Cells - Dr Magrann
... move the vesicle to the plasma membrane where it is released from the cell and picked up by the bloodstream and taken to where it is needed in the body. The bloodstream drops off sugars to the cell, which are taken to the mitochondria to be broken down into ATP, which is the energy molecule used to ...
... move the vesicle to the plasma membrane where it is released from the cell and picked up by the bloodstream and taken to where it is needed in the body. The bloodstream drops off sugars to the cell, which are taken to the mitochondria to be broken down into ATP, which is the energy molecule used to ...
Human Embryology and Natural Stem Cells iPS…..induced
... begins in fetal ovary before birth - then goes into meiotic arrest one egg a month resumes meiosis at puberty - ends at menopause Ovulation - release of oocyte from ovary - Meiosis I > first Polar Body forms Fertilization - sperm enters the oocyte - Meiosis II > second Polar Body forms Females rarel ...
... begins in fetal ovary before birth - then goes into meiotic arrest one egg a month resumes meiosis at puberty - ends at menopause Ovulation - release of oocyte from ovary - Meiosis I > first Polar Body forms Fertilization - sperm enters the oocyte - Meiosis II > second Polar Body forms Females rarel ...
AP Biology Unit 1- The Chemistry of Life
... in a compartmentalized world. One way the living world stays compartmentalized is with membranes. Define:_______ ________________________________________________________________________ Cells and cell organelles Define organelle:____________________________________ __________________________________ ...
... in a compartmentalized world. One way the living world stays compartmentalized is with membranes. Define:_______ ________________________________________________________________________ Cells and cell organelles Define organelle:____________________________________ __________________________________ ...
B.4.A compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
... Coevolution – the concurrent evolution of two species completely dependent on each other For example, if a plant is pollinated by one type of insect. If the insect population evolves, the plant population must evolve to maintain its existence. Adaptation – an inherited characteristic that allows for ...
... Coevolution – the concurrent evolution of two species completely dependent on each other For example, if a plant is pollinated by one type of insect. If the insect population evolves, the plant population must evolve to maintain its existence. Adaptation – an inherited characteristic that allows for ...
Cells - TeacherWeb
... worn-out parts of a cell into smaller units. They deliver these materials to the cytoplasm for use in constructing new proteins. If the membrane of a lysosome breaks, the enzymes released may also destroy the cell itself, giving lysosomes the name "suicide bag". Lysosomes would be like waste process ...
... worn-out parts of a cell into smaller units. They deliver these materials to the cytoplasm for use in constructing new proteins. If the membrane of a lysosome breaks, the enzymes released may also destroy the cell itself, giving lysosomes the name "suicide bag". Lysosomes would be like waste process ...
EOC Review power point (1)
... food in your body and to build new molecules & organelles. • Enzymes are used over & over but are very SPECIFIC in the rxn they participate in. • Enzymes can be denatured or destroyed by changes in temperature, pH or salt ...
... food in your body and to build new molecules & organelles. • Enzymes are used over & over but are very SPECIFIC in the rxn they participate in. • Enzymes can be denatured or destroyed by changes in temperature, pH or salt ...
Worcester Public Schools High School Course Syllabus – District
... There are social, ethical and legal issues associated with different aspects of Biology. Many new technologies used in Biology have both positive and negative attributes. Cells have organized structures and systems necessary to support chemical reactions needed to maintain the living condition. Thro ...
... There are social, ethical and legal issues associated with different aspects of Biology. Many new technologies used in Biology have both positive and negative attributes. Cells have organized structures and systems necessary to support chemical reactions needed to maintain the living condition. Thro ...
Chapter Three: Cells: The Basic Units of Life Teacher Notes Lesson
... -mitochondria are the size of some bacteria -mitochondria have their own DNA and can divide within a cell -Chloroplasts-organelles in plant and algae cells in which photosynthesis takes place -have two membranes and their own DNA -use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to make sugar and oxygen -are ...
... -mitochondria are the size of some bacteria -mitochondria have their own DNA and can divide within a cell -Chloroplasts-organelles in plant and algae cells in which photosynthesis takes place -have two membranes and their own DNA -use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to make sugar and oxygen -are ...
What You Must Know to Pass the Regents Biology Exam
... • Occurs in the fallopian tube • A fertilized egg is called a zygote and has the normal number of chromosomes (2n) • The fetus develops in the uterus ...
... • Occurs in the fallopian tube • A fertilized egg is called a zygote and has the normal number of chromosomes (2n) • The fetus develops in the uterus ...
Cells - Images
... – system of membranes that move materials from one part of the cell to another. ...
... – system of membranes that move materials from one part of the cell to another. ...
Chap 2 - CRCBiologyY11
... • The Golgi complex (also called Golgi body or Golgi apparatus) is a prominent feature of cells that make a lot of protein, as its role is to transport protein out of the cell. ...
... • The Golgi complex (also called Golgi body or Golgi apparatus) is a prominent feature of cells that make a lot of protein, as its role is to transport protein out of the cell. ...
Biology End-of-Course Test: Heritage High School 2013
... contain only 4 parts (Remember NONE of these are membrane-bound organelles!): (1) DNA, (2) Cytoplasm, (3) Ribosomes, (4) Cell Membrane 2) Bacteria are the only organisms that have are prokaryotic cells. 3) Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles. Both Plant and Animal have these types of ...
... contain only 4 parts (Remember NONE of these are membrane-bound organelles!): (1) DNA, (2) Cytoplasm, (3) Ribosomes, (4) Cell Membrane 2) Bacteria are the only organisms that have are prokaryotic cells. 3) Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles. Both Plant and Animal have these types of ...
Characteristics of Life
... of heredity. Genes are coded in a molecule called deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and determine an organism’s traits. The passing of traits from parent to offspring is called heredity. Heredity is the reason children tend to resemble their parents. Sometimes damage causes genes to change. A change in th ...
... of heredity. Genes are coded in a molecule called deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and determine an organism’s traits. The passing of traits from parent to offspring is called heredity. Heredity is the reason children tend to resemble their parents. Sometimes damage causes genes to change. A change in th ...
The Characteristics of Living Things: Biology Scientists are
... The Characteristics of Living Things: Biology Scientists are discovering new species at an exponential rate. In the Andes a bat the size of a raspberry was recently discovered and in Singapore a nematode (small flatworm) that lives only inside the lungs of the changeable lizard was found! By those w ...
... The Characteristics of Living Things: Biology Scientists are discovering new species at an exponential rate. In the Andes a bat the size of a raspberry was recently discovered and in Singapore a nematode (small flatworm) that lives only inside the lungs of the changeable lizard was found! By those w ...
Biology 2nd QTR EQT Review To which group does an organism
... 71. Two organisms in the same order will also have to be in which other taxons? 72. Refer to the illustration below. An analysis of DNA from these organisms would indicate what about their nucleotide sequence? ...
... 71. Two organisms in the same order will also have to be in which other taxons? 72. Refer to the illustration below. An analysis of DNA from these organisms would indicate what about their nucleotide sequence? ...
Final Review - Iowa State University
... 65. Photosynthetic organisms belong in which of the following groups? a. Bacteria b. Protista c. Plantae d. Fungi e. A, B and C only f. All of the above 66. If a diploid cell undergoes ____________________ the resulting cells are haploid a. Mitosis b. Meiosis c. Cell Cycle d. Cancer 67. Homologous c ...
... 65. Photosynthetic organisms belong in which of the following groups? a. Bacteria b. Protista c. Plantae d. Fungi e. A, B and C only f. All of the above 66. If a diploid cell undergoes ____________________ the resulting cells are haploid a. Mitosis b. Meiosis c. Cell Cycle d. Cancer 67. Homologous c ...
Answers
... 15. (4 pts) Regarding William Paley. a. Who was he? b. What was his iconic example? c. In what way does the existence of vestigial structures such as the human coccyx, undercut Paley’s argument? a. Wm. Paley (1743-1805) was an English minister and philosopher best known for his use of apparent desi ...
... 15. (4 pts) Regarding William Paley. a. Who was he? b. What was his iconic example? c. In what way does the existence of vestigial structures such as the human coccyx, undercut Paley’s argument? a. Wm. Paley (1743-1805) was an English minister and philosopher best known for his use of apparent desi ...
Evolution notes 2014Debbie
... many of the lichens died, and the trees became blackened by soot. This caused most of the light-colored moths to die off from predation. The dark-colored moths did well because they could hide on the dark trees. ...
... many of the lichens died, and the trees became blackened by soot. This caused most of the light-colored moths to die off from predation. The dark-colored moths did well because they could hide on the dark trees. ...
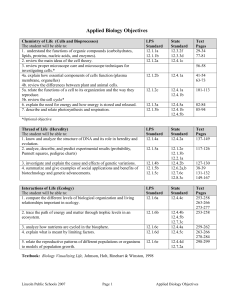
Biology Objectives - Lincoln Public Schools
... 4a. explain how essential components of cells function (plasma membrane, organelles) 4b. review the differences between plant and animal cells. 5a. relate the functions of a cell to its organization and the way they reproduce. 5b. review the cell cycle* 6. explain the need for energy and how energy ...
... 4a. explain how essential components of cells function (plasma membrane, organelles) 4b. review the differences between plant and animal cells. 5a. relate the functions of a cell to its organization and the way they reproduce. 5b. review the cell cycle* 6. explain the need for energy and how energy ...
A View of Life
... – Fully developed in one group but are reduced in another group. Ex: whale/snake hindlimbs; wings on flightless birds, ??humans ...
... – Fully developed in one group but are reduced in another group. Ex: whale/snake hindlimbs; wings on flightless birds, ??humans ...
Chapter 13: Genetic Engineering (24 questions)
... 5. The manifestation of genetic drift that follows the colonization of a new habitat by a few individuals is called ____________________. 6. Members of a population can ____________, which is not possible if they are separated. 7. How many phenotypes can polygenic traits have? How many genotypes? 8. ...
... 5. The manifestation of genetic drift that follows the colonization of a new habitat by a few individuals is called ____________________. 6. Members of a population can ____________, which is not possible if they are separated. 7. How many phenotypes can polygenic traits have? How many genotypes? 8. ...
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CELL All Materials
... C. Integral proteins or transmembrane proteins are embedded & extend across the entire cell membrane. These are exposed to both the inside of the cell & the exterior environment. D. Other integral proteins extend only to the inside or only to the exterior surface. E. Cell membrane proteins help move ...
... C. Integral proteins or transmembrane proteins are embedded & extend across the entire cell membrane. These are exposed to both the inside of the cell & the exterior environment. D. Other integral proteins extend only to the inside or only to the exterior surface. E. Cell membrane proteins help move ...
Symbiogenesis

Symbiogenesis, or endosymbiotic theory, is an evolutionary theory that explains the origin of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotes. It states that several key organelles of eukaryotes originated as a symbiosis between separate single-celled organisms. According to this theory, mitochondria, plastids (for example chloroplasts), and possibly other organelles representing formerly free-living bacteria were taken inside another cell as an endosymbiont around 1.5 billion years ago. Molecular and biochemical evidence suggest that mitochondria developed from proteobacteria (in particular, Rickettsiales, the SAR11 clade, or close relatives) and chloroplasts from cyanobacteria (in particular, nitrogen-fixing filamentous cyanobacteria).