Vocab: Unit 3 Handout made by: Jessica Jones and Hanna Cho
... Genome: complete instructions for making an organism, genetic material in the organism’s chromosomes Identical twins: (monozygotic twins) develop from a single fertilized egg that splits in two Fraternal twins: (dizygotic twins) develop from separate fertilized eggs, share a fetal environment Molecu ...
... Genome: complete instructions for making an organism, genetic material in the organism’s chromosomes Identical twins: (monozygotic twins) develop from a single fertilized egg that splits in two Fraternal twins: (dizygotic twins) develop from separate fertilized eggs, share a fetal environment Molecu ...
Sample
... Modern imaging techniques have allow researcher to 'see' the where and when of brain functioning, but some might argue that this is modern phrenology in that it tells us little about the underlying psychology. Do you agree? Some might argue that cognitive psychology is a thing in the past and that i ...
... Modern imaging techniques have allow researcher to 'see' the where and when of brain functioning, but some might argue that this is modern phrenology in that it tells us little about the underlying psychology. Do you agree? Some might argue that cognitive psychology is a thing in the past and that i ...
Connecting to your need For Rithme
... • We generally think of music as something created by humans for entertainment purposes. Without knowingly, music can make us smarter. ...
... • We generally think of music as something created by humans for entertainment purposes. Without knowingly, music can make us smarter. ...
unit 2: biological bases of behavior
... Summarize the criticisms of evolutionary explanations of human behaviors, and describe the evolutionary psychologists’ responses to those criticisms. ...
... Summarize the criticisms of evolutionary explanations of human behaviors, and describe the evolutionary psychologists’ responses to those criticisms. ...
Document
... • Parietal Lobe: • Can be divided into two functional regions. • The first function integrates sensory information to form a single perception (cognition). • The second function constructs a spatial coordinate system to represent the world around us. ...
... • Parietal Lobe: • Can be divided into two functional regions. • The first function integrates sensory information to form a single perception (cognition). • The second function constructs a spatial coordinate system to represent the world around us. ...
The Nervous System
... Attaches to dendrites of another cell Continues until reaches muscle cells Signal goes in only one direction ...
... Attaches to dendrites of another cell Continues until reaches muscle cells Signal goes in only one direction ...
Biopsychology
... Shows what behaviors(/cognitions) occur if we stimulate or damage (lesion) a particular area of the brain. Electroencephalogram (EEG) & Evoked Potentials The EEG measures the brain's electrical activity using electrodes placed on the scalp. Indicates a person’s state of arousal. The Evoked Pot ...
... Shows what behaviors(/cognitions) occur if we stimulate or damage (lesion) a particular area of the brain. Electroencephalogram (EEG) & Evoked Potentials The EEG measures the brain's electrical activity using electrodes placed on the scalp. Indicates a person’s state of arousal. The Evoked Pot ...
Nature 411, 189 - 193 (2001)
... in the control of psychomotor behavior. Neuroanatomical methods combined with transmitter localization procedures were used to study the chemical organization of the forebrain in each major group of vertebrates. The various components of the basal ganglia appear well developed in amniote vertebrates ...
... in the control of psychomotor behavior. Neuroanatomical methods combined with transmitter localization procedures were used to study the chemical organization of the forebrain in each major group of vertebrates. The various components of the basal ganglia appear well developed in amniote vertebrates ...
Nervous System
... homeostasis & processes information Accepts sensory signals & channels them to cerebrum for interpretation (e.g. thalmus may have a consciousness of pain but does not know the location of the pain – the cerebrum interprets the signal and we know where it hurts) ...
... homeostasis & processes information Accepts sensory signals & channels them to cerebrum for interpretation (e.g. thalmus may have a consciousness of pain but does not know the location of the pain – the cerebrum interprets the signal and we know where it hurts) ...
Characterization of GPR101 transcripts structure, expression and
... assays and fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) imaging. Results: Two GPR101 isoforms have been identified, characterized by different 5’ UTRs and a common 6.2 kb-long 3’UTR. A CpG-enriched promoter region was predicted within 1 kb upstream of the putative transcription start site. GPR101 i ...
... assays and fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) imaging. Results: Two GPR101 isoforms have been identified, characterized by different 5’ UTRs and a common 6.2 kb-long 3’UTR. A CpG-enriched promoter region was predicted within 1 kb upstream of the putative transcription start site. GPR101 i ...
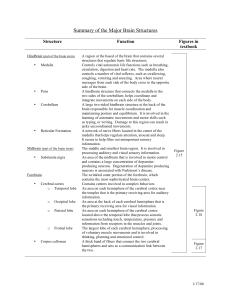
Summary of the Major Brain Structures
... A region at the based of the brain that contains several structures that regulate basic life structures. Controls vital autonomic life functions such as breathing, circulation, digestion and heart rate. The medulla also controls a number of vital reflexes, such as swallowing, coughing, vomiting and ...
... A region at the based of the brain that contains several structures that regulate basic life structures. Controls vital autonomic life functions such as breathing, circulation, digestion and heart rate. The medulla also controls a number of vital reflexes, such as swallowing, coughing, vomiting and ...
An Integrative Approach to Psychopathology
... – Explain behavior in terms of a single cause – Could mean a paradigm, school, or conceptual approach – Tendency to ignore information from other areas ...
... – Explain behavior in terms of a single cause – Could mean a paradigm, school, or conceptual approach – Tendency to ignore information from other areas ...
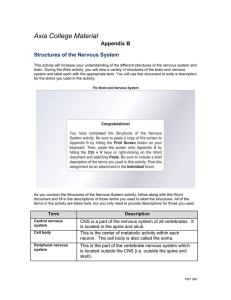
Axia College Material Appendix B Structures of the Nervous System
... neuron. The cell body is also called the soma. This is the part of the vertebrate nervous system which is located outside the CNS (i.e. outside the spine and ...
... neuron. The cell body is also called the soma. This is the part of the vertebrate nervous system which is located outside the CNS (i.e. outside the spine and ...
Nervous System
... • The brain requires oxygen for aerobic metabolism. Lack of oxygen for more than 5 minutes can kill brain cells. • The brain requires glucose for metabolism. Lack of glucose for more than 15 minutes kills brain cells. • Neurons cannot undergo mitosis. ...
... • The brain requires oxygen for aerobic metabolism. Lack of oxygen for more than 5 minutes can kill brain cells. • The brain requires glucose for metabolism. Lack of glucose for more than 15 minutes kills brain cells. • Neurons cannot undergo mitosis. ...
Introduction to the Brain
... meninges. The outer layer of the meninges is called Copyright Headway, 2011. This is one of a range of factsheets made available by Headway. We have taken great care to ensure all information is accurate but these factsheets are only intended as a guide and recommend that medical or professional sup ...
... meninges. The outer layer of the meninges is called Copyright Headway, 2011. This is one of a range of factsheets made available by Headway. We have taken great care to ensure all information is accurate but these factsheets are only intended as a guide and recommend that medical or professional sup ...
Introduction to the Brain
... meninges. The outer layer of the meninges is called Copyright Headway, 2009. This is one of a range of factsheets made available by Headway. We have taken great care to ensure all information is accurate but these factsheets are only intended as a guide and recommend that medical or professional sup ...
... meninges. The outer layer of the meninges is called Copyright Headway, 2009. This is one of a range of factsheets made available by Headway. We have taken great care to ensure all information is accurate but these factsheets are only intended as a guide and recommend that medical or professional sup ...
Neuroscience
... persons personality (inappropriate emotions, socially unacceptable behavior, fewer inhibitions, failure to make longterm plans, easily distracted, difficulty understanding a string of facts or events) ...
... persons personality (inappropriate emotions, socially unacceptable behavior, fewer inhibitions, failure to make longterm plans, easily distracted, difficulty understanding a string of facts or events) ...
Evolution2
... Why is Brain Size Important? All organs and systems of the body confront design problems and limits as they become larger or smaller 2 major ways in which larger brains can be modified to reduce design problems: 1) Brain becomes more modular such that connections between neurons are local a. Don ...
... Why is Brain Size Important? All organs and systems of the body confront design problems and limits as they become larger or smaller 2 major ways in which larger brains can be modified to reduce design problems: 1) Brain becomes more modular such that connections between neurons are local a. Don ...
Courses and research in cognitive science in Bratislava
... Project: From sensory-motor processes to higher cognition: Computational modeling of mental development in an embodied cognitive agent Slovak Grant Agency for Science (2014-2016, Farkaš et al.) ...
... Project: From sensory-motor processes to higher cognition: Computational modeling of mental development in an embodied cognitive agent Slovak Grant Agency for Science (2014-2016, Farkaš et al.) ...
Biopsychology and Perception
... Baucum, D. (1996). Psychology. New York: Barron’s Educational Series, Inc. Fogiel, M. (Ed.) (1994). Advanced Placement Examination in Psychology, New Jersey: Research and Education Association. Fogiel, M. (Ed.) (1994). REA's Problem Solvers: Psychology, New Jersey: Research and Education Association ...
... Baucum, D. (1996). Psychology. New York: Barron’s Educational Series, Inc. Fogiel, M. (Ed.) (1994). Advanced Placement Examination in Psychology, New Jersey: Research and Education Association. Fogiel, M. (Ed.) (1994). REA's Problem Solvers: Psychology, New Jersey: Research and Education Association ...
Brain 2012 - student version
... Figure 3B.13 Left hemisphere tissue devoted to each body part in the motor cortex and the sensory cortex As you can see from this classic though inexact representation, the amount of cortex devoted to a body part is not proportional to that part’s size. Rather, the brain devotes more tissue to sens ...
... Figure 3B.13 Left hemisphere tissue devoted to each body part in the motor cortex and the sensory cortex As you can see from this classic though inexact representation, the amount of cortex devoted to a body part is not proportional to that part’s size. Rather, the brain devotes more tissue to sens ...