pain and emotion interactions in subregions of the cingulate gyrus
... stimulation of the body, and these medially-located structures are collectively referred to as the medial pain system. These include the midline and intralaminar thalamic nuclei (MITN), which project to the limbic cortex, the periaqueductal grey, the amygdala and the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC)6 ...
... stimulation of the body, and these medially-located structures are collectively referred to as the medial pain system. These include the midline and intralaminar thalamic nuclei (MITN), which project to the limbic cortex, the periaqueductal grey, the amygdala and the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC)6 ...
Developing an Effective Parenting Style
... shaped and reshaped, which is greatest early in life. • principles of growth and development. Statements of the general patterns in which growth and development take place in people. © Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. ...
... shaped and reshaped, which is greatest early in life. • principles of growth and development. Statements of the general patterns in which growth and development take place in people. © Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. ...
child development - Goodheart
... shaped and reshaped, which is greatest early in life. • principles of growth and development. Statements of the general patterns in which growth and development take place in people. © Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. ...
... shaped and reshaped, which is greatest early in life. • principles of growth and development. Statements of the general patterns in which growth and development take place in people. © Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. ...
The Nervous System - Division of Social Sciences
... approximately two glial cells for every neuron (other brain regions have up to 10 times as many). That’s a glia index of 2.0. The index in comparable regions in rodents is 0.4, in worms 0.17. There is work that supports the theory that a high concentration of glia may actually boost the ability to t ...
... approximately two glial cells for every neuron (other brain regions have up to 10 times as many). That’s a glia index of 2.0. The index in comparable regions in rodents is 0.4, in worms 0.17. There is work that supports the theory that a high concentration of glia may actually boost the ability to t ...
Common and Distinct Neural Substrates for Pragmatic, Semantic
... et al., 1993). Such designs sometimes assume a hierarchical model of language processing in which different ...
... et al., 1993). Such designs sometimes assume a hierarchical model of language processing in which different ...
Neurocircuitry of Addiction
... Another conceptualization of the motivational changes associated with addiction is derived from early work on conditioned reinforcement, incentive motivation, behavioral sensitization, and maladaptive stimulus–response learning, all of which are subsumed under the motivational conceptualization of i ...
... Another conceptualization of the motivational changes associated with addiction is derived from early work on conditioned reinforcement, incentive motivation, behavioral sensitization, and maladaptive stimulus–response learning, all of which are subsumed under the motivational conceptualization of i ...
Memory - WordPress.com
... cerebral artery from either a transient ischemic attack or an embolism. Transient global amnesia can be a one-time event, but Markowitsch suggests that, even so, some of the memory loss can be permanent. Indeed, Mazzucchi and colleagues showed that a significant chronic memory loss is typical in tra ...
... cerebral artery from either a transient ischemic attack or an embolism. Transient global amnesia can be a one-time event, but Markowitsch suggests that, even so, some of the memory loss can be permanent. Indeed, Mazzucchi and colleagues showed that a significant chronic memory loss is typical in tra ...
Biological Foundations of Behavior
... Human Diversity: Sex Differences in the Cerebral Cortex • Female brain – average size smaller than that of male brain – More folds and complex ...
... Human Diversity: Sex Differences in the Cerebral Cortex • Female brain – average size smaller than that of male brain – More folds and complex ...
LIFE-SPAN DEVELOPMENT
... Human Diversity: Sex Differences in the Cerebral Cortex • Female brain – average size smaller than that of male brain – More folds and complex ...
... Human Diversity: Sex Differences in the Cerebral Cortex • Female brain – average size smaller than that of male brain – More folds and complex ...
View PDF - Center for Complex Systems and Brain Sciences
... In a recent comparison of IL and PL projections in the rat, we showed that, with a few exceptions, PL and IL distribute differently throughout the brain (Vertes, 2004). These differential patterns of projections are summarized in Fig. 1. As illustrated (Fig. 1), IL distributes significantly to: (1) ...
... In a recent comparison of IL and PL projections in the rat, we showed that, with a few exceptions, PL and IL distribute differently throughout the brain (Vertes, 2004). These differential patterns of projections are summarized in Fig. 1. As illustrated (Fig. 1), IL distributes significantly to: (1) ...
The World of Psychology
... conscious human patients undergoing neurosurgery Mapped the primary motor cortex in humans ...
... conscious human patients undergoing neurosurgery Mapped the primary motor cortex in humans ...
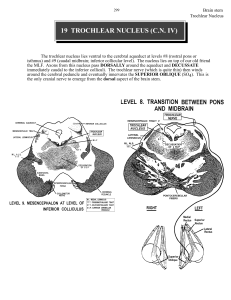
19 TROCHLEAR NUCLEUS (C.N. IV)
... or bradykinesia and a slow and shuffling gait and postural instability. You do not have to worry about the laterality (right or left) of these deficits at this time. The most consistent pathological finding in Parkinson’s disease is degeneration of the melanin-containing cells in the pars compacta ( ...
... or bradykinesia and a slow and shuffling gait and postural instability. You do not have to worry about the laterality (right or left) of these deficits at this time. The most consistent pathological finding in Parkinson’s disease is degeneration of the melanin-containing cells in the pars compacta ( ...
Ch 49
... • The PNS transmits information to and from the CNS and regulates movement and the internal environment • In the PNS, afferent neurons transmit information to the CNS and efferent neurons transmit information away from the CNS • Cranial nerves originate in the brain and mostly terminate in organs of ...
... • The PNS transmits information to and from the CNS and regulates movement and the internal environment • In the PNS, afferent neurons transmit information to the CNS and efferent neurons transmit information away from the CNS • Cranial nerves originate in the brain and mostly terminate in organs of ...
video slide - Welcome to HCC Southeast Commons
... • The PNS transmits information to and from the CNS and regulates movement and the internal environment • In the PNS, afferent neurons transmit information to the CNS and efferent neurons transmit information away from the CNS • Cranial nerves originate in the brain and mostly terminate in organs of ...
... • The PNS transmits information to and from the CNS and regulates movement and the internal environment • In the PNS, afferent neurons transmit information to the CNS and efferent neurons transmit information away from the CNS • Cranial nerves originate in the brain and mostly terminate in organs of ...
The limbic system
... The efferent fibers from the hippocampal region form three groups: precommissural fornix, postcommissural fornix and nonfornical fibers. The precommissural fibers of the fornix may originate from the cornu ammonis or the subiculum. These fibers travel within the fimbria, crura and body of the fornix ...
... The efferent fibers from the hippocampal region form three groups: precommissural fornix, postcommissural fornix and nonfornical fibers. The precommissural fibers of the fornix may originate from the cornu ammonis or the subiculum. These fibers travel within the fimbria, crura and body of the fornix ...
Nerves
... • The PNS transmits information to and from the CNS and regulates movement and the internal environment • In the PNS, afferent neurons transmit information to the CNS and efferent neurons transmit information away from the CNS • Cranial nerves originate in the brain and mostly terminate in organs of ...
... • The PNS transmits information to and from the CNS and regulates movement and the internal environment • In the PNS, afferent neurons transmit information to the CNS and efferent neurons transmit information away from the CNS • Cranial nerves originate in the brain and mostly terminate in organs of ...
Neuronal DNA Content Variation (DCV) With Regional
... DCV varied between individual brains. These results identify DCV as a new feature of the human brain, encompassing and further extending genomic alterations produced by aneuploidy, which may contribute to neural diversity in normal and pathophysiological states, altered functions of normal and disea ...
... DCV varied between individual brains. These results identify DCV as a new feature of the human brain, encompassing and further extending genomic alterations produced by aneuploidy, which may contribute to neural diversity in normal and pathophysiological states, altered functions of normal and disea ...
Imitation: is cognitive neuroscience solving the correspondence
... It is now widely acknowledged that the inferior parietal cortex is involved in imitation, but the role of the posterior part of the inferior frontal gyrus (BA 44/45) remains controversial. The posterior inferior frontal gyrus (pIFG) is thought to be the human homologue of premotor area F5 in monkeys ...
... It is now widely acknowledged that the inferior parietal cortex is involved in imitation, but the role of the posterior part of the inferior frontal gyrus (BA 44/45) remains controversial. The posterior inferior frontal gyrus (pIFG) is thought to be the human homologue of premotor area F5 in monkeys ...
Brain regions involved in heading estimation and steering control in
... The brain regions required for judging heading direction and actively steering towards a goal could be damaged by stroke. Identifying the neural correlates responsible for goal-directed locomotion is important for the understanding of the mechanism underlying neuroplasticity and functional recovery. ...
... The brain regions required for judging heading direction and actively steering towards a goal could be damaged by stroke. Identifying the neural correlates responsible for goal-directed locomotion is important for the understanding of the mechanism underlying neuroplasticity and functional recovery. ...
from ups
... the effects of ischaemia: Halothane anaesthesia was used during the surgery and intracardiac perfusion was employed to reduce the brain temperature, to increase the intracerebral concentration of glucose and magnesium and to decrease that of calcium. The spread of stimulating current has been determ ...
... the effects of ischaemia: Halothane anaesthesia was used during the surgery and intracardiac perfusion was employed to reduce the brain temperature, to increase the intracerebral concentration of glucose and magnesium and to decrease that of calcium. The spread of stimulating current has been determ ...
What Can an Orbitofrontal Cortex- Endowed Animal
... [LO] areas).4 This latter group of structures (AIv, AIp, VLO, LO) receives direct projections from rodent piriform cortex and responds with short-latency action potentials to electrical stimulation of the olfactory bulb.5 From electrophysiological recordings in rodents, it is evident that these same ...
... [LO] areas).4 This latter group of structures (AIv, AIp, VLO, LO) receives direct projections from rodent piriform cortex and responds with short-latency action potentials to electrical stimulation of the olfactory bulb.5 From electrophysiological recordings in rodents, it is evident that these same ...
Differential responses in three thalamic nuclei in moderately
... et al., 2002) and experimental animals (Smith et al., 1997; Pierce et al., 1998). In experimental animals, tissue loss from Brain Vol. 127 No. 11 ...
... et al., 2002) and experimental animals (Smith et al., 1997; Pierce et al., 1998). In experimental animals, tissue loss from Brain Vol. 127 No. 11 ...
1 Neural Affective Decision Theory: Choices, Brains, and Emotions
... ANDREA simulates how interactions of the dopamine and serotonin systems with the amygdala and other brain areas may enable this asymmetric assessment of positive and negative outcomes. Principle 4. Framing. The last principle states that judgments and decisions vary depending on how the context and ...
... ANDREA simulates how interactions of the dopamine and serotonin systems with the amygdala and other brain areas may enable this asymmetric assessment of positive and negative outcomes. Principle 4. Framing. The last principle states that judgments and decisions vary depending on how the context and ...