Mader/Biology, 11/e – Chapter Outline
... e. Prevention of polyspermy depends on changes in the egg plasma membrane when the sperm touches the egg and depolarizes the egg plasma membrane; this is called “fast block.” f. Vesicles in the egg called cortical granules secrete enzymes that turn the zona pellucida, forming an impenetrable fertili ...
... e. Prevention of polyspermy depends on changes in the egg plasma membrane when the sperm touches the egg and depolarizes the egg plasma membrane; this is called “fast block.” f. Vesicles in the egg called cortical granules secrete enzymes that turn the zona pellucida, forming an impenetrable fertili ...
Keywords - 기초의과학연구센터 MRC
... NSCs. We found that insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) levels in CSF were increased by TMT, suggesting that IGF-1 induced by TMT play a prosurvival function for grafted NSC. The current study tested the hypothesis that IGF-1 is a key factor to regulate the survival of NSCs following transplantatio ...
... NSCs. We found that insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) levels in CSF were increased by TMT, suggesting that IGF-1 induced by TMT play a prosurvival function for grafted NSC. The current study tested the hypothesis that IGF-1 is a key factor to regulate the survival of NSCs following transplantatio ...
What is the function of the Muscular System? What is the function of
... Then she recruits her younger brother to help her. It takes Susie 10 strikes to pound the steel nail all the way into the pine. It takes her younger brother 23 strikes to hammer the aluminum nail into the oak. Susie concludes that the oak is denser. Why is her conclusion ...
... Then she recruits her younger brother to help her. It takes Susie 10 strikes to pound the steel nail all the way into the pine. It takes her younger brother 23 strikes to hammer the aluminum nail into the oak. Susie concludes that the oak is denser. Why is her conclusion ...
Laboratory 4: Cell Structure and Function
... Cells are the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Cells differ enormously in size, shape, and function; some are free living, independent organisms, while others are immovably fixed as part of tissues of multicellular organisms. All cells exchange materials with their immediate en ...
... Cells are the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. Cells differ enormously in size, shape, and function; some are free living, independent organisms, while others are immovably fixed as part of tissues of multicellular organisms. All cells exchange materials with their immediate en ...
connective tissue
... and relays commands for response • Consists of excitable neurons and supporting neuroglial cells ...
... and relays commands for response • Consists of excitable neurons and supporting neuroglial cells ...
meiosis - astone
... of cells Can be taken from an adult and then reintroduced without risk of rejection Several types: Hematopoietic – forms blood cells Stromal cells – forms bone cartilage, fat Some types of brain stem cells ...
... of cells Can be taken from an adult and then reintroduced without risk of rejection Several types: Hematopoietic – forms blood cells Stromal cells – forms bone cartilage, fat Some types of brain stem cells ...
Test Review Mrs. Benham
... 304-7 Explain structural and functional relationships between and among cells, tissues, organs and systems in the human body 110-2 Compare the early idea that living organisms were made of air, fire and water with the modern cell theory 1. What elements were people believed to be made of in the past ...
... 304-7 Explain structural and functional relationships between and among cells, tissues, organs and systems in the human body 110-2 Compare the early idea that living organisms were made of air, fire and water with the modern cell theory 1. What elements were people believed to be made of in the past ...
LESSON 1. CELLS & TISSUES Lesson Aim
... To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes. THE CELL All living matter is composed of functional units called cells. At one end of the scale in the animal kingdom, there are unicellular organisms composed of a single cell (e ...
... To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes. THE CELL All living matter is composed of functional units called cells. At one end of the scale in the animal kingdom, there are unicellular organisms composed of a single cell (e ...
Chapter 24 – The Body`s Defenses against Pathogens State
... Will this reduce viral replication or bacterial growth? ...
... Will this reduce viral replication or bacterial growth? ...
CELL WALL - Winona ISD
... The Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) consists of nerves that branch off from the spinal cord and brain, out to the rest of the body. Information is carried between the CNS, muscles and glands. Glands are groups of cells that produce substances that the body uses. For example, glan ...
... The Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) consists of nerves that branch off from the spinal cord and brain, out to the rest of the body. Information is carried between the CNS, muscles and glands. Glands are groups of cells that produce substances that the body uses. For example, glan ...
Cell
... They are involved in food digestion in one-celled animals. Lysosomes destroy damaged or old cell parts or cells in multicellular animals. Although they have been seen only in animal cells, plant cells are now ...
... They are involved in food digestion in one-celled animals. Lysosomes destroy damaged or old cell parts or cells in multicellular animals. Although they have been seen only in animal cells, plant cells are now ...
Grade 11 College Biology – Unit 3
... NERVOUS CONTROL and HOMEOSTASIS – Human nervous system has two parts CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM – brain and the spinal cord PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM – all nerves outside the brain and spinal cord that relay information to the Central Nervous System and other body parts. This system is divided into tw ...
... NERVOUS CONTROL and HOMEOSTASIS – Human nervous system has two parts CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM – brain and the spinal cord PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM – all nerves outside the brain and spinal cord that relay information to the Central Nervous System and other body parts. This system is divided into tw ...
Quiz 4 1407 - HCC Learning Web
... 35) Steroid and peptide hormones typically have in common _____. A) the building blocks from which they are synthesized B) their solubility in cell membranes C) their requirement for travel through the bloodstream D) their reliance on signal transduction in the cell 36) Which of the following are s ...
... 35) Steroid and peptide hormones typically have in common _____. A) the building blocks from which they are synthesized B) their solubility in cell membranes C) their requirement for travel through the bloodstream D) their reliance on signal transduction in the cell 36) Which of the following are s ...
AP Bio Human Anatomy
... that large. Not true if hybrinating.. – 60% of nutritional intake goes to body heat – 10X more energy needed than a reptile of comparable size. (eat more and digest/ absorb more ...
... that large. Not true if hybrinating.. – 60% of nutritional intake goes to body heat – 10X more energy needed than a reptile of comparable size. (eat more and digest/ absorb more ...
Tissues
... I just want you to SEE what these tissues types look like I also want you to see SOME of their functions & locations ...
... I just want you to SEE what these tissues types look like I also want you to see SOME of their functions & locations ...
Cell - St. Pius X High School
... 2. Which one is larger? 3. Which one does not have a membrane bound nucleus? 4. What are the three main parts of the cell (that all cells have)? 5. What are the 3 components of the cell theory? 6. What theory explains how eukaryotes evolved? 7. What limits the size of cells? 8. Explain why this limi ...
... 2. Which one is larger? 3. Which one does not have a membrane bound nucleus? 4. What are the three main parts of the cell (that all cells have)? 5. What are the 3 components of the cell theory? 6. What theory explains how eukaryotes evolved? 7. What limits the size of cells? 8. Explain why this limi ...
Objectives For Chapter 25
... nurtures developing individuals, and gives birth. Humans usually have one child per birth, but multiple births, such as those of twins or triplets, are possible. Human reproduction can be affected by cancer, infertility, and disease. ...
... nurtures developing individuals, and gives birth. Humans usually have one child per birth, but multiple births, such as those of twins or triplets, are possible. Human reproduction can be affected by cancer, infertility, and disease. ...
Biology - Shelbyville Central Schools
... Many organisms start as one cell. That cell divides and become two, two becomes four, four becomes eight, and so on. Multi-cellular organisms grow because cell division increases the number of cells. Even after growth stops, cell division is important. Every day, billions of red blood cells wear out ...
... Many organisms start as one cell. That cell divides and become two, two becomes four, four becomes eight, and so on. Multi-cellular organisms grow because cell division increases the number of cells. Even after growth stops, cell division is important. Every day, billions of red blood cells wear out ...
Skill Builder _6B homeostasis
... inside and outside the cell. The adjusting of systems within a cell is called homeostatic regulation. Because the internal and external environments of a cell are constantly changing, adjustments must be made continuously to stay at or near the set point (the normal level or range). Homeostasis can ...
... inside and outside the cell. The adjusting of systems within a cell is called homeostatic regulation. Because the internal and external environments of a cell are constantly changing, adjustments must be made continuously to stay at or near the set point (the normal level or range). Homeostasis can ...
Document
... The development of optical lenses and their combination in compound microscope led to the establishment of the cell theory. In 17th Century • Robert Hooke (1665) first observed honeycomb like structures in a thin slice of cork and he called them as ‘cells’. • Leewenhock (1674) discovered free cells ...
... The development of optical lenses and their combination in compound microscope led to the establishment of the cell theory. In 17th Century • Robert Hooke (1665) first observed honeycomb like structures in a thin slice of cork and he called them as ‘cells’. • Leewenhock (1674) discovered free cells ...
I. Circulatory System
... A) Food is broken down so that it is small enough to enter the body tissues/cells. 1. Food is broken down mechanically and chemically. 2. Nutrients and water are absorbed into the body in the small and large intestines. B) The digestive system is a one way passage through the body that includes the ...
... A) Food is broken down so that it is small enough to enter the body tissues/cells. 1. Food is broken down mechanically and chemically. 2. Nutrients and water are absorbed into the body in the small and large intestines. B) The digestive system is a one way passage through the body that includes the ...
The essence of multicellularity - Introduction to concepts of gene
... or the genes that govern protein synthesis, are expressed in every cell. Such OS-like genes are called “house-keeping genes”. Thus, overall, the profiles of expressed proteins in a cell is distinct for each cell type, but they overlap because of the shared housekeeping genes. In summary, a cell type ...
... or the genes that govern protein synthesis, are expressed in every cell. Such OS-like genes are called “house-keeping genes”. Thus, overall, the profiles of expressed proteins in a cell is distinct for each cell type, but they overlap because of the shared housekeeping genes. In summary, a cell type ...
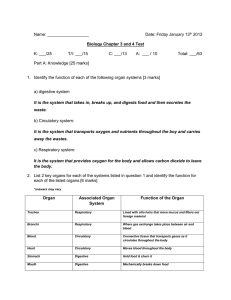
Name: Date: Friday January 13th 2012 Biology Chapter 3 and 4 Test
... -in normal heart, blood that is low in oxygen returns from body to the right filling chamber. It passes a valve into the right pumping chamber, and then travels out to lungs to receive oxygen. The blood then travels to the left filling chamber, across a valve to the left pumping chamber, and out to ...
... -in normal heart, blood that is low in oxygen returns from body to the right filling chamber. It passes a valve into the right pumping chamber, and then travels out to lungs to receive oxygen. The blood then travels to the left filling chamber, across a valve to the left pumping chamber, and out to ...
Neuronal lineage marker

A Neuronal lineage marker is an endogenous tag that is expressed in different cells along neurogenesis and differentiated cells as neurons. It allows detection and identification of cells by using different techniques. A neuronal lineage marker can be either DNA, mRNA or RNA expressed in a cell of interest. It can also be a protein tag, as a partial protein, a protein or a epitope that discriminates between different cell types or different states of a common cell. An ideal marker is specific to a given cell type in normal conditions and/or during injury. Cell markers are very valuable tools for examining the function of cells in normal conditions as well as during disease. The discovery of various proteins specific to certain cells led to the production of cell-type-specific antibodies that have been used to identify cells.The techniques used for its detection can be immunohistochemistry, immunocytochemistry, methods that utilize transcriptional modulators and site-specific recombinases to label specific neuronal population, in situ hybridization or fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). A neuronal lineage marker can be a neuronal antigen that is recognized by an autoantibody for example Hu, which is highly restricted to neuronal nuclei. By immunohistochemistry, anti-Hu stains the nuclei of neurons. To localize mRNA in brain tissue, one can use a fragment of DNA or RNA as a neuronal lineage marker, a hybridization probe that detects the presence of nucleotide sequences that are complementary to the sequence in the probe. This technique is known as in situ hybridization. Its application have been carried out in all different tissues, but particularly useful in neuroscience. Using this technique, it is possible to locate gene expression to specific cell types in specific regions and observe how changes in this distribution occur throughout the development and correlate with the behavioral manipulations.Although immunohistochemistry is the staple methodology for identifying neuronal cell types, since it is relatively low in cost and a wide range of immunohistochemical markers are available to help distinguish the phenotype of cells in the brain, sometimes it is time-consuming to produce a good antibody. Therefore, one of the most convenient methods for the rapid assessment of the expression of a cloned ion channel could be in situ hybridization histochemistry.After cells are isolated from tissue or differentiated from pluripotent precursors, the resulting population needs to be characterized to confirm whether the target population has been obtained. Depending on the goal of a particular study, one can use neural stem cells markers, neural progenitor cell markers, neuron markers or PNS neuronal markers.