered popular culture with the publication in 1968 of The Double Helix: A Personal Account of the Discovery of the Structure of DNA, by James Watson.The DNA double helix polymer of nucleic acids, held together by nucleotides which base pair together. In B-DNA, the most common double helical structure, the double helix is right-handed with about 10–10.5 base pairs per turn. This translates into about 20-21 nucleotides per turn. The double helix structure of DNA contains a major groove and minor groove. In B-DNA the major groove is wider than the minor groove. Given the difference in widths of the major groove and minor groove, many proteins which bind to B-DNA do so through the wider major groove.