Making Mirrors: Premotor Cortex Stimulation
... (PMv or PMd first in both Experiments 1 and 2) was counterbalanced across participants, all of whom took part in both experiments. The study was approved by the Mid and South Buckinghamshire Research Ethics Committee (reference number 08/H0607/65) and carried out in accordance with the Declaration o ...
... (PMv or PMd first in both Experiments 1 and 2) was counterbalanced across participants, all of whom took part in both experiments. The study was approved by the Mid and South Buckinghamshire Research Ethics Committee (reference number 08/H0607/65) and carried out in accordance with the Declaration o ...
Thalamocortidal Axons Extend Along a Chondroitin Sulfate
... Scattered faint immunolabeling for CSPGs is present throughout the ventricular zone; a band of intense labeling is evident in association with the pia-arachnoid (Fig. 1B). As the first postmitotic neurons form the preplate (El 1 to early E 13), immunolabeling for CSPGs becomes intense around these c ...
... Scattered faint immunolabeling for CSPGs is present throughout the ventricular zone; a band of intense labeling is evident in association with the pia-arachnoid (Fig. 1B). As the first postmitotic neurons form the preplate (El 1 to early E 13), immunolabeling for CSPGs becomes intense around these c ...
Low Quality
... Located within the hypothalamus, the suprachiasmatic nucleus, or SCN, is made up of a cluster of about 50,000 brain cells. The SCN is the master clock that helps ...
... Located within the hypothalamus, the suprachiasmatic nucleus, or SCN, is made up of a cluster of about 50,000 brain cells. The SCN is the master clock that helps ...
Fluorescent in situ hybridization technique for cell type identification
... compare the same thing. In the cerebral cortex, there are two fundamental cell types, excitatory and inhibitory neurons [23]. These two types can be unambiguously identified by expression of vesicular glutamate transporter 1 (VGluT1) and GABA or GABA synthesizing enzyme GAD, respectively [10,33]. Th ...
... compare the same thing. In the cerebral cortex, there are two fundamental cell types, excitatory and inhibitory neurons [23]. These two types can be unambiguously identified by expression of vesicular glutamate transporter 1 (VGluT1) and GABA or GABA synthesizing enzyme GAD, respectively [10,33]. Th ...
Specialized prefrontal "auditory fields": organization of primate
... auditory, but the role of auditory information in prefrontal functions is not well understood. Pathways from auditory association cortices reach distinct sites in the lateral, orbital, and medial surfaces of the prefrontal cortex in rhesus monkeys. Among prefrontal areas, frontopolar area 10 has the ...
... auditory, but the role of auditory information in prefrontal functions is not well understood. Pathways from auditory association cortices reach distinct sites in the lateral, orbital, and medial surfaces of the prefrontal cortex in rhesus monkeys. Among prefrontal areas, frontopolar area 10 has the ...
The functional role of dorso-lateral premotor cortex
... term premotor activation has been used in the literature. Most papers on mental rotation (including our own so far) seem to adopt a rather loose anatomical definition, labeling activations as pertaining to premotor cortex when they are anterior to the central sulcus and in and around the dorsal part ...
... term premotor activation has been used in the literature. Most papers on mental rotation (including our own so far) seem to adopt a rather loose anatomical definition, labeling activations as pertaining to premotor cortex when they are anterior to the central sulcus and in and around the dorsal part ...
MR Imaging–Detectable Metabolic Alterations in Attention Deficit
... MR spectroscopy represents one of the most suitable in vivo tool to assess neurochemical dysfunction in several brain disorders, including attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. This is the most common neuropsychiatric disorder in childhood and adolescence, which persists into adulthood (in approx ...
... MR spectroscopy represents one of the most suitable in vivo tool to assess neurochemical dysfunction in several brain disorders, including attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. This is the most common neuropsychiatric disorder in childhood and adolescence, which persists into adulthood (in approx ...
Parallel basal ganglia circuits for voluntary and
... However, animals and humans with basal ganglia dysfunctions show deficits that may not simply be classified as movement disorders. For example, animals with large lesions in the striatum may ignore a moving object or obsessively follow it (Denny-Brown, 1962). Patients with Parkinson’s disease may have ...
... However, animals and humans with basal ganglia dysfunctions show deficits that may not simply be classified as movement disorders. For example, animals with large lesions in the striatum may ignore a moving object or obsessively follow it (Denny-Brown, 1962). Patients with Parkinson’s disease may have ...
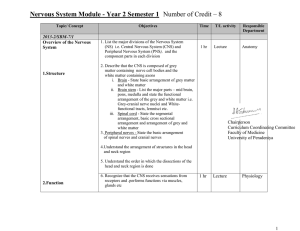
Nervous System Module - Year 2 Semester 1 Number of Credit – 8
... 1. List the major divisions of the Nervous System (NS) i.e. Central Nervous System (CNS) and Peripheral Nervous System (PNS), and the component parts in each division ...
... 1. List the major divisions of the Nervous System (NS) i.e. Central Nervous System (CNS) and Peripheral Nervous System (PNS), and the component parts in each division ...
The functional role of the parieto-frontal mirror circuit
... Brain imaging studies have shown that, as in the monkey, this action observation–action execution mirror circuit is formed by two main regions: the inferior section of the precentral gyrus plus the posterior part of the inferior frontal gyrus; and the inferior parietal lobule, including the cortex l ...
... Brain imaging studies have shown that, as in the monkey, this action observation–action execution mirror circuit is formed by two main regions: the inferior section of the precentral gyrus plus the posterior part of the inferior frontal gyrus; and the inferior parietal lobule, including the cortex l ...
Neuroimaging and ADHD: fMRI, PET, DTI Findings, and
... 2010; Silk, Vance, Rinehart, Bradshaw, & Cunnington, 2008). In addition to circuitry, specific structures and areas of the brain have also received attention and include, among others, the prefrontal cortex, anterior cingulate cortex, caudate, globus pallidus, parietal regions, temporal regions, cor ...
... 2010; Silk, Vance, Rinehart, Bradshaw, & Cunnington, 2008). In addition to circuitry, specific structures and areas of the brain have also received attention and include, among others, the prefrontal cortex, anterior cingulate cortex, caudate, globus pallidus, parietal regions, temporal regions, cor ...
PDF
... purple=proximal+wrist/forearm; yellow=digit+wrist; and grey=proximal). Dashed white line indicates intended infarct territory. In the case illustrated here, a large vein that bisected the DFL was intentionally spared but not its branches. White box encloses the enlarged region shown in middle and ri ...
... purple=proximal+wrist/forearm; yellow=digit+wrist; and grey=proximal). Dashed white line indicates intended infarct territory. In the case illustrated here, a large vein that bisected the DFL was intentionally spared but not its branches. White box encloses the enlarged region shown in middle and ri ...
Immunocytochemical Distribution of the
... selective synthetic ligands that bind to the 2 receptor types (Rinaldi-Carmona and others 1994, 1998) soon followed. Most of the physiological and behavioral effects of cannabinoids appear to be mediated by the CB1 receptor (Zimmer and others 1999), which is highly expressed and widely distributed i ...
... selective synthetic ligands that bind to the 2 receptor types (Rinaldi-Carmona and others 1994, 1998) soon followed. Most of the physiological and behavioral effects of cannabinoids appear to be mediated by the CB1 receptor (Zimmer and others 1999), which is highly expressed and widely distributed i ...
Chapter 3
... Suddenly, he stumbled and fell. Despite feeling a sharp pain initially, he got up and continued to run until he completed the race. Upon crossing the finish line he fell down writhing in pain. When checked out, it was discovered that Mobombi had broken his leg. He was able to run the remainder of th ...
... Suddenly, he stumbled and fell. Despite feeling a sharp pain initially, he got up and continued to run until he completed the race. Upon crossing the finish line he fell down writhing in pain. When checked out, it was discovered that Mobombi had broken his leg. He was able to run the remainder of th ...
The Neuroscientist
... often been assumed to simple relay information from the IC to auditory cortex. However, the multiple subdivisions of the MGB have diverse connections with brain circuits responsible for a number of functions, including conditioned avoidance behavior (reviewed Winer 1992). There is also physiological ...
... often been assumed to simple relay information from the IC to auditory cortex. However, the multiple subdivisions of the MGB have diverse connections with brain circuits responsible for a number of functions, including conditioned avoidance behavior (reviewed Winer 1992). There is also physiological ...
The functional role of the parieto-frontal mirror circuit: interpretations
... brain imaging studies have shown that, as in the monkey, this action observation–action execution mirror circuit is formed by two main regions: the inferior section of the precentral gyrus plus the posterior part of the inferior frontal gyrus; and the inferior parietal lobule, including the cortex l ...
... brain imaging studies have shown that, as in the monkey, this action observation–action execution mirror circuit is formed by two main regions: the inferior section of the precentral gyrus plus the posterior part of the inferior frontal gyrus; and the inferior parietal lobule, including the cortex l ...
REPRESENTATION OF CENTRAL VISUAL FIELDS IN
... lesion was fairly superficial, involving layers 1-4, whereas in others the lesions were slightly deeper, involving all 6 layers. There did not appear to be any appreciable difference in the ensuing degeneration. Survival in all monkeys with lesions in the striate cortex was limite0 to 8 or 9 days. F ...
... lesion was fairly superficial, involving layers 1-4, whereas in others the lesions were slightly deeper, involving all 6 layers. There did not appear to be any appreciable difference in the ensuing degeneration. Survival in all monkeys with lesions in the striate cortex was limite0 to 8 or 9 days. F ...
Basal Ganglia YAYDAR 2012-2013
... Function of Basal Nuclei Basically the activity of basal nuclei begins by information received from sensory cortex, thalamus, substantia nigra, and red nucleus, according to thoughts of mind. • These information is integrated within corpus striatum and channeled within globus pallidus and outflow b ...
... Function of Basal Nuclei Basically the activity of basal nuclei begins by information received from sensory cortex, thalamus, substantia nigra, and red nucleus, according to thoughts of mind. • These information is integrated within corpus striatum and channeled within globus pallidus and outflow b ...
How do you feel -- now? The anterior insula and
... activation in subjects viewing photos of their own face or body with activation when these subjects viewed photos of a close colleague or scrambled images. During visual self-recognition of either body part they found selective activation of the AIC and the adjacent inferior frontal gyrus (IFG) and ...
... activation in subjects viewing photos of their own face or body with activation when these subjects viewed photos of a close colleague or scrambled images. During visual self-recognition of either body part they found selective activation of the AIC and the adjacent inferior frontal gyrus (IFG) and ...
Lights, Camembert, Action! - Human Reward and Decision Making lab
... instances.33 However, given that in many cases, animals (including humans) can distinguish a predictive cue from the UCS itself, as indicated by distinct behavioral responses in these two cases, it seems likely from that there are at least two distinct associative mechanisms in the brain, one based ...
... instances.33 However, given that in many cases, animals (including humans) can distinguish a predictive cue from the UCS itself, as indicated by distinct behavioral responses in these two cases, it seems likely from that there are at least two distinct associative mechanisms in the brain, one based ...
Evolutionarily conserved prefrontal-amygdalar dysfunction in early
... can initiate a broad spectrum of defensive responses via efferent projections to the brain regions that directly mediate many of the behavioral, physiological and cognitive features of anxiety.11,18,19 There is consensus that neuropsychiatric disorders, like other complex mental processes, reflect al ...
... can initiate a broad spectrum of defensive responses via efferent projections to the brain regions that directly mediate many of the behavioral, physiological and cognitive features of anxiety.11,18,19 There is consensus that neuropsychiatric disorders, like other complex mental processes, reflect al ...
Response Suppression in V1 Agrees with Psychophysics of
... of different pedestal contrasts within the scan, distracting scanner noise, and some general discomfort while lying in the scanner may all have contributed to this small difference. Stimulus and task. The stimulus was a contrast-reversing (4 Hz), sinusoidal grating (1.1 cycles/degree), presented for ...
... of different pedestal contrasts within the scan, distracting scanner noise, and some general discomfort while lying in the scanner may all have contributed to this small difference. Stimulus and task. The stimulus was a contrast-reversing (4 Hz), sinusoidal grating (1.1 cycles/degree), presented for ...
Human brain
The human brain is the main organ of the human nervous system. It is located in the head, protected by the skull. It has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but with a more developed cerebral cortex. Large animals such as whales and elephants have larger brains in absolute terms, but when measured using a measure of relative brain size, which compensates for body size, the quotient for the human brain is almost twice as large as that of a bottlenose dolphin, and three times as large as that of a chimpanzee. Much of the size of the human brain comes from the cerebral cortex, especially the frontal lobes, which are associated with executive functions such as self-control, planning, reasoning, and abstract thought. The area of the cerebral cortex devoted to vision, the visual cortex, is also greatly enlarged in humans compared to other animals.The human cerebral cortex is a thick layer of neural tissue that covers most of the brain. This layer is folded in a way that increases the amount of surface that can fit into the volume available. The pattern of folds is similar across individuals, although there are many small variations. The cortex is divided into four lobes – the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and occipital lobe. (Some classification systems also include a limbic lobe and treat the insular cortex as a lobe.) Within each lobe are numerous cortical areas, each associated with a particular function, including vision, motor control, and language. The left and right sides of the cortex are broadly similar in shape, and most cortical areas are replicated on both sides. Some areas, though, show strong lateralization, particularly areas that are involved in language. In most people, the left hemisphere is dominant for language, with the right hemisphere playing only a minor role. There are other functions, such as visual-spatial ability, for which the right hemisphere is usually dominant.Despite being protected by the thick bones of the skull, suspended in cerebrospinal fluid, and isolated from the bloodstream by the blood–brain barrier, the human brain is susceptible to damage and disease. The most common forms of physical damage are closed head injuries such as a blow to the head, a stroke, or poisoning by a variety of chemicals which can act as neurotoxins, such as ethanol alcohol. Infection of the brain, though serious, is rare because of the biological barriers which protect it. The human brain is also susceptible to degenerative disorders, such as Parkinson's disease, and Alzheimer's disease, (mostly as the result of aging) and multiple sclerosis. A number of psychiatric conditions, such as schizophrenia and clinical depression, are thought to be associated with brain dysfunctions, although the nature of these is not well understood. The brain can also be the site of brain tumors and these can be benign or malignant.There are some techniques for studying the brain that are used in other animals that are just not suitable for use in humans and vice versa. It is easier to obtain individual brain cells taken from other animals, for study. It is also possible to use invasive techniques in other animals such as inserting electrodes into the brain or disabling certains parts of the brain in order to examine the effects on behaviour – techniques that are not possible to be used in humans. However, only humans can respond to complex verbal instructions or be of use in the study of important brain functions such as language and other complex cognitive tasks, but studies from humans and from other animals, can be of mutual help. Medical imaging technologies such as functional neuroimaging and EEG recordings are important techniques in studying the brain. The complete functional understanding of the human brain is an ongoing challenge for neuroscience.