are all made up of specialized nerve cells called neurons. Neurons
... typical fat cell is 0.1mm in diameter - some may be twice that size and others are half that size. The fat stored is in a semi-liquid state, and is composed primarily of triglycerides and cholesteryl ester. An average adult has 30 billion fat cells with a weight of 30 lbs. If excess weight is gained ...
... typical fat cell is 0.1mm in diameter - some may be twice that size and others are half that size. The fat stored is in a semi-liquid state, and is composed primarily of triglycerides and cholesteryl ester. An average adult has 30 billion fat cells with a weight of 30 lbs. If excess weight is gained ...
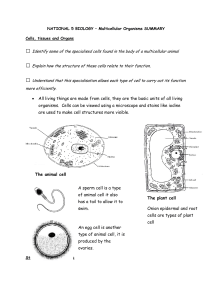
• All living things are made from cells, they are the basic units of all
... NATIONAL 5 BIOLOGY – Multicellular Organisms SUMMARY Cells, tissues and Organs ...
... NATIONAL 5 BIOLOGY – Multicellular Organisms SUMMARY Cells, tissues and Organs ...
• All living things are made from cells, they are the basic units of all
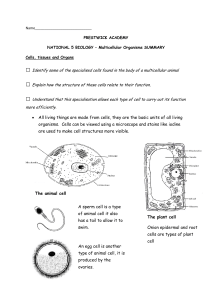
... PRESTWICK ACADEMY NATIONAL 5 BIOLOGY – Multicellular Organisms SUMMARY Cells, tissues and Organs ...
... PRESTWICK ACADEMY NATIONAL 5 BIOLOGY – Multicellular Organisms SUMMARY Cells, tissues and Organs ...
Unit IV- Nervous System
... 2. Name the structures through which food passes in the alimentary canal of man from entrance to exit include sphincters 4. For the following secretion state where they are produced and what they help digest: a. Saliva - carbohydrate digestion b. Gastric Juice - breaks down proteins, and HCl and mu ...
... 2. Name the structures through which food passes in the alimentary canal of man from entrance to exit include sphincters 4. For the following secretion state where they are produced and what they help digest: a. Saliva - carbohydrate digestion b. Gastric Juice - breaks down proteins, and HCl and mu ...
Introduction to Cells
... All Cells Need? • Ok, regardless if an organism is unicellular or multicellular – prokaryotic or eukaryotic…what do they all need to function???? ...
... All Cells Need? • Ok, regardless if an organism is unicellular or multicellular – prokaryotic or eukaryotic…what do they all need to function???? ...
Document
... • As life evolved on earth a multiplicity of physical factors participated in the complicated selection process. For many factors, there are clear examples of the role of physical forces in determining the pathways in evolution. • A notable exception is gravity. The force of gravity has been relativ ...
... • As life evolved on earth a multiplicity of physical factors participated in the complicated selection process. For many factors, there are clear examples of the role of physical forces in determining the pathways in evolution. • A notable exception is gravity. The force of gravity has been relativ ...
Module A-1 (Principles of Biology)
... C) all cells regenerate and contain the same basic structures D) organisms that lack certain organelles reproduce by binary fission 21. Base your answer to the following question on the diagrams below of two cells, X and Y, and on your knowledge of biology. ...
... C) all cells regenerate and contain the same basic structures D) organisms that lack certain organelles reproduce by binary fission 21. Base your answer to the following question on the diagrams below of two cells, X and Y, and on your knowledge of biology. ...
ANATOMICAL POSITION
... 1. Cells are of various heights. All cells rest on the basement membrane, but only the tallest cells reach the free surface. Variation in height of the cells and the location of nuclei give the appearance of a stratified epithelium. Frequently ciliated. ...
... 1. Cells are of various heights. All cells rest on the basement membrane, but only the tallest cells reach the free surface. Variation in height of the cells and the location of nuclei give the appearance of a stratified epithelium. Frequently ciliated. ...
PP text version
... receptors for growth factors are present or active on some cells and not on others. e.g. Speeman & Mangold’s organizer ...
... receptors for growth factors are present or active on some cells and not on others. e.g. Speeman & Mangold’s organizer ...
Body Systems
... below epidermal layer, consists of nerve cells , blood vessels, hair follicles and sweat glands ...
... below epidermal layer, consists of nerve cells , blood vessels, hair follicles and sweat glands ...
Unit 2 - Cells and Body Systems 1.0 Characteristics of Living Things
... 2.0 Cells play a vital role ...
... 2.0 Cells play a vital role ...
./ ` . `.`4 Body Tissues 13. Figure 3-6: A. Simple squamous epLthelium
... 25. Generally speaking , stratified ephheHa consisting of several cell layers are mo re effective w here abrasion is a pro blem than are simple epithe lia (consisting of one cell layer). 26. Streptomycin inhibits bacte rial protein synthesis. If the bacreria are unable r.o synthes ize new protei ...
... 25. Generally speaking , stratified ephheHa consisting of several cell layers are mo re effective w here abrasion is a pro blem than are simple epithe lia (consisting of one cell layer). 26. Streptomycin inhibits bacte rial protein synthesis. If the bacreria are unable r.o synthes ize new protei ...
CENTRO ESCOLAR UNIVERSITY Biological Sciences Department
... Licensure Exam for Teachers (LET) Table of Specification (TOS) Competencies 1. Describe the development of Cell Theory 2. Differentiate prokaryotic from eukaryotic cell 3. Compare the structure and function of a plant and an animal cell 4. Explain the process of transporting materials into and out ...
... Licensure Exam for Teachers (LET) Table of Specification (TOS) Competencies 1. Describe the development of Cell Theory 2. Differentiate prokaryotic from eukaryotic cell 3. Compare the structure and function of a plant and an animal cell 4. Explain the process of transporting materials into and out ...
Cells - Body Systems
... • cells work together to help your body function well • cells come in different shape and sizes ...
... • cells work together to help your body function well • cells come in different shape and sizes ...
Human Body Systems
... • Bacteria are very useful to the human digestive system because they produce enzymes that digest the polysaccharides in plant cell walls. When we eat plant material, some of it contributes to the fiber in our diet, which is good for a healthy colon, but without the enzymes released by friendly bact ...
... • Bacteria are very useful to the human digestive system because they produce enzymes that digest the polysaccharides in plant cell walls. When we eat plant material, some of it contributes to the fiber in our diet, which is good for a healthy colon, but without the enzymes released by friendly bact ...
Key - Edquest
... insects hiding in the bark of trees seeds and nuts found on the ground Organisms have different structures for similar functions. An example that illustrates this would be … bird wings – spiracles human lung – snake tongue barnacles – web feet fish gills – plant leaves There are two types adaptation ...
... insects hiding in the bark of trees seeds and nuts found on the ground Organisms have different structures for similar functions. An example that illustrates this would be … bird wings – spiracles human lung – snake tongue barnacles – web feet fish gills – plant leaves There are two types adaptation ...
The Tissue Level of Organization
... – 3) Smooth: non-striated & composed of long, slender singlenucleus cells • Line blood vessels, urinary bladder, resp. & digest. tracts • Under INVOLUNTARY control of nervous system ...
... – 3) Smooth: non-striated & composed of long, slender singlenucleus cells • Line blood vessels, urinary bladder, resp. & digest. tracts • Under INVOLUNTARY control of nervous system ...
Outline
... __________ two centrioles that are functional during animal cell division Endoplasmic reticulum Provides passage for the ___________ of substances in the cytoplasm Mitochondria Serve as sites of cellular respiration and energy production Store ATP Golgi apparatus Manufactures ____________ and packag ...
... __________ two centrioles that are functional during animal cell division Endoplasmic reticulum Provides passage for the ___________ of substances in the cytoplasm Mitochondria Serve as sites of cellular respiration and energy production Store ATP Golgi apparatus Manufactures ____________ and packag ...
LT #4 I can describe that cells differentiate to form
... LT #4 I can express that cells differentiate to form specialized cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms. ...
... LT #4 I can express that cells differentiate to form specialized cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms. ...
Honors Biology Chapter 8 Mitosis Notes 3-13
... Duplication Eukaryotic cells are generally larger than prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells have many more genes than prokaryotic cells and they are located on more than one chromosome. Genetic material located in the nucleus. Genetic Material Terms: Chromatin – diffuse mass of long, thin fiber ...
... Duplication Eukaryotic cells are generally larger than prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells have many more genes than prokaryotic cells and they are located on more than one chromosome. Genetic material located in the nucleus. Genetic Material Terms: Chromatin – diffuse mass of long, thin fiber ...
Notes Pages
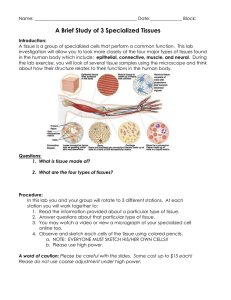
... All cells were formed in your body from just one cell, the fertilized egg. Cells take on different jobs, (specialize) as they are formed in the egg. Cells that all work together to form a specific function form tissues. There are four types of tissues: o Epithelial Tissue Skin is an epithelial tis ...
... All cells were formed in your body from just one cell, the fertilized egg. Cells take on different jobs, (specialize) as they are formed in the egg. Cells that all work together to form a specific function form tissues. There are four types of tissues: o Epithelial Tissue Skin is an epithelial tis ...
Neuronal lineage marker

A Neuronal lineage marker is an endogenous tag that is expressed in different cells along neurogenesis and differentiated cells as neurons. It allows detection and identification of cells by using different techniques. A neuronal lineage marker can be either DNA, mRNA or RNA expressed in a cell of interest. It can also be a protein tag, as a partial protein, a protein or a epitope that discriminates between different cell types or different states of a common cell. An ideal marker is specific to a given cell type in normal conditions and/or during injury. Cell markers are very valuable tools for examining the function of cells in normal conditions as well as during disease. The discovery of various proteins specific to certain cells led to the production of cell-type-specific antibodies that have been used to identify cells.The techniques used for its detection can be immunohistochemistry, immunocytochemistry, methods that utilize transcriptional modulators and site-specific recombinases to label specific neuronal population, in situ hybridization or fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). A neuronal lineage marker can be a neuronal antigen that is recognized by an autoantibody for example Hu, which is highly restricted to neuronal nuclei. By immunohistochemistry, anti-Hu stains the nuclei of neurons. To localize mRNA in brain tissue, one can use a fragment of DNA or RNA as a neuronal lineage marker, a hybridization probe that detects the presence of nucleotide sequences that are complementary to the sequence in the probe. This technique is known as in situ hybridization. Its application have been carried out in all different tissues, but particularly useful in neuroscience. Using this technique, it is possible to locate gene expression to specific cell types in specific regions and observe how changes in this distribution occur throughout the development and correlate with the behavioral manipulations.Although immunohistochemistry is the staple methodology for identifying neuronal cell types, since it is relatively low in cost and a wide range of immunohistochemical markers are available to help distinguish the phenotype of cells in the brain, sometimes it is time-consuming to produce a good antibody. Therefore, one of the most convenient methods for the rapid assessment of the expression of a cloned ion channel could be in situ hybridization histochemistry.After cells are isolated from tissue or differentiated from pluripotent precursors, the resulting population needs to be characterized to confirm whether the target population has been obtained. Depending on the goal of a particular study, one can use neural stem cells markers, neural progenitor cell markers, neuron markers or PNS neuronal markers.