Cells
... o A food chain is a pathway of energy transfer through feeding patterns of organisms o 1st trophic level is a producer o 2nd trophic level is a primary consumer o 3rd trophic level is a secondary consumer o 4th trophic level is a tertiary consumer o Last trophic level is a decomposer Every time an o ...
... o A food chain is a pathway of energy transfer through feeding patterns of organisms o 1st trophic level is a producer o 2nd trophic level is a primary consumer o 3rd trophic level is a secondary consumer o 4th trophic level is a tertiary consumer o Last trophic level is a decomposer Every time an o ...
Biology Midterm Study Guide Ch 1-9 spring 11
... these figures, the most acidic rainfall in New York State has a pH of _________. 23. Identify the reactant(s) in the chemical reaction, CO2 + H2O H2CO3. ...
... these figures, the most acidic rainfall in New York State has a pH of _________. 23. Identify the reactant(s) in the chemical reaction, CO2 + H2O H2CO3. ...
Evolution
... exaggerated and they are no longer used as proof by itself, there are still many similarities between the species. ...
... exaggerated and they are no longer used as proof by itself, there are still many similarities between the species. ...
File - Hawk Nation Biology
... Explain the Endosymbiotic theory developed by Lynn Margulis in 1985. Prokaryotic cell engulfed another prokaryotic cell and created a eukaryotic cell. The two prokaryotic cells created a mutualistic relationship. This is the beginning of chloroplast and mitochondria. ...
... Explain the Endosymbiotic theory developed by Lynn Margulis in 1985. Prokaryotic cell engulfed another prokaryotic cell and created a eukaryotic cell. The two prokaryotic cells created a mutualistic relationship. This is the beginning of chloroplast and mitochondria. ...
EOC Review Answer Key- Friday
... 12. How do cells maintain homeostasis: Consider pH, temperature, blood glucose, water balance (hormone systems maintains homeostasis); insulin and glucagon work together to maintain blood sugar; osmosis regulates water; temperature regulation through sweating, shivering, blood vessels opening wide a ...
... 12. How do cells maintain homeostasis: Consider pH, temperature, blood glucose, water balance (hormone systems maintains homeostasis); insulin and glucagon work together to maintain blood sugar; osmosis regulates water; temperature regulation through sweating, shivering, blood vessels opening wide a ...
Biology Keystone Exam Review Packet
... A) Sodium and potassium ions move by active transport, and glucose moves by osmosis. B) Sodium and potassium ions move by active transport, and glucose moves by facilitated diffusion. Due to the fact that they are highly charged molecules (and “hate” the nonpolar cell membrane and can’t pass through ...
... A) Sodium and potassium ions move by active transport, and glucose moves by osmosis. B) Sodium and potassium ions move by active transport, and glucose moves by facilitated diffusion. Due to the fact that they are highly charged molecules (and “hate” the nonpolar cell membrane and can’t pass through ...
What is the purpose of mitosis?
... Darwin’s theory of natural selection? • organisms overproduce • this causes competition • some variations have an adaptive value because they give a survival advantage • the survivors pass on their characteristics to their offspring and these adaptations increase in the population ...
... Darwin’s theory of natural selection? • organisms overproduce • this causes competition • some variations have an adaptive value because they give a survival advantage • the survivors pass on their characteristics to their offspring and these adaptations increase in the population ...
Topic One: Chemistry of Living Things
... Anaerobic respiration: Process that extracts energy from glucose without using oxygen. Gives less energy, so only used by some simple organisms (some bacteria, yeast). These organisms do not need to breathe in oxygen. C) Carbon Dioxide (______): With water, used by plants to make glucose (photosyn ...
... Anaerobic respiration: Process that extracts energy from glucose without using oxygen. Gives less energy, so only used by some simple organisms (some bacteria, yeast). These organisms do not need to breathe in oxygen. C) Carbon Dioxide (______): With water, used by plants to make glucose (photosyn ...
An Introduction to Cells
... structural features that enable it to perform those functions. • 3-2 Describe the organelles of a typical cell, and indicate the specific functions of each. • 3-3 Explain the functions of the cell nucleus and discuss the nature and importance of the genetic code. • 3-4 Summarize the role of DNA in p ...
... structural features that enable it to perform those functions. • 3-2 Describe the organelles of a typical cell, and indicate the specific functions of each. • 3-3 Explain the functions of the cell nucleus and discuss the nature and importance of the genetic code. • 3-4 Summarize the role of DNA in p ...
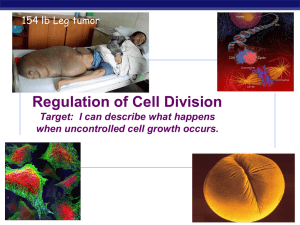
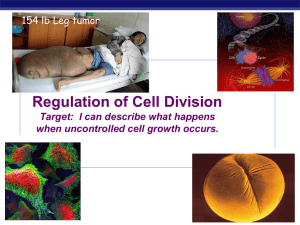
Chapter 12. Regulation of the Cell Cycle
... cell cycle controlled by STOP & GO chemical signals at critical points signals indicate if key cellular processes have been completed correctly ...
... cell cycle controlled by STOP & GO chemical signals at critical points signals indicate if key cellular processes have been completed correctly ...
Chapter 12. Regulation of the Cell Cycle
... cell cycle controlled by STOP & GO chemical signals at critical points signals indicate if key cellular processes have been completed correctly ...
... cell cycle controlled by STOP & GO chemical signals at critical points signals indicate if key cellular processes have been completed correctly ...
Name
... 1. __________________________ command center of the cell; contains DNA 2. __________________________ small organelle in the nucleus that makes ribosomes 3. __________________________ the site of protein synthesis in prokaryotes and eukaryotes 4. __________________________ transport system of the cel ...
... 1. __________________________ command center of the cell; contains DNA 2. __________________________ small organelle in the nucleus that makes ribosomes 3. __________________________ the site of protein synthesis in prokaryotes and eukaryotes 4. __________________________ transport system of the cel ...
Foundations Midterm Review Basic Biology: 1. An autotroph is
... 6. When do enzymes work the best? ___right temperature and pH__(usually of the animal it is in)_______________________ 7. What happens to an enzyme if it becomes too hot or too cold? __doesn’t work_____________ 8. What happens to an enzyme if the pH is too high or too low? ___doesn’t work___________ ...
... 6. When do enzymes work the best? ___right temperature and pH__(usually of the animal it is in)_______________________ 7. What happens to an enzyme if it becomes too hot or too cold? __doesn’t work_____________ 8. What happens to an enzyme if the pH is too high or too low? ___doesn’t work___________ ...
Basic Biology
... 6. When do enzymes work the best? ___right temperature and pH__(usually of the animal it is in)_______________________ 7. What happens to an enzyme if it becomes too hot or too cold? __doesn’t work_____________ 8. What happens to an enzyme if the pH is too high or too low? ___doesn’t work___________ ...
... 6. When do enzymes work the best? ___right temperature and pH__(usually of the animal it is in)_______________________ 7. What happens to an enzyme if it becomes too hot or too cold? __doesn’t work_____________ 8. What happens to an enzyme if the pH is too high or too low? ___doesn’t work___________ ...
Cells and Tissues
... DNA in all of its fine forms: • Chromosomes: Tightly wound DNA. Resemble an X because two chromatids are held together.Supercoiled. • Centromere holds the chromosomes (Two sister Chromatids) together. • Chromatid: A single tightly wound strand of DNA. ...
... DNA in all of its fine forms: • Chromosomes: Tightly wound DNA. Resemble an X because two chromatids are held together.Supercoiled. • Centromere holds the chromosomes (Two sister Chromatids) together. • Chromatid: A single tightly wound strand of DNA. ...
Control, Genome and Environment ALM June 10
... E.g. blood type is either A, B, AB or O Continuous variation is quantitative differences between phenotypes- there is a wide range of variation within the population with no distinct catagories E.g. height (j) explain the basis of continuous and discontinuous variation by reference to the number of ...
... E.g. blood type is either A, B, AB or O Continuous variation is quantitative differences between phenotypes- there is a wide range of variation within the population with no distinct catagories E.g. height (j) explain the basis of continuous and discontinuous variation by reference to the number of ...
Biology Keystone Exam Review Packet
... A) Sodium and potassium ions move by active transport, and glucose moves by osmosis. B) Sodium and potassium ions move by active transport, and glucose moves by facilitated diffusion. Due to the fact that they are highly charged molecules (and “hate” the nonpolar cell membrane and can’t pass through ...
... A) Sodium and potassium ions move by active transport, and glucose moves by osmosis. B) Sodium and potassium ions move by active transport, and glucose moves by facilitated diffusion. Due to the fact that they are highly charged molecules (and “hate” the nonpolar cell membrane and can’t pass through ...
The Six Kingdoms - Chapin High School
... 3. Which of the following statements about mutations is false? a. Environmental factors including radiation and chemicals can cause mutations to occur. b. Enzymes in cells can fix mutations by replacing incorrect nucleotides with correct ones. c. All mutations are harmful to both the organism and th ...
... 3. Which of the following statements about mutations is false? a. Environmental factors including radiation and chemicals can cause mutations to occur. b. Enzymes in cells can fix mutations by replacing incorrect nucleotides with correct ones. c. All mutations are harmful to both the organism and th ...
File
... 3. Which of the following statements about mutations is false? a. Environmental factors including radiation and chemicals can cause mutations to occur. b. Enzymes in cells can fix mutations by replacing incorrect nucleotides with correct ones. c. All mutations are harmful to both the organism and th ...
... 3. Which of the following statements about mutations is false? a. Environmental factors including radiation and chemicals can cause mutations to occur. b. Enzymes in cells can fix mutations by replacing incorrect nucleotides with correct ones. c. All mutations are harmful to both the organism and th ...
The Six Kingdoms - Orangefield ISD
... 3. Which of the following statements about mutations is false? a. Environmental factors including radiation and chemicals can cause mutations to occur. b. Enzymes in cells can fix mutations by replacing incorrect nucleotides with correct ones. c. All mutations are harmful to both the organism and th ...
... 3. Which of the following statements about mutations is false? a. Environmental factors including radiation and chemicals can cause mutations to occur. b. Enzymes in cells can fix mutations by replacing incorrect nucleotides with correct ones. c. All mutations are harmful to both the organism and th ...
EOCT REVIEW STUDY GUIDE
... of nucleic acids. Deoxyribonucleic acid, DNA, records the instructions and transmits them from generation to generation. Ribonucleic acid, RNA “reads” the instructions and carries them out. ENERGY FOR LIVING CELLS Cells require chemical energy to make tasks necessary for life. This energy is stored ...
... of nucleic acids. Deoxyribonucleic acid, DNA, records the instructions and transmits them from generation to generation. Ribonucleic acid, RNA “reads” the instructions and carries them out. ENERGY FOR LIVING CELLS Cells require chemical energy to make tasks necessary for life. This energy is stored ...
What You Absolutely Need to Know To Pass the NYS Living
... • Diffusion is the movement of molecules from high concentrations to low concentrations. Requires no energy (passive transport). • Large molecules (like proteins and starches) cannot pass through the cell membrane without the help of transport proteins floating in ...
... • Diffusion is the movement of molecules from high concentrations to low concentrations. Requires no energy (passive transport). • Large molecules (like proteins and starches) cannot pass through the cell membrane without the help of transport proteins floating in ...
Regents Packet Green
... 2. Both the x and y axis of the graph must be labeled or titled. These labels are typically the same ones used in the data table. Once again units of measurement must be written with the title. 3. The independent variable is always plotted on the x-axis. 4. The dependent variable is always plotted ...
... 2. Both the x and y axis of the graph must be labeled or titled. These labels are typically the same ones used in the data table. Once again units of measurement must be written with the title. 3. The independent variable is always plotted on the x-axis. 4. The dependent variable is always plotted ...
EOCT REVIEW
... the reaction happen faster- called catalysts • If you didn’t have enzymes, reactions would happen too slowly and you might die waiting for the rxn to occur. • Enzymes are used to break down food in your body and to build new molecules & organelles. • Enzymes are used over & over but are very SPECIFI ...
... the reaction happen faster- called catalysts • If you didn’t have enzymes, reactions would happen too slowly and you might die waiting for the rxn to occur. • Enzymes are used to break down food in your body and to build new molecules & organelles. • Enzymes are used over & over but are very SPECIFI ...
ch1lecture.pdf
... changes over many generations • _________ and __________ offspring allow a species to evolve • Evolutionary theory states that modern organisms descended with ___________ from pre-existing life-forms • _________________ is a process where organisms with certain adaptations survive and reproduce more ...
... changes over many generations • _________ and __________ offspring allow a species to evolve • Evolutionary theory states that modern organisms descended with ___________ from pre-existing life-forms • _________________ is a process where organisms with certain adaptations survive and reproduce more ...
Symbiogenesis

Symbiogenesis, or endosymbiotic theory, is an evolutionary theory that explains the origin of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotes. It states that several key organelles of eukaryotes originated as a symbiosis between separate single-celled organisms. According to this theory, mitochondria, plastids (for example chloroplasts), and possibly other organelles representing formerly free-living bacteria were taken inside another cell as an endosymbiont around 1.5 billion years ago. Molecular and biochemical evidence suggest that mitochondria developed from proteobacteria (in particular, Rickettsiales, the SAR11 clade, or close relatives) and chloroplasts from cyanobacteria (in particular, nitrogen-fixing filamentous cyanobacteria).