10. Use a different colour for each stage of
... 3.________________________________________ help build muscles, skin, hair, and nails. Examples of foods containing this nutrient are _____________________________and ________________________________________. 4.Fats are used to build _______________________ and can be stored by the body for _________ ...
... 3.________________________________________ help build muscles, skin, hair, and nails. Examples of foods containing this nutrient are _____________________________and ________________________________________. 4.Fats are used to build _______________________ and can be stored by the body for _________ ...
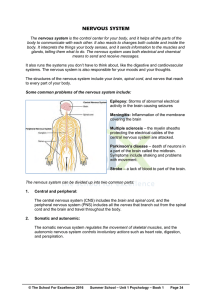
NERVOUS SYSTEM
... The nervous system is the control center for your body, and it helps all the parts of the body to communicate with each other. It also reacts to changes both outside and inside the body. It interprets the things your body senses, and it sends information to the muscles and glands, telling them what ...
... The nervous system is the control center for your body, and it helps all the parts of the body to communicate with each other. It also reacts to changes both outside and inside the body. It interprets the things your body senses, and it sends information to the muscles and glands, telling them what ...
Date____________________ Period - Mrs-Lamberts-Biology
... What if the cell wants to put MORE ____________ into mitochondria when there is already glucose in there What if cell needs to move molecules really _______? (can’t wait for it to diffuse) Cell example: We need a ______ to ______ molecules across cell membranes that _______ across by ___________ ...
... What if the cell wants to put MORE ____________ into mitochondria when there is already glucose in there What if cell needs to move molecules really _______? (can’t wait for it to diffuse) Cell example: We need a ______ to ______ molecules across cell membranes that _______ across by ___________ ...
PART - Humble ISD
... A __________ is an organ containing a bundle of nerve cells called ____________. Neurons carry electrical messages called ________________ throughout the body. Because neurons never touch, chemical signalers called ____________________ must travel through the space called _______________ between two ...
... A __________ is an organ containing a bundle of nerve cells called ____________. Neurons carry electrical messages called ________________ throughout the body. Because neurons never touch, chemical signalers called ____________________ must travel through the space called _______________ between two ...
2016 Course Outline
... Central Concepts: There is a relationship between the organization of cells into tissues and the organization of tissues into organs. The structures and functions of organs determine their relationships within body systems of an organism. Homeostasis allows the body to perform its normal functions. ...
... Central Concepts: There is a relationship between the organization of cells into tissues and the organization of tissues into organs. The structures and functions of organs determine their relationships within body systems of an organism. Homeostasis allows the body to perform its normal functions. ...
Basis of Cell Structure and Function
... Cell Shape is Related to Cell Function • The cells that line blood vessels and alveoli are shaped very flat and thin. The thin shape of cells (simple squamous epithelium) allows for passage of materials (O2, CO2) through the cell. • Cells that absorb things typically have microvilli. Microvilli inc ...
... Cell Shape is Related to Cell Function • The cells that line blood vessels and alveoli are shaped very flat and thin. The thin shape of cells (simple squamous epithelium) allows for passage of materials (O2, CO2) through the cell. • Cells that absorb things typically have microvilli. Microvilli inc ...
chapter-8-human-organization-student-notes
... Includes two types of cells: ________ and __________ cells ...
... Includes two types of cells: ________ and __________ cells ...
Chapter 3: Cells
... and ______________________________________________________________ . 26. The enzymes of peroxisomes function to _____________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 27. The structure of a centrosome is ____________________________________ 28. A centrosome ...
... and ______________________________________________________________ . 26. The enzymes of peroxisomes function to _____________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 27. The structure of a centrosome is ____________________________________ 28. A centrosome ...
What is a Cell? All living things are made up of cells. Each of us has
... membrane. The inside of a cell is watery and jelly-like. Cells are very small - you can't see them just using your eyes. You need to use a microscope, which makes them look many times bigger that they actually are. If a cell is cut in half, it will not survive. So a cell can be considered as the sma ...
... membrane. The inside of a cell is watery and jelly-like. Cells are very small - you can't see them just using your eyes. You need to use a microscope, which makes them look many times bigger that they actually are. If a cell is cut in half, it will not survive. So a cell can be considered as the sma ...
1.2b Cells
... • The protein is then taken out and carried through the canals of the reticulum like a boat going down a canal in Venice. The protein then floats into the Golgi complex, where it will be packaged for shipment like a Fed-Ex center. • Some of these proteins will be used to make enzymes. Enzymes are re ...
... • The protein is then taken out and carried through the canals of the reticulum like a boat going down a canal in Venice. The protein then floats into the Golgi complex, where it will be packaged for shipment like a Fed-Ex center. • Some of these proteins will be used to make enzymes. Enzymes are re ...
Developmental Biology
... • The bicoid research is important for three reasons: – It identified a specific protein required for some early steps in pattern formation – It increased understanding of the mother’s role in embryo development – It demonstrated a key developmental principle that a gradient of molecules can determ ...
... • The bicoid research is important for three reasons: – It identified a specific protein required for some early steps in pattern formation – It increased understanding of the mother’s role in embryo development – It demonstrated a key developmental principle that a gradient of molecules can determ ...
Human Embryology and Natural Stem Cells iPS…..induced
... End of pregnancy - two deliveries - 1. deliver baby, 2. deliver placenta ...
... End of pregnancy - two deliveries - 1. deliver baby, 2. deliver placenta ...
summing-up - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... between the various parts of the body. It consists of neurons, cells that have short and branched appendages called dendrites, and a long extension called an axon. Around the neurons are supporting cells that function to isolate and protect them, as well as to speed the transmission of nerve impulse ...
... between the various parts of the body. It consists of neurons, cells that have short and branched appendages called dendrites, and a long extension called an axon. Around the neurons are supporting cells that function to isolate and protect them, as well as to speed the transmission of nerve impulse ...
Chapter Outline
... the surface of the egg, forming a moat that prevents entrance of any other sperm. h. The diploid zygote forms when a nuclear envelope surrounds the sperm and egg chromosomes. B. Embryonic Development ...
... the surface of the egg, forming a moat that prevents entrance of any other sperm. h. The diploid zygote forms when a nuclear envelope surrounds the sperm and egg chromosomes. B. Embryonic Development ...
Basic Biological Principles
... each cell contains all of the components necessary for its own survival. In multicellular, or many-celled, organisms, each cell has a different set of functions, and they are dependent on other cells for their ...
... each cell contains all of the components necessary for its own survival. In multicellular, or many-celled, organisms, each cell has a different set of functions, and they are dependent on other cells for their ...
Vertebrate Tissues
... • Cells are mainly fibroblasts (cells that produce fibers in the matrix) • Matrix = gel-like ground substance and many collagen and elastin fibers • Binds skin to organs & fills space between muscles • Has many blood vessels that nourish nearby epithelial cells ...
... • Cells are mainly fibroblasts (cells that produce fibers in the matrix) • Matrix = gel-like ground substance and many collagen and elastin fibers • Binds skin to organs & fills space between muscles • Has many blood vessels that nourish nearby epithelial cells ...
Communicable Diseases
... Macrophage- Bite virus and send antigen to Tcells Helper T cells – act as messenger calling B cells B Cells – create antibody to help kill pathogens and remove pathogens (interlocking parts) Virus can no longer invade body’s cells Kept on file – body has immunity Killer T Cells – destroy v ...
... Macrophage- Bite virus and send antigen to Tcells Helper T cells – act as messenger calling B cells B Cells – create antibody to help kill pathogens and remove pathogens (interlocking parts) Virus can no longer invade body’s cells Kept on file – body has immunity Killer T Cells – destroy v ...
Chelsea
... Students know why an individual with a compromised immune system (for example, a person with AIDS) may be unable to fight off and survive infections by microorganisms that are usually benign. Students know the roles of phagocytes, B-lymphocytes, and T-lymphocytes in the immune system. ...
... Students know why an individual with a compromised immune system (for example, a person with AIDS) may be unable to fight off and survive infections by microorganisms that are usually benign. Students know the roles of phagocytes, B-lymphocytes, and T-lymphocytes in the immune system. ...
Word Bank: diaphragm capillaries oxygen ATP alveoli blood CO 2
... A) All humans (and most other organisms) begin life as a ___________cell. 1. This single cell is called a_____________. 2. The nucleus of this cell has _______the genes needed to become a complete organism. B) Humans grow as a result of ___________cell division). 1. This quickly increases the number ...
... A) All humans (and most other organisms) begin life as a ___________cell. 1. This single cell is called a_____________. 2. The nucleus of this cell has _______the genes needed to become a complete organism. B) Humans grow as a result of ___________cell division). 1. This quickly increases the number ...
Study guide packet part 1
... C. Ribosomes- these make the proteins in the cell D. Mitochondria- “powerhouse” of the cell. Provides energy by Cellular respiration. E. Cell wall- this is not in animals. Provides protection and support for the cell F. Chloroplast- this is only in plants and protists. This is where photosynthesis h ...
... C. Ribosomes- these make the proteins in the cell D. Mitochondria- “powerhouse” of the cell. Provides energy by Cellular respiration. E. Cell wall- this is not in animals. Provides protection and support for the cell F. Chloroplast- this is only in plants and protists. This is where photosynthesis h ...
Exam 2A key
... 5. Pick either the fish or bird respiratory system and explain the features that make it especially efficient. Make specific reference to each of the basic requirements of systems that exchange materials with the environment by diffusion and highlight the countercurrent exchange mechanism seen in f ...
... 5. Pick either the fish or bird respiratory system and explain the features that make it especially efficient. Make specific reference to each of the basic requirements of systems that exchange materials with the environment by diffusion and highlight the countercurrent exchange mechanism seen in f ...
HumanBodyVocabulary
... 3. Nervous system: The system of cells, tissues, and organs that regulates the body's responses to internal and external stimuli. In vertebrates it consists of the brain, spinal cord, nerves, ganglia, and parts of the receptor and effector organs. 4. Cell body: The portion of a nerve cell that conta ...
... 3. Nervous system: The system of cells, tissues, and organs that regulates the body's responses to internal and external stimuli. In vertebrates it consists of the brain, spinal cord, nerves, ganglia, and parts of the receptor and effector organs. 4. Cell body: The portion of a nerve cell that conta ...
Neuronal lineage marker

A Neuronal lineage marker is an endogenous tag that is expressed in different cells along neurogenesis and differentiated cells as neurons. It allows detection and identification of cells by using different techniques. A neuronal lineage marker can be either DNA, mRNA or RNA expressed in a cell of interest. It can also be a protein tag, as a partial protein, a protein or a epitope that discriminates between different cell types or different states of a common cell. An ideal marker is specific to a given cell type in normal conditions and/or during injury. Cell markers are very valuable tools for examining the function of cells in normal conditions as well as during disease. The discovery of various proteins specific to certain cells led to the production of cell-type-specific antibodies that have been used to identify cells.The techniques used for its detection can be immunohistochemistry, immunocytochemistry, methods that utilize transcriptional modulators and site-specific recombinases to label specific neuronal population, in situ hybridization or fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). A neuronal lineage marker can be a neuronal antigen that is recognized by an autoantibody for example Hu, which is highly restricted to neuronal nuclei. By immunohistochemistry, anti-Hu stains the nuclei of neurons. To localize mRNA in brain tissue, one can use a fragment of DNA or RNA as a neuronal lineage marker, a hybridization probe that detects the presence of nucleotide sequences that are complementary to the sequence in the probe. This technique is known as in situ hybridization. Its application have been carried out in all different tissues, but particularly useful in neuroscience. Using this technique, it is possible to locate gene expression to specific cell types in specific regions and observe how changes in this distribution occur throughout the development and correlate with the behavioral manipulations.Although immunohistochemistry is the staple methodology for identifying neuronal cell types, since it is relatively low in cost and a wide range of immunohistochemical markers are available to help distinguish the phenotype of cells in the brain, sometimes it is time-consuming to produce a good antibody. Therefore, one of the most convenient methods for the rapid assessment of the expression of a cloned ion channel could be in situ hybridization histochemistry.After cells are isolated from tissue or differentiated from pluripotent precursors, the resulting population needs to be characterized to confirm whether the target population has been obtained. Depending on the goal of a particular study, one can use neural stem cells markers, neural progenitor cell markers, neuron markers or PNS neuronal markers.