Biology B2 Revision Notes
... that produce high quality calves; making copies of animals that have been genetically modified e.g. cows that produce insulin in milk Disadvs – difficult; low success rate for cloned embryos; health problems in cloned mammals; if one animal is susceptible to a disease, all the clones will be too 1.2 ...
... that produce high quality calves; making copies of animals that have been genetically modified e.g. cows that produce insulin in milk Disadvs – difficult; low success rate for cloned embryos; health problems in cloned mammals; if one animal is susceptible to a disease, all the clones will be too 1.2 ...
Chapter 43
... Tissues are groups of cells of a single type and function • Early in development, the cells of the growing embryo differentiate into the three fundamental embryonic tissues called germ layers -endoderm -mesoderm -ectoderm • Four principal kinds of tissues in adult vertebrates -epithelial, connectiv ...
... Tissues are groups of cells of a single type and function • Early in development, the cells of the growing embryo differentiate into the three fundamental embryonic tissues called germ layers -endoderm -mesoderm -ectoderm • Four principal kinds of tissues in adult vertebrates -epithelial, connectiv ...
Review PPT – Life Science – Cells and Human
... – When organisms grow, they increase in size (unicellular) or number of cells (multicellular). Changes that occur in an organism during its lifetime are called development. ...
... – When organisms grow, they increase in size (unicellular) or number of cells (multicellular). Changes that occur in an organism during its lifetime are called development. ...
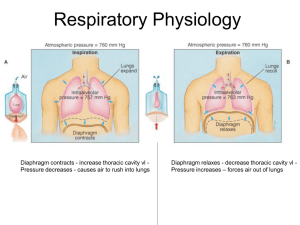
Respiratory Physiology
... Lung cancer –most common cancer and most common cause of cancer deaths in U.S. males. There are several forms of lung cancer, but the most common (and most rapidly increasing) types are those involving the epithelial cells lining the bronchi and bronchioles. Ordinarily, the lining of these airways c ...
... Lung cancer –most common cancer and most common cause of cancer deaths in U.S. males. There are several forms of lung cancer, but the most common (and most rapidly increasing) types are those involving the epithelial cells lining the bronchi and bronchioles. Ordinarily, the lining of these airways c ...
INTERNAL STRUCTURES OF INSECT
... What happen when you attack the fly????? 3 components 1)brain central 2)ventral nerve cord nervous system (CNS) 3)peripheral nervous system (extend outside the central nervos system to serve the limbs and organs ...
... What happen when you attack the fly????? 3 components 1)brain central 2)ventral nerve cord nervous system (CNS) 3)peripheral nervous system (extend outside the central nervos system to serve the limbs and organs ...
Reproduction and Development
... Almost all human tissue can repair itself to some extent. Much of this repair is due to the activity of stem cells. These cells resemble those of a developing embryo in their ability to reproduce repeatedly, forming exact copies of themselves. They may also form many other different kinds of cells. ...
... Almost all human tissue can repair itself to some extent. Much of this repair is due to the activity of stem cells. These cells resemble those of a developing embryo in their ability to reproduce repeatedly, forming exact copies of themselves. They may also form many other different kinds of cells. ...
Human Body Systems - Liberty Union High School District
... Nerve Impulse: A progressive _________________________________________ and ___________________ activity along a _________________________ that ______________________ or __________ the action of a ______________________, ________________, or other ______________________________ *This is how the inf ...
... Nerve Impulse: A progressive _________________________________________ and ___________________ activity along a _________________________ that ______________________ or __________ the action of a ______________________, ________________, or other ______________________________ *This is how the inf ...
UNIT 3 PART 1 LIFE FUNCTIONS
... specialized cells called neurons, that carry electrical signals (impulses) throughout the organism. ...
... specialized cells called neurons, that carry electrical signals (impulses) throughout the organism. ...
Levels of Organization Notes (pg 418-427)
... Complex jobs in organisms require more than one type of tissue. Organs are groups of different tissues working together to perform a particular job. Your stomach is an organ that breaks down food. It is made of all four types of tissue: muscle, epithelial, nervous, and connective. Each type of tissu ...
... Complex jobs in organisms require more than one type of tissue. Organs are groups of different tissues working together to perform a particular job. Your stomach is an organ that breaks down food. It is made of all four types of tissue: muscle, epithelial, nervous, and connective. Each type of tissu ...
Hematology Introduction
... metabolism, for example urea, and uric acid. 6- Protection: versus invading microorganisms ...
... metabolism, for example urea, and uric acid. 6- Protection: versus invading microorganisms ...
Cell Structure and Function - Mrs. Gann`s 6th grade class
... As cells divide, they differentiate, which means they become different from one another. Early on the cells organize themselves into three groups, called germ layers. One layer will form the skin and nerves. Another layer becomes the lining of the digestive tract. The third layer becomes all the ot ...
... As cells divide, they differentiate, which means they become different from one another. Early on the cells organize themselves into three groups, called germ layers. One layer will form the skin and nerves. Another layer becomes the lining of the digestive tract. The third layer becomes all the ot ...
animal cells and tissues
... the control center compares the message (information) to a set normal point. If conditions deviate from a set point, biochemical reactions are initiated to change conditions back to the set point. Effectors receive the information from the control center to act against the disturbing condition and r ...
... the control center compares the message (information) to a set normal point. If conditions deviate from a set point, biochemical reactions are initiated to change conditions back to the set point. Effectors receive the information from the control center to act against the disturbing condition and r ...
1 Cells Cells -Cells are the building blocks of living things
... -makes proteins for the membrane -modifies proteins: folds amino acids into polypeptide chains -forms tubes and channels: amino acids made in ribosomes get folded and glucose chain is added as receptors/cell markers -carries proteins and other out of cells through these channels -makes materials for ...
... -makes proteins for the membrane -modifies proteins: folds amino acids into polypeptide chains -forms tubes and channels: amino acids made in ribosomes get folded and glucose chain is added as receptors/cell markers -carries proteins and other out of cells through these channels -makes materials for ...
Cells Cells -Cells are the building blocks of living things
... -makes proteins for the membrane -modifies proteins: folds amino acids into polypeptide chains -forms tubes and channels: amino acids made in ribosomes get folded and glucose chain is added as receptors/cell markers -carries proteins and other out of cells through these channels -makes materials for ...
... -makes proteins for the membrane -modifies proteins: folds amino acids into polypeptide chains -forms tubes and channels: amino acids made in ribosomes get folded and glucose chain is added as receptors/cell markers -carries proteins and other out of cells through these channels -makes materials for ...
THE LIVING ENVIRONMENT VOCABULARY
... down large food particles into smaller ones. The ability to make things look larger than they are. Rod-shaped cell structures that produce most of the energy needed to carry out the cell’s function. The stage of the cell cycle during which the cell’s nucleus divides into two new nuclei and one copy ...
... down large food particles into smaller ones. The ability to make things look larger than they are. Rod-shaped cell structures that produce most of the energy needed to carry out the cell’s function. The stage of the cell cycle during which the cell’s nucleus divides into two new nuclei and one copy ...
Study Guide Cells Unit Test
... knee was as good as new. Bandages serve as barriers that help prevent infection and further injury. But what if there were such a thing as a living bandage that actually helped your body heal? It sounds like science fiction, but it’s not! The Main Factor An injury to the skin, such as a scraped knee ...
... knee was as good as new. Bandages serve as barriers that help prevent infection and further injury. But what if there were such a thing as a living bandage that actually helped your body heal? It sounds like science fiction, but it’s not! The Main Factor An injury to the skin, such as a scraped knee ...
BIOLOGY 4.1 CELL BIOLOGY NEED TO KNOW REVISION
... Differentiation is the generation of specialised cells which acquire different organelles to enable them to carry out specific functions. ...
... Differentiation is the generation of specialised cells which acquire different organelles to enable them to carry out specific functions. ...
Unit 3 part 1 PPT
... • A stimulus is anything that causes a receptor to start impulses. • Receptors are specialized structures sensitive to certain changes, forces, or chemicals both in and out of the organism. They are proteins on the surface of cell membranes. • Stimulation of a receptor sends an impulse to an effect ...
... • A stimulus is anything that causes a receptor to start impulses. • Receptors are specialized structures sensitive to certain changes, forces, or chemicals both in and out of the organism. They are proteins on the surface of cell membranes. • Stimulation of a receptor sends an impulse to an effect ...
Animal Systems: REGULATION
... - the ability of the body or a cell to seek and maintain stability within its internal environment when dealing with external changes The nervous system maintains homeostasis by… The excretory system regulates the concentration of water and other components of body fluids like salts and ...
... - the ability of the body or a cell to seek and maintain stability within its internal environment when dealing with external changes The nervous system maintains homeostasis by… The excretory system regulates the concentration of water and other components of body fluids like salts and ...
unit 6. living things/biosphere
... Plant cells have a rigid cell wall which surrounds the plasmatic membrane. The cell wall gives the cell its shape and strengthens it. Plant cells are usually polyhedral, but animal cells are various shapes: round, square, star-like. Plant cells have unique organelles called chloroplast which are res ...
... Plant cells have a rigid cell wall which surrounds the plasmatic membrane. The cell wall gives the cell its shape and strengthens it. Plant cells are usually polyhedral, but animal cells are various shapes: round, square, star-like. Plant cells have unique organelles called chloroplast which are res ...
Asexual Reproduction - Effingham County Schools
... During the third week, three layers of cells form in the embryo. What do each of these three layers become? 6. The top layer will become the brain, spinal cord, and the backbone. The middle layer will become the heart and the blood vessels. The inner layer becomes the respiratory and digestive syste ...
... During the third week, three layers of cells form in the embryo. What do each of these three layers become? 6. The top layer will become the brain, spinal cord, and the backbone. The middle layer will become the heart and the blood vessels. The inner layer becomes the respiratory and digestive syste ...
Getting to Know: Cell Theory
... others to make your body function properly. Each of these systems is made of specialized cells that perform special functions. ...
... others to make your body function properly. Each of these systems is made of specialized cells that perform special functions. ...
Cells1 - ClickBiology
... animal cells, and describe the functions of their parts. • Describe the difference between animal cells and plant cells. • Explain the structure and function of specialised cells: red blood cell, muscle cells, ciliated cells, xylem vessels and root hair cells. • Define the terms tissue, organ and or ...
... animal cells, and describe the functions of their parts. • Describe the difference between animal cells and plant cells. • Explain the structure and function of specialised cells: red blood cell, muscle cells, ciliated cells, xylem vessels and root hair cells. • Define the terms tissue, organ and or ...
Edexcel AS Level Biology
... animal cells, and describe the functions of their parts. • Describe the difference between animal cells and plant cells. • Explain the structure and function of specialised cells: red blood cell, muscle cells, ciliated cells, xylem vessels and root hair cells. • Define the terms tissue, organ and or ...
... animal cells, and describe the functions of their parts. • Describe the difference between animal cells and plant cells. • Explain the structure and function of specialised cells: red blood cell, muscle cells, ciliated cells, xylem vessels and root hair cells. • Define the terms tissue, organ and or ...
Neuronal lineage marker

A Neuronal lineage marker is an endogenous tag that is expressed in different cells along neurogenesis and differentiated cells as neurons. It allows detection and identification of cells by using different techniques. A neuronal lineage marker can be either DNA, mRNA or RNA expressed in a cell of interest. It can also be a protein tag, as a partial protein, a protein or a epitope that discriminates between different cell types or different states of a common cell. An ideal marker is specific to a given cell type in normal conditions and/or during injury. Cell markers are very valuable tools for examining the function of cells in normal conditions as well as during disease. The discovery of various proteins specific to certain cells led to the production of cell-type-specific antibodies that have been used to identify cells.The techniques used for its detection can be immunohistochemistry, immunocytochemistry, methods that utilize transcriptional modulators and site-specific recombinases to label specific neuronal population, in situ hybridization or fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). A neuronal lineage marker can be a neuronal antigen that is recognized by an autoantibody for example Hu, which is highly restricted to neuronal nuclei. By immunohistochemistry, anti-Hu stains the nuclei of neurons. To localize mRNA in brain tissue, one can use a fragment of DNA or RNA as a neuronal lineage marker, a hybridization probe that detects the presence of nucleotide sequences that are complementary to the sequence in the probe. This technique is known as in situ hybridization. Its application have been carried out in all different tissues, but particularly useful in neuroscience. Using this technique, it is possible to locate gene expression to specific cell types in specific regions and observe how changes in this distribution occur throughout the development and correlate with the behavioral manipulations.Although immunohistochemistry is the staple methodology for identifying neuronal cell types, since it is relatively low in cost and a wide range of immunohistochemical markers are available to help distinguish the phenotype of cells in the brain, sometimes it is time-consuming to produce a good antibody. Therefore, one of the most convenient methods for the rapid assessment of the expression of a cloned ion channel could be in situ hybridization histochemistry.After cells are isolated from tissue or differentiated from pluripotent precursors, the resulting population needs to be characterized to confirm whether the target population has been obtained. Depending on the goal of a particular study, one can use neural stem cells markers, neural progenitor cell markers, neuron markers or PNS neuronal markers.