7-Levels of Organization lesson 7
... • Identify an activity you were involved in recently. What systems of your body cooperated to make the activity possible? ...
... • Identify an activity you were involved in recently. What systems of your body cooperated to make the activity possible? ...
Chap 2 - CRCBiologyY11
... Other organelles • Vacuoles – large fluid-filled sacs, mainly found in plant cells or single celled animals. Contain water and some dissolved solutes, can have a contractile mechanism to help pump water out of some freshwater protists. • Endosomes – involved with endocytosis in animal cells, pass n ...
... Other organelles • Vacuoles – large fluid-filled sacs, mainly found in plant cells or single celled animals. Contain water and some dissolved solutes, can have a contractile mechanism to help pump water out of some freshwater protists. • Endosomes – involved with endocytosis in animal cells, pass n ...
Keystone Countdown
... 10. is the space between the cell membrane and nucleus? 11. contains enzymes that detoxify cells? 12. The three parts of the cell theory are? 13. What are some differences between plant and animal cells? ...
... 10. is the space between the cell membrane and nucleus? 11. contains enzymes that detoxify cells? 12. The three parts of the cell theory are? 13. What are some differences between plant and animal cells? ...
Organization and Regulation of Body Systems Tissues, Organs and Nervous, Endocrine and Reproductive
... 2. GABA is inhibitory neurotransmitter 3. Dopamine: Critical role in the reward system , makes you feel good. (also implicated in Parkinson's and schizophrenia) Why are Nicotine, Cocaine, and Heroin Addictive Nicotine causes neurons to release dopamine Cocaine blocks the reentering of dopamine ...
... 2. GABA is inhibitory neurotransmitter 3. Dopamine: Critical role in the reward system , makes you feel good. (also implicated in Parkinson's and schizophrenia) Why are Nicotine, Cocaine, and Heroin Addictive Nicotine causes neurons to release dopamine Cocaine blocks the reentering of dopamine ...
Human Systems and Transport Across the
... The immune system uses many cellular features, such as proteins and carbohydrates, to identify foreign invaders and protect our bodies from harm. Many of the functions that occur within the human body are a result of some form of transportation or communication. Communication is the backbone of the ...
... The immune system uses many cellular features, such as proteins and carbohydrates, to identify foreign invaders and protect our bodies from harm. Many of the functions that occur within the human body are a result of some form of transportation or communication. Communication is the backbone of the ...
March 21,200O Food and Drug Administration
... in the lungs and other organs. Selem~“is *ar%s’sem%ltrace mmeral that works to prevent oxidative cell damage,a major contributor to cellular destruction. The body needs Selenium to produce glutathione peroxidase,a critical enzyme which is necessaryfor the antioxidant protection of red blood cells an ...
... in the lungs and other organs. Selem~“is *ar%s’sem%ltrace mmeral that works to prevent oxidative cell damage,a major contributor to cellular destruction. The body needs Selenium to produce glutathione peroxidase,a critical enzyme which is necessaryfor the antioxidant protection of red blood cells an ...
Microbiology/Cells/Nutrition Vocabulary 1 Abiotic
... 8. Bacteria- one-celled prokaryotes, some of which cause disease. 9. Binary Fission- a form of asexual reproduction, 10. Biotechnology- the manipulation of living things to make useful products. 11. Biotic- living part of an ecosystem. 12. Cancer- uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. 1 ...
... 8. Bacteria- one-celled prokaryotes, some of which cause disease. 9. Binary Fission- a form of asexual reproduction, 10. Biotechnology- the manipulation of living things to make useful products. 11. Biotic- living part of an ecosystem. 12. Cancer- uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. 1 ...
Stem Cell Line Glossary Adult stem cells: Also known as somatic
... Stem cells that can give rise to several different types of cells, but the number is limited. Niches: Places in the body where adult stem cells can be found. This microenvironment is a storage space for stem cells and will ultimately determine what the stem cell will become. The niche contains stimu ...
... Stem cells that can give rise to several different types of cells, but the number is limited. Niches: Places in the body where adult stem cells can be found. This microenvironment is a storage space for stem cells and will ultimately determine what the stem cell will become. The niche contains stimu ...
Cell
... reproduce to form new cells. This results in growth occurring all over the organism’s body giving a rounded shape. ...
... reproduce to form new cells. This results in growth occurring all over the organism’s body giving a rounded shape. ...
The Cell
... • allows for control of materials in and out of the cell (homeostasis of cells) State one way in which the following organelles work together: (3 marks) a) lysosomes and phagocytic vesicles. • Fuse together to digest bacteria or viruses b) microtubules and cilia • cilia are made of of microtubules; ...
... • allows for control of materials in and out of the cell (homeostasis of cells) State one way in which the following organelles work together: (3 marks) a) lysosomes and phagocytic vesicles. • Fuse together to digest bacteria or viruses b) microtubules and cilia • cilia are made of of microtubules; ...
Study
... There are two types of cells. Cells that do not have their genetic material enclosed in a nucleus are called prokaryotic. Bacterial cells are prokaryotic. Cells that do have ...
... There are two types of cells. Cells that do not have their genetic material enclosed in a nucleus are called prokaryotic. Bacterial cells are prokaryotic. Cells that do have ...
The Cell
... allows for control of materials in and out of the cell (homeostasis of cells) State one way in which the following organelles work together: (3 marks) a) lysosomes and phagocytic vesicles. Fuse together to digest bacteria or viruses b) microtubules and cilia cilia are made of of microtubules; ...
... allows for control of materials in and out of the cell (homeostasis of cells) State one way in which the following organelles work together: (3 marks) a) lysosomes and phagocytic vesicles. Fuse together to digest bacteria or viruses b) microtubules and cilia cilia are made of of microtubules; ...
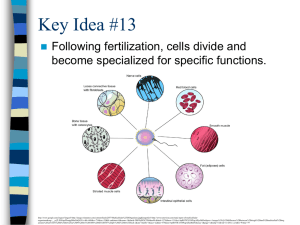
Key Idea #9 - Mona Shores Blogs
... engineers, farmers, etc, everyone learns a specific skill which they can then use to help everyone else. Just like people, cells specialize in important jobs. ...
... engineers, farmers, etc, everyone learns a specific skill which they can then use to help everyone else. Just like people, cells specialize in important jobs. ...
Additional Biology
... When gametes join at fertilisation, a single body cell with new pairs of chromosomes is formed. A new individual then develops by this cell repeatedly dividing by mitosis Most types of animal cells differentiate at an early stage whereas many plant cells retain the ability to differentiate throughou ...
... When gametes join at fertilisation, a single body cell with new pairs of chromosomes is formed. A new individual then develops by this cell repeatedly dividing by mitosis Most types of animal cells differentiate at an early stage whereas many plant cells retain the ability to differentiate throughou ...
Structural Levels of Organization
... Nerve cells: are long and may have the length of several feet (from muscles of the foot to the brain) ...
... Nerve cells: are long and may have the length of several feet (from muscles of the foot to the brain) ...
Grade 8 Science Cells and Systems
... gastric juices, cilia hairs; secondary defense system - white blood cells, antibodies ...
... gastric juices, cilia hairs; secondary defense system - white blood cells, antibodies ...
Chapter 5 Tissues
... -bind structures, provide support, serve as framework, fill spaces, store fat, produce blood cells, protect against infections, and repair tissue damage matrix-intercellular material of connective tissue Major Cell types 1. Fibroblasts- produce fibers by secreting proteins into the matrix - most com ...
... -bind structures, provide support, serve as framework, fill spaces, store fat, produce blood cells, protect against infections, and repair tissue damage matrix-intercellular material of connective tissue Major Cell types 1. Fibroblasts- produce fibers by secreting proteins into the matrix - most com ...
Levels of Organization-Plants
... Throughout your body, tissues are grouped together so they can work together. An organ is a group of tissues that work together doing certain jobs. ...
... Throughout your body, tissues are grouped together so they can work together. An organ is a group of tissues that work together doing certain jobs. ...
Cells: Practice Questions #1 1.
... If this activity requires the use of energy, which substance would be the source of this energy? A. B. C. D. ...
... If this activity requires the use of energy, which substance would be the source of this energy? A. B. C. D. ...
Levels of Organization
... When the time is right, an animal cell or a plant cell _________________ into two, forming new cells called __________________ cells. The two new cells are _________________ the same as the original cell. This process is called ____________ ___________________. ...
... When the time is right, an animal cell or a plant cell _________________ into two, forming new cells called __________________ cells. The two new cells are _________________ the same as the original cell. This process is called ____________ ___________________. ...
08 - Cell Diversity
... the plant into the leaves and out of tiny holes under the leaves called 'stomata'. This movement of water is called the 'transpiration stream'. Transpiration is the loss of water vapour from the surface of a plant. Phloem carries food from the leaves to all other parts of the plant. ...
... the plant into the leaves and out of tiny holes under the leaves called 'stomata'. This movement of water is called the 'transpiration stream'. Transpiration is the loss of water vapour from the surface of a plant. Phloem carries food from the leaves to all other parts of the plant. ...
Levels of Organization
... When the time is right, an animal cell or a plant cell _________________ into two, forming new cells called __________________ cells. The two new cells are _________________ the same as the original cell. This process is called ____________ ___________________. ...
... When the time is right, an animal cell or a plant cell _________________ into two, forming new cells called __________________ cells. The two new cells are _________________ the same as the original cell. This process is called ____________ ___________________. ...
File - Biology with Ms. Murillo
... 49. What are the female reproductive organs? What are the female gametes called and where are they produced? ovaries- produce female gametes (ova or egg) 50. What is internal fertilization? Where does fertilization occur in the human female? internal fertilization: The eggs are fertilized within the ...
... 49. What are the female reproductive organs? What are the female gametes called and where are they produced? ovaries- produce female gametes (ova or egg) 50. What is internal fertilization? Where does fertilization occur in the human female? internal fertilization: The eggs are fertilized within the ...
Course Specifications
... First cells in the evolution of the earth and definition of life Chemical substances of biological material and all kinds of chemical bonds and interactions important in the function of cells Structure of pro- and of eukaryotic cells; intercellular interactions and exchange Cell cycle , cell activit ...
... First cells in the evolution of the earth and definition of life Chemical substances of biological material and all kinds of chemical bonds and interactions important in the function of cells Structure of pro- and of eukaryotic cells; intercellular interactions and exchange Cell cycle , cell activit ...
Neuronal lineage marker

A Neuronal lineage marker is an endogenous tag that is expressed in different cells along neurogenesis and differentiated cells as neurons. It allows detection and identification of cells by using different techniques. A neuronal lineage marker can be either DNA, mRNA or RNA expressed in a cell of interest. It can also be a protein tag, as a partial protein, a protein or a epitope that discriminates between different cell types or different states of a common cell. An ideal marker is specific to a given cell type in normal conditions and/or during injury. Cell markers are very valuable tools for examining the function of cells in normal conditions as well as during disease. The discovery of various proteins specific to certain cells led to the production of cell-type-specific antibodies that have been used to identify cells.The techniques used for its detection can be immunohistochemistry, immunocytochemistry, methods that utilize transcriptional modulators and site-specific recombinases to label specific neuronal population, in situ hybridization or fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). A neuronal lineage marker can be a neuronal antigen that is recognized by an autoantibody for example Hu, which is highly restricted to neuronal nuclei. By immunohistochemistry, anti-Hu stains the nuclei of neurons. To localize mRNA in brain tissue, one can use a fragment of DNA or RNA as a neuronal lineage marker, a hybridization probe that detects the presence of nucleotide sequences that are complementary to the sequence in the probe. This technique is known as in situ hybridization. Its application have been carried out in all different tissues, but particularly useful in neuroscience. Using this technique, it is possible to locate gene expression to specific cell types in specific regions and observe how changes in this distribution occur throughout the development and correlate with the behavioral manipulations.Although immunohistochemistry is the staple methodology for identifying neuronal cell types, since it is relatively low in cost and a wide range of immunohistochemical markers are available to help distinguish the phenotype of cells in the brain, sometimes it is time-consuming to produce a good antibody. Therefore, one of the most convenient methods for the rapid assessment of the expression of a cloned ion channel could be in situ hybridization histochemistry.After cells are isolated from tissue or differentiated from pluripotent precursors, the resulting population needs to be characterized to confirm whether the target population has been obtained. Depending on the goal of a particular study, one can use neural stem cells markers, neural progenitor cell markers, neuron markers or PNS neuronal markers.