* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Asexual Reproduction - Effingham County Schools
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Induced pluripotent stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
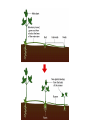
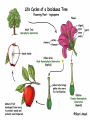
Reproduction All Systems Go… 1. How does the body grow? Do cells get larger as your body increases in size? 2. What do bone cells, muscle cells, and nerve cells have in common? All Systems Go… 1. How does the body grow? Do cells get larger as your body increases in size? 1. Growth occurs when cells divide to create new cells. Your body always has the same size cells as you grow you just have more of them. 2. What do bone cells, muscle cells, and nerve cells have in common? 2. All cells in the body are all descendants of the first cell. All Systems Go… 3. What is a zygote and when is it formed? 4. What is a blastocyst and when is it formed? All Systems Go… 3. What is a zygote and when is it formed? 3. A zygote is the first cell of a person. It is formed when a sperm fertilizes an egg during reproduction. 4. What is a blastocyst and when is it formed? 4. A blastocyst forms by the end of the first week. It is a ball of cells. All Systems Go… 5. When will the embryo’s cells begin to become different types of cells? 6. During the third week, three layers of cells form in the embryo. What do each of these three layers become? All Systems Go… 5. When will the embryo’s cells begin to become different types of cells? 5. Between the 2nd and 3rd weeks of development the embryo’s cell will begin to become different types of cells like muscle and nerve cells. 6. During the third week, three layers of cells form in the embryo. What do each of these three layers become? 6. The top layer will become the brain, spinal cord, and the backbone. The middle layer will become the heart and the blood vessels. The inner layer becomes the respiratory and digestive systems. All Systems Go… 7. When will the embryo’s heart begin to beat? 7. The heart begins to beat by the 4th week. 8. Describe the importance of cell division? (Why is it important for cell to divide?) 8. Cells must be able to divide for the body to grow. Cells must also divide to help the body repair injuries, replace old cells, and replace worn out cells. Asexual Reproduction • Examples of organisms that reproduce asexually – Hydra – Sea Star – Strawberry – Archaebacteria – Eubacteria – Euglena – Paramecium – Yeast 9 Asexual Reproduction • Requires only one parent • Offspring have 100% the same DNA as the parent. – In other words, the offspring are exact “clones” of the parent. – Most unicellular organisms reproduce this way. – Movie 10 Binary Fission- asexual reproduction that occurs in single celled organisms in which genetic material is copied and one cell divides into two identical daughter cells. EX: happens in bacteria, amoeba, some algae Budding- Parent produces a bud that detaches and develops into offspring which is identical to parent Ex: happens in yeast, hydra, corals Asexual Reproduction • Budding – Hydra • Movie Budding is a means of asexual reproduction whereby a new individual develops from an outgrowth of a parent, splits off, and lives independently. 13 FragmentationFragmentation is a form of asexual reproduction where a new organism grows from a fragment of the parent. Each fragment develops into a mature, fully grown individual. Ex: Starfish, flatworms, and some fungi. Sexual Reproduction • Examples of organisms that reproduce sexually – Chickens – Iguanas – Lobsters – Sharks – Humans – Butterflies – Sunflowers – Roses 18 Sexual Reproduction Type of reproduction in which male and female reproductive cells combine to form new offspring with genetic material from both parents. ***Offspring has genetic material from each parent which creates- Offspring NOT identical to parent! (genetic variation)_ Sexual Reproduction • Happens 2 ways – Internally (inside) • The egg is fertilized by sperm inside the female – Mammals, birds, reptiles, insects, spiders – Externally (outside) • The egg is fertilized by sperm outside the female • The female lays the eggs and then the male fertilizes them. – Fish and some amphibians – Plants and fungi (pollen and spores) 20 Sexual Reproduction in Animals • involves specialized sex cells called gametes • the union of a male and female gamete results in the formation of a zygote that develops into a new individual Sexual Reproduction in Plants Female Parts Male Parts (Pistil) •Involves specialized cells called gametes •The union of pollen (male gamete) + ovule (female gamete) = results •Some Organisms do both kinds of reproduction • most plants that produce seeds (sexual reproduction) can also reproduce asexually by things like cuttings or runners • this gives them an advantage for survival sponges and hydra mosses Which is Better? It depends! Asexual Reproduction • advantages – does not require special cells or a lot of energy – can produce offspring quickly – in a stable environment creates large, thriving population • disadvantages – limited ability to adapt – face massive die-off if environment changes Sexual Reproduction • advantages – lots of variation within a species – able to live in a variety of environmental settings – able to adapt to changes in the environment • disadvantages – needs time & energy – produce small populations Make a Venn Diagram Asexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Both Types of reproduction in living organisms Pass DNA from parent to offspring 26 Ever think about how things grow? • • • • How do your fingernails grow? How does your hair grow longer? How does a flower get taller? How does the mycelium of a fungus reach farther? Where does this new material come from? III. Cell division is a process by which a cell divides into two or more cells, called daughter cells. ***Your body is constantly making new cells to replace old ones! Cell Division A. Mitosis- Division of the nucleus in eukaryotic cells in which each cell receives a copy of the original chromosome. 1. Chromosome- organized structure of DNA and protein that forms in the cell nucleus during cell division 2. Homologous chromosome- chromosomes with matching information. Remember: DNA is found in the nucleus. It is organized into a chromosome before it is copied. 2. Homologous chromosomes a. Cells must copy the genetic information in the nucleus before it divides into two nuclei. B. Meiosis – division of the nucleus in eukaryotic cells in which each cell receives half a set of genetic information. Meiosis results in the production of egg or sperm cells. DNA is copied and condenses to form chromosomes The chromosomes line up along the center of the cell The chromosomes are pulled apart to opposite sides of the cell The cell divides Plants grow from the tips out by constantly making new cells! Cell Division































![Chapter 3 - Cell_Division_Test_Study_Guide[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009683824_1-add56d75145939ff28543ed83f830e06-150x150.png)






