* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Final Review - Iowa State University
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Symbiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
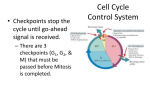
Leader: Alecia Course: Biology 211 Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Instructor: Dr. Deitloff Date: 12/12/13 1. Who wrote On the Origin of Species? a. Lamarck b. Linneas c. Cuvier d. Darwin 2. The number of tree species on campus is an example of a. Species abundance b. Species Richness c. Relative Abundance d. Relative Richness 3. The similarity of bees and wasps is an example of a. Cryptic coloration b. Batesian Mimicry c. Mullerian Mimicry d. Character displacement 4. Mycorrhizae are example of a. Commensalism b. Parasitism c. Mutualism d. Herbivory 5. The packs of wolves in Yellowstone National Park would be what kind of distribution pattern? a. Random b. Uniform c. Clustered d. Clumped 6. If a red flower pollinates a white flower and produces pink flowered offspring, what inheritance pattern occurred? a. Complete Dominance b. Codominance c. Polygenic Inheritance d. Incomplete Dominance 7. Which of the following is NOT a trait possessed by chordates? a. Notochord b. Vertebral column c. Muscular, post anal tail d. Pharyngeal slits 8. What is cephalization? a. Division of the body into 3 distinct layers b. Development of a head c. An invagination of the blastula to form the gastrula d. The presence of radial cleavage 9. The fusion of two compatible mycelia is called a. Karyogamy Supplemental Instruction 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 294-6624 www.si.iastate.edu b. Mitosis c. Mycosis d. Plasmogamy 10. The beneficial relationships between a fungus and plant roots are a. Lichens b. Molds c. Mycorrhizae d. Haustoria 11. A plant embryo and nutrients inside a protective coat is called a. a spore b. a protonema c. a seed d. vascular tissue 12. The flowering plants are called a. Bryophytes b. Seedless, Vascular plants c. Gymnosperms d. Angiosperms 13. The closest relatives of land plants are a. the Oomycetes b. Green Algae c. Red Algae d. Golden Algae 14. Sister chromatids separate in what phase of Meiosis? a. Anaphase II b. Anaphase I c. Metaphase II d. Metaphase I 15. Which of the following increases genetic diversity? a. Synapsis b. Mitosis c. Shugoshin d. Crossing over 16. Meiosis results in the production of daughter cells a. 4 unique, haploid b. 4 identical, haploid c. 2 genetically identical d. 2 unique, haploid 17. Chromosomes with the same centromere position, staining pattern, and length are called a. Autosomes b. Homologs c. Genes d. Gametes 18. Cytokinesis in animal cells is initiated by the formation of the a. Cell plate b. Nuclear Envelope c. Cleavage Furrow d. Mitotic Spindle 19. Dwarf mistletoes are flowering plants that grow on certain forest trees. They obtain nutrients and water from the vascular tissues of the trees. The trees derive no known benefits from the dwarf mistletoes. Which of the following best describes the interactions between dwarf mistletoes and trees? a. Facilitation b. Competition c. Mutualism d. Parasitism e. Commensalism 20. Which of the following is the unit of evolution? In other words, which of the following can evolve in the Darwinian sense? a. gene b. chromosome c. individual d. population e. species 21. Which of the following is not an abiotic factor that shapes ecosystems? a. soil minerals b. predators c. fire d. rainfall e. volcanic eruptions 22. Both echinoderm and cnidarian adults have radially symmetrical bodies. This is an example of: a. coevolution b. mutualism c. convergent evolution d. common ancestry e. competition 23. __. 24. 25. 26. 27. In plants, spores are __ and produced by __; gametes are __ and produced by a. Haploid, mitosis; haploid mitosis b. Haploid, meiosis; haploid meiosis c. Diploid, mitosis; haploid, mitosis d. Haploid, meiosis; haploid, mitosis Fungi play the role of: a. Decomposers b. Pathogens c. Food source d. All of the above ____ compose the ____ of fungi. a. Hyphae, spores b. Mycelium, hyphae c. Hyphae, mycelium d. Fruiting bodies, hyphae Sponges lack what defining characteristic? a. Choanocytes b. Cnidocytes c. True tissues d. Bilateral symmetry Meiosis II is similar to mitosis because a. Sister chromatids separate 28. 29. 30. b. Homologous chromosomes separate c. DNA replication precedes the division d. They both take the same amount of time Eumetazoa are divided into the groups a. Protostome and deuterostome b. Metazoan and ametazoa c. Lophotrophozoa and ecdysozoa d. Radiata and bilateria Cryptic coloration could be renamed: a. Batesian mimicry b. Camouflage c. Mullerian mimicry d. You can’t see me All populations in an area plus the abiotic elements compose the: a. Community b. Biosphere c. Ecosystem d. Population 31. If the birth rate is higher than the death rate: a. The population will remain the same b. The population will increase c. The population will decrease d. Not enough information 32. Assemblage of populations of different species is considered to be a __________ a. Community b. Ecosystem c. Population d. Organization 33. What stage of interphase are the chromosomes replicated? a. G1 b. S c. G2 d. M phase 34. A population is a. group of individuals of the same species that live in the same area b. a group of individuals that are genetically similar c. a single individual within a group of individuals that live in the same area d. a group of individuals that have become isolated over time 35. Which is not a characteristic of a hypothesis? 36. a. It is falsifiable. b. It is testable. c. It is a prediction. d. It is always correct. Which describes a Theory? a. It is a fact accepted by scientists. b. It can never be proven true. c. It is not supported well by evidence. d. A Phylogenetic tree is a theory. 37. The field of biology that is concerned with the describing, naming, and classifying living and extinct organisms and viruses. a. Systematics b. Ontogeny c. Taxonomy d. Phylogeny 38. A common ancestral species and its entire descendant species from a phylogenetic tree is called a _____________ a. Clade b. Family c. Ancestors d. Node 39. _______________ is a change in frequency of genes in a natural population a. Mutations b. Descent with Modification c. Evolution d. Adaptation 40. What resulted in the transfer of mitochondria, plastids, and many genes from bacteria to eukaryotes? a. Endosymbiosis b. Horizontal gene transfer c. Mitosis d. Binary Fission 41. Which of the following is not part of the alteration of generations cycle? a. Haploid zygote b. Diploid sporophyte c. Haploid gamete d. Multicellular cells 42. Which of the following is an example of microevolution a. Formation of a new species b. Crossing over in meiosis c. Asexual reproduction d. Cloning 43. Which of the following is not a condition for Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? a. Extremely large population size b. No gene flow c. Mutations must occur d. No natural selection occurs e. All of the above are conditions for Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium 44. Which of the following is the most important factor in the distribution of organisms in the environment? a. Light b. Temperature c. Salinity d. Water availability 45. The greenhouse effect is a. A new phenomenon resulting from industrialization b. Due to the absorption of solar ration by atmospheric gas c. Responsible for the natural warming of the earth d. Both B & C 46. An examination of the temperature tolerances of locusts would be best described by which ecological subdiscipline? a. Organismal ecology b. Population ecology c. Community ecology d. Ecosystem ecology 47. Which distribution pattern does territoriality produce? a. Random b. Uniform c. Clumped d. None of the above 48. The number of individuals per unit area determines a populations a. Survivorship b. Mortality c. Age distribution d. Density e. Niche 49. In the equation for biotic potential (dN/dt = rN) what does N stand for? a. The carrying capacity for the environment b. The change in time c. The population size d. The intrinsic rate of natural increase of the population e. The age distribution of the population 50. Which of these is not a density-dependent factor that could act to limit the population growth as population size increases? a. Waste accumulation b. Fire c. Inhibitory pheromones d. Lowered immune function due to stress 51. Clumped patterns of dispersion are indicative of an environment in which resources are unevenly distributed a. True b. False 52. Parents feeding chicks in a nest is a(n): a. Innate behavior b. FAP c. Classical conditioning d. Operant behavior 53. The behavior of a Cuckoo newborn pushing eggs and young chicks out of a nest is an example of: a. Habituation b. FAP c. Classical conditioning d. Operant behavior 54. Certain organisms have a limited time window when a behavior, such as speech production, can be learned. This critical period is known as a. Habituation b. Associative learning c. Imprinting d. Maturation 55. A cuckoo may lay its eggs in a warbler’s nest. The cuckoo’s young will displace the warbler’s young and will be raised by the warbler. This is an example of a. Commensalism b. Mutualism c. Parasitism d. Herbivory 56. Ostriches and gazelles feed next to each other. They both watch for predators and alert each other to danger. Since the visual abilities of the two species are different, they each can identify threats the other animal would not as readily see. This is an example of a. Commensalism b. Mutualism c. Parasitism d. Herbivory 57. Why doesn’t an area, such as tundra, support the area hypothesis for latitudinal gradient? a. The tundra is a large area with high species richness b. The tundra is a large area with low species richness c. The tundra is a small area with high species richness d. The tundra is a small area with low species richness 58. Which of these is not an example of a disturbance? a. Fires b. Flood c. Volcanic activity d. Humans e. All of the above are examples of disturbance 59. Which of the following is a characteristic of Prokaryotes, but NOT Eukaryotes a. They have DNA b. They have mitochondria c. They have ribosomes d. They do not have organelles 60. According to recent molecular data, Area are most closely related to a. Bacteria b. Eukarya 61. Which of the following is NOT an adaptation for plants to move into terrestrial environments? a. Vascular tissue b. Alteration of generations c. Seeds d. Flower and fruits e. None of the above are adaptations of plants to move to land f. All of the above are adaptations of plants to move to land 62. Which of the following is NOT an adaptation of animals to move into terrestrial environments? a. Aerobic cellular respiration b. Respiratory systems improved for extracting oxygen from atmosphere c. Resistance to desiccation d. Modifications to limbs or appendages for movement on land e. None of the above are adaptations of animals to move to land f. All of the above are adaptations of animals to move to land 63. The gametophyte generation of plants produces ___________ and is ___________________ a. Gametes, diploid b. Gametes, haploid c. Spores, diploid d. Spores, haploid 64. The sporophyte generation of plants is ____________________ and produces______________ a. Diploid, gametes b. Haploid, gametes c. Diploid, spores d. Haploid, spores 65. Photosynthetic organisms belong in which of the following groups? a. Bacteria b. Protista c. Plantae d. Fungi e. A, B and C only f. All of the above 66. If a diploid cell undergoes ____________________ the resulting cells are haploid a. Mitosis b. Meiosis c. Cell Cycle d. Cancer 67. Homologous chromosomes for a tetrad and line up at the metaphase plate during a. Mitosis b. Meiosis I c. Meiosis II d. Cell Cycle 68. Genetic diversity increases due to which of the following processes? a. Sexual reproduction b. Crossing over c. Independent assortment during meiosis d. Chromosomes segregation during meiosis e. A,B,C only f. All of the above 69. An alternative version of a gene is called __________________________________ a. A loci b. An allele c. Codominance d. A sex chromosome 70. The theory of biological evolution describes _________________________________ a. How the universe began b. How organisms have diversified from the first living organisms to the diversity of life we see today c. How life began d. A and B only e. A and C only f. B and C only g. All of the above h. None of the above 71. According to the phylogenetic tree, which group of plants is most closely related to flowering plants? a. Conifers and Gnetophytes b. Ginkgo c. Cycads d. Pteridophytes e. A, B, and C and equally related to flowering plants 72. Within Protostomia, invertebrates are divided into two groups _______________________ and _______________________ a. Radiata and Bilatera b. Lophotrochozoa and Ecdysozoa c. Parazoa and Eumetazoa d. Protostomia and Deuterostomia 73. Reptiles are a __________________________ group a. Monophyletic b. Paraphyletic c. Polyphyletic 74. _______________ describes an evolutionary process whereby bacterial genes can be incorporated into the DNA material of another bacteria and eukaryote a. Vertical gene transfer b. Horizontal gene transfer c. Natural Selection d. Genetic Drift 75. ______________ describes an evolutionary process whereby parent pass genetic material onto their offspring a. Vertical gene transfer b. Horizontal gene transfer c. Natural Selection d. Genetic Drift 76. ___________ describes an evolutionary process whereby allele frequencies within a population change randomly a. Vertical gene transfer b. Horizontal gene transfer c. Natural Selection d. Genetic Drift 77. ____________ describes an evolutionary process whereby allele frequencies within a population change due to some alleles having differential survival and reproductive success a. Vertical gene transfer b. Horizontal gene transfer c. Natural Selection d. Genetic Drift